Identifying Leukocytes | Review and Practice
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explains how to differentiate between the various types of white blood cells (WBCs), divided into two main categories: granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes, monocytes). Key identification methods include size comparison to red blood cells, color (especially for eosinophils and basophils), and the distinct appearance of their nuclei. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding these features to avoid common identification mistakes and provides opportunities for practice with example images, guiding viewers through the process of WBC identification.
Takeaways
- 😀 Granulocytes and agranulocytes are the two main groups of white blood cells.
- 😀 Granulocytes include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils, while agranulocytes include lymphocytes and monocytes.
- 😀 The size of white blood cells can be compared to red blood cells to help identify them: neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils are about 2-3 times the size of a red blood cell.
- 😀 Lymphocytes have a nucleus that is approximately the size of a red blood cell, while monocytes are the largest and can easily fit five red blood cells inside.
- 😀 Eosinophils appear red due to their granules, while basophils are dark purple and also grainy in appearance.
- 😀 The neutrophil's multi-lobed nucleus is a key identifying feature, while eosinophils typically have two circular nuclei.
- 😀 Basophils are heavily stained, making their nucleus difficult to see, while lymphocytes have a clear, circular nucleus.
- 😀 Monocytes have a large, irregular, chunky nucleus, often resembling a kidney bean or thick horseshoe shape.
- 😀 Avoid making the mistake of confusing basophils with lymphocytes based solely on color—lymphocytes have a clear cytoplasm halo and no granules.
- 😀 Practice identifying the different white blood cells by examining their size, color, nucleus shape, and graininess for more accurate identification.
Q & A
What are the two main groups of white blood cells?
-The two main groups of white blood cells are granulocytes and agranulocytes.
What are the types of granulocytes?
-The types of granulocytes are neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
What are the types of agranulocytes?
-The types of agranulocytes are lymphocytes and monocytes.
How can you differentiate white blood cells based on size?
-To differentiate white blood cells by size, you compare them to the red blood cells around them. For example, a neutrophil is about two to three times the size of a red blood cell, while a monocyte can fit five red blood cells.
How do the nuclei of granulocytes differ?
-Granulocytes have distinct nuclei: neutrophils have a multi-lobed nucleus, eosinophils typically have two circular nuclei, and basophils have a stained dark purple nucleus that is often hard to see.
What is the color difference between eosinophils and basophils?
-Eosinophils are red in color when compared to red blood cells, while basophils are dark purple.
What characteristic helps identify a lymphocyte?
-A lymphocyte can be identified by its large, circular nucleus, which is approximately the size of one red blood cell, and the presence of a small halo of cytoplasm.
How does the size of a monocyte help in its identification?
-A monocyte is the largest white blood cell, easily fitting five red blood cells inside, making its size a key feature for identification.
What is a common mistake when identifying neutrophils and monocytes?
-A common mistake is confusing immature neutrophils with monocytes. Immature neutrophils have a singular, skinny nucleus and are roughly the size of two to three red blood cells, while monocytes are larger and have a chunky, irregular nucleus.
Why is texture important in identifying granulocytes?
-The texture is important because granulocytes, such as eosinophils and basophils, are grainy due to the presence of granules, while neutrophils may or may not appear grainy.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

White Blood Cells

Cells of the Immune System (PART II - AGRANULOCYTES) (FL-Immuno/03)

Hematopoesis (Pembentukan Sel Darah)

Hematology - Introduction - Hematopoiesis: Let's Make RBCs, WBCs, and Platelets -Hematology Playlist

PLASMA DARAH, ERITROSIT, LEUKOSIT, DAN PLATELET
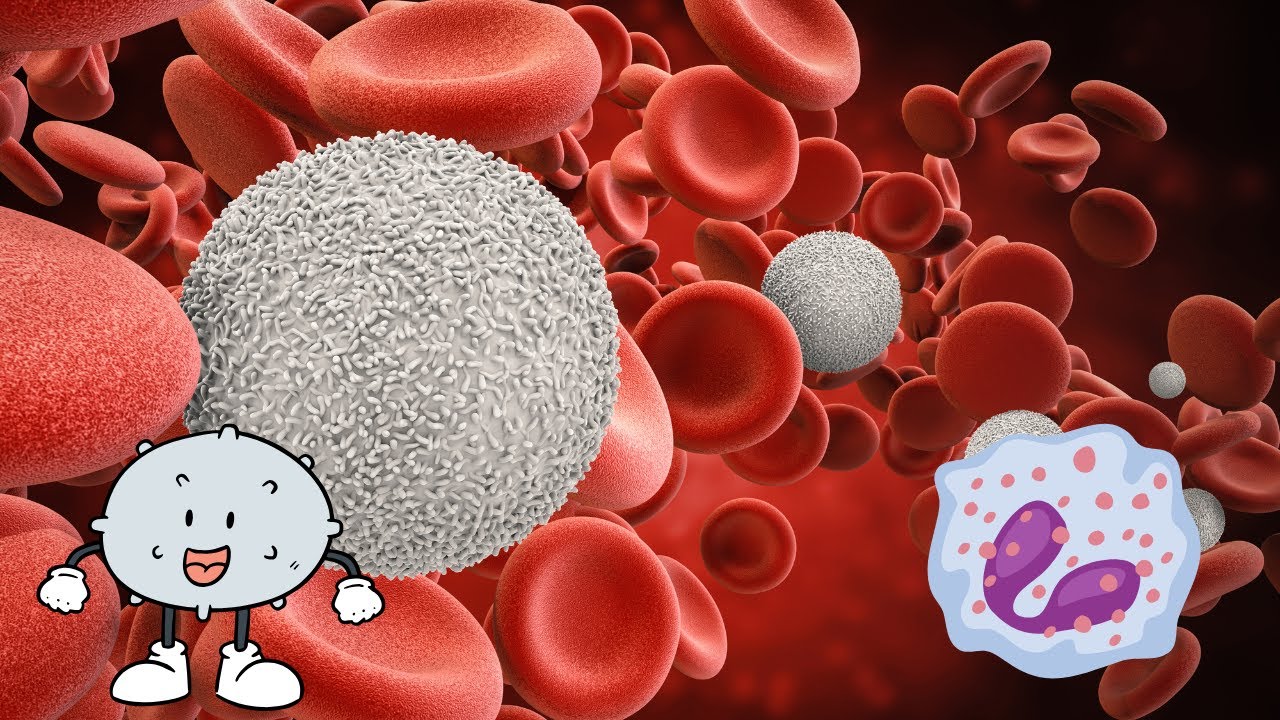
Understanding White Blood Cells and Their Role in the Immune System (5 Minutes)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
