Lesson 11 - Momentum And Impulse in Physics
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the essential concepts of momentum and impulse in physics, building on prior topics of work and energy. It defines momentum (P) as the product of mass (m) and velocity (v), emphasizing that it is a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction. The speaker compares momentum to kinetic energy, highlighting their similarities, especially in how both involve mass and velocity. The conservation of momentum in collisions is underscored as a fundamental principle in physics, while the origin of force will be explored in future discussions, setting the stage for deeper understanding.
Takeaways
- 😀 Momentum is a concept that describes the quantity of motion an object has.
- 😀 The formula for momentum (P) is mass (m) multiplied by velocity (v), expressed as P = m * v.
- 😀 Momentum is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
- 😀 Objects with greater mass or higher velocity will have more momentum.
- 😀 Momentum shares similarities with kinetic energy, but is defined differently: energy involves mass and velocity squared.
- 😀 The principles of momentum are useful for calculations in physics, particularly in collision scenarios.
- 😀 Conservation of momentum is a key concept, indicating that momentum is preserved in isolated systems during collisions.
- 😀 The discussion of momentum builds on earlier topics related to energy in physics.
- 😀 Understanding the forces acting on objects helps to explain changes in momentum.
- 😀 The presentation emphasizes the practical application of these concepts in solving physics problems.
Q & A
What is the definition of momentum according to the transcript?
-Momentum (P) is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity, expressed mathematically as P = mv.
Why is momentum considered a vector quantity?
-Momentum is a vector because it has both magnitude and direction, which is derived from the multiplication of mass (a scalar) by velocity (a vector).
How does the concept of momentum relate to kinetic energy?
-Both momentum and kinetic energy involve mass and velocity, but kinetic energy includes the square of the velocity, represented by the formula KE = 1/2 mv².
What is meant by the conservation of momentum?
-The conservation of momentum refers to the principle that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant before and after a collision.
What analogy does the speaker use to explain momentum?
-The speaker compares the momentum of a bowling ball to that of a ping-pong ball, suggesting that at the same speed, the bowling ball has more momentum due to its greater mass.
What does the speaker say about the origins of force in problems?
-The speaker notes that while force is often presented in problems, the source of that force has not yet been thoroughly discussed and will be addressed later.
What is the significance of understanding momentum in physics?
-Understanding momentum is crucial because it helps explain and predict the behavior of moving objects, particularly in collisions where momentum is conserved.
How is momentum typically represented in physics literature?
-In physics literature, momentum is commonly represented by the letter P.
What is the implication of momentum being a conserved quantity?
-The implication is that in isolated systems, the total momentum before and after an interaction remains unchanged, which is fundamental for solving collision problems.
What does the speaker indicate about the complexity of defining momentum?
-The speaker admits that while the equation for momentum is simple, the deeper understanding of what momentum means in a physical context is complex and not fully understood.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

FISIKA Kelas 10 - Momentum & Impuls | GIA Academy

08 01 Fisika Dasar 1- Momentum Dan Impuls

FISIKA KELAS X | MOMENTUM, IMPULS, dan TUMBUKAN (PART 1) - Konsep Dasar Momentum dan Impuls

Fisika SMA - Impuls & Momentum (3) - Hukum Kekekalan Momentum (I)

Fisika SMA - Impuls & Momentum (1) - Pengenalan Impuls dan Momentum, Rumus Impuls dan Momentum (I)
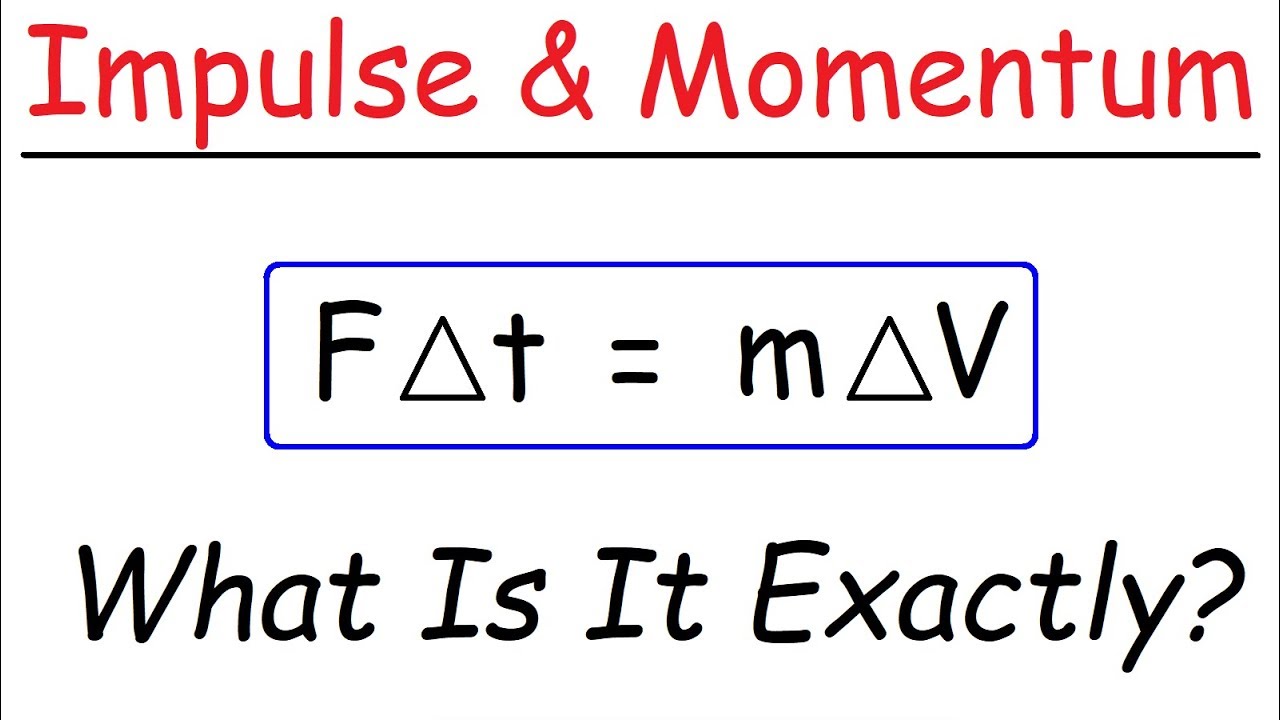
Introduction to Impulse & Momentum - Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
