JARINGAN TUBUH MANUSIA
Summary
TLDRThis educational video provides a detailed overview of human histology, covering the seven major tissue types: epithelial, muscle, bone, blood, nervous, adipose, and connective tissue. It explains the structure, function, and classification of each tissue type, including examples like smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle, as well as various forms of connective tissues such as cartilage and bone. The video highlights how each tissue supports the body's functions, from movement and structure to protection and communication, making it an informative introduction to the subject of histology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Histology is the study of tissues in the human body, and it involves understanding the different types of tissues and their functions.
- 😀 Tissues are made up of cells that share similar shape and function, and they are essential in forming the organs of living organisms.
- 😀 There are seven main types of tissue in the human body: epithelium, muscle, bone, blood, nerve, adipose, and connective tissues.
- 😀 Epithelium tissue serves various functions such as protection, secretion, absorption, transport, lubrication, and reproduction.
- 😀 Epithelium tissue can be classified based on cell shape (squamous, cuboidal, and columnar) and the number of cell layers (simple or stratified).
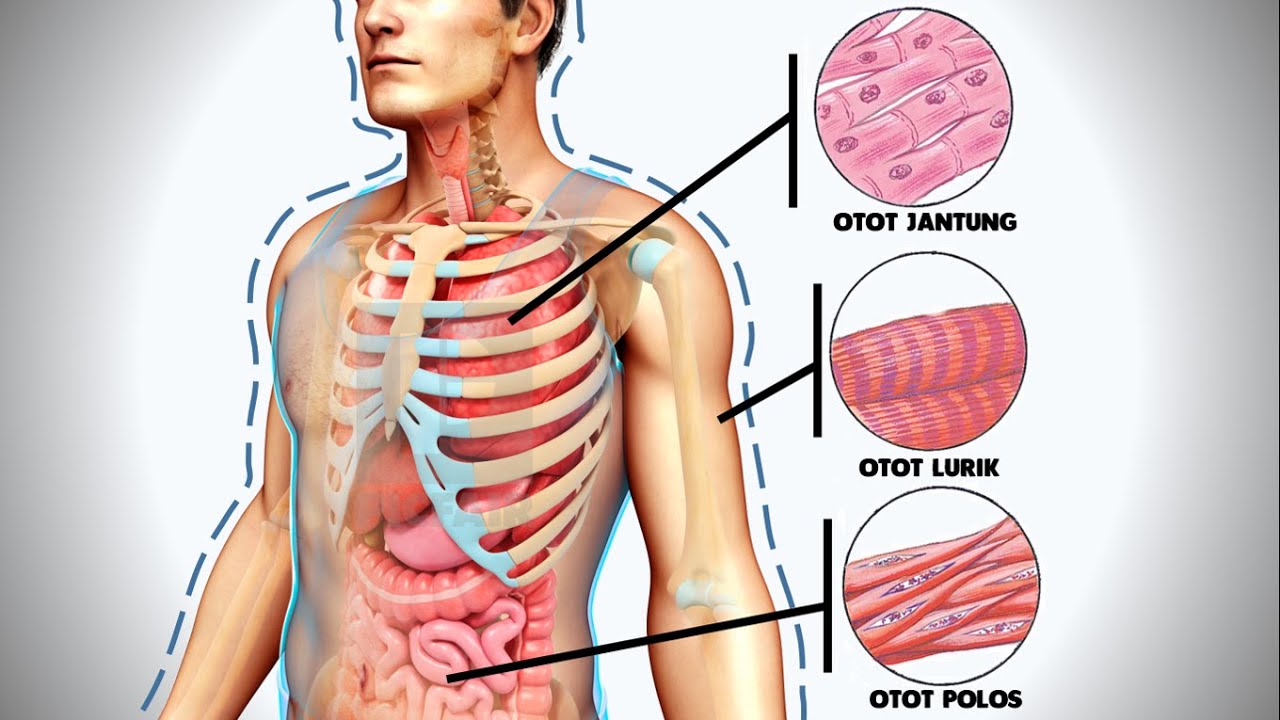
- 😀 Muscle tissue is responsible for movement and can be categorized into three types: smooth, cardiac, and striated muscle.
- 😀 Smooth muscle operates involuntarily and is found in organs like the digestive system and blood vessels.
- 😀 Cardiac muscle, found only in the heart, also operates involuntarily, with cells having a single nucleus.
- 😀 Striated muscle (skeletal muscle) is under voluntary control, contains multiple nuclei, and allows for rapid, controlled movements.
- 😀 Bone tissue is classified into cartilage (elastic, hyaline, fibrous) and hard bone (compact and spongy), which support and protect the body.
- 😀 Blood tissue is a fluid tissue that transports nutrients, waste, and immune cells, playing a key role in the body’s defense against infection.
- 😀 Nervous tissue enables communication between different parts of the body by transmitting signals through neurons, forming the body’s coordination system.
- 😀 Adipose tissue stores fat, cushions organs, and regulates body temperature while serving as an energy reserve.
- 😀 Connective tissue provides structural support to organs and tissues, with types including loose, dense, adipose, fibrous, and bone tissue.
Q & A
What is the definition of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue is a group of cells that form protective layers on both internal and external surfaces of the body. Its functions include protection, secretion, absorption, transport, lubrication, and reproduction.
How is epithelial tissue classified?
-Epithelial tissue is classified based on the number of layers (single-layered or multi-layered) and the shape of its cells (squamous, cuboidal, or columnar).
What are the main functions of muscle tissue?
-Muscle tissue's primary function is to facilitate movement. It helps move organs and parts of the body actively through contraction.
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
-The three types of muscle tissue are smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle. Each has different characteristics in terms of control, speed, and location in the body.
What is the difference between smooth and skeletal muscle tissue?
-Smooth muscle is involuntary, works slowly and steadily, and is found in organs like the digestive tract and blood vessels. Skeletal muscle is voluntary, works quickly and irregularly, and is attached to bones for movement.
What are the two main classifications of bone tissue?
-Bone tissue is classified into two types: cartilage (which includes elastic, hyaline, and fibrous cartilage) and bone (which is further divided into compact and spongy bone).
What is the function of blood tissue?
-Blood tissue serves to transport essential substances like nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body, while also playing a role in immune defense and waste removal.
What are the components of nervous tissue?
-Nervous tissue consists of neurons, which include the cell body, dendrites (receive signals), and axon (transmits signals). Its main function is to receive and transmit stimuli to coordinate body functions.
What is the role of adipose tissue in the body?
-Adipose tissue is responsible for storing fat, protecting organs, and regulating body temperature. It also serves as an energy reserve.
What is the function of connective tissue?
-Connective tissue binds and supports other tissues in the body. It also helps in the transport of nutrients and waste products, and it includes various subtypes such as loose connective tissue, adipose tissue, fibrous connective tissue, cartilage, bone, and blood.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
Media Pembelajaran Jaringan Hewan - Kelas Daring Biologi SMA Kelas XI

Animal Tissues - Class 9 Tutorial

TECIDOS DO CORPO HUMANO | Resumo de Biologia Enem. Professora Cláudia Aguiar

Intro to Histology: The Four Tissue Types | Corporis

Cells and tissues: types and characteristics - Human histology | Kenhub

HISTOLOGIA: UM SUPER MAPA MENTAL PARA O ENEM E VESTIBULARES
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
