Vietnam War | The 20th century | World history | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThe Vietnam War, rooted in French colonialism and marked by the rise of the Viet Minh under Ho Chi Minh, escalated in the 1960s as the U.S. intervened to support the anti-communist South Vietnam. Key events like the Gulf of Tonkin incident and the Tet Offensive shifted public opinion, revealing the war's complexities and moral dilemmas, including the My Lai Massacre. The Pentagon Papers exposed governmental deceit, culminating in the U.S. withdrawal after the Paris Peace Accords. Ultimately, the North's victory in 1975 led to significant casualties and showcased the limits of American power, reshaping U.S. foreign policy for years to come.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Vietnam War's roots trace back to French colonization of Southeast Asia in the late 1800s.
- 😀 The Viet Minh, led by Ho Chi Minh, emerged as a liberation movement seeking independence from French rule during World War II.
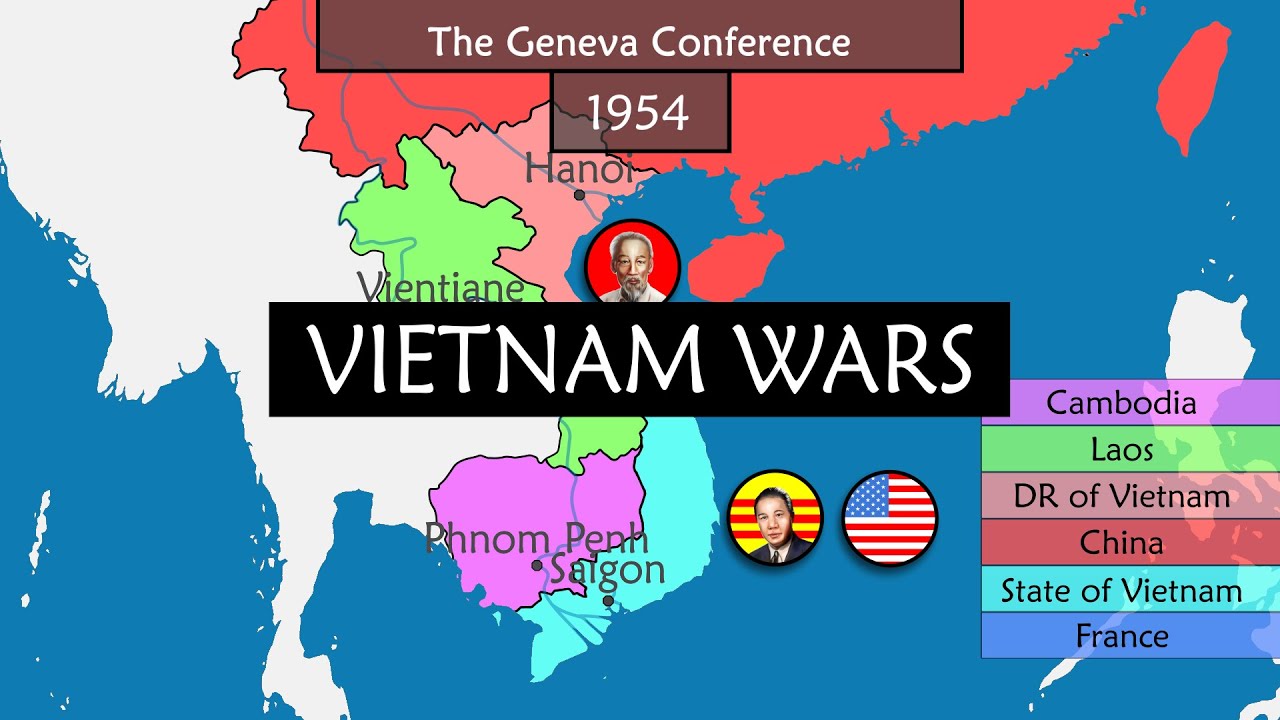
- 😀 The Geneva Conference of 1954 partitioned Vietnam at the 17th parallel, creating North and South Vietnam amid promises of future elections.
- 😀 Ngo Dinh Diem, a corrupt and authoritarian leader, took control of South Vietnam, receiving support from the United States due to his anti-communist stance.
- 😀 The U.S. escalated its involvement in Vietnam, initially sending advisers before committing more troops in response to perceived threats from communism.
- 😀 The Gulf of Tonkin incident in 1964 led to the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, granting President Johnson the authority to escalate military involvement.
- 😀 The Tet Offensive in 1968 challenged U.S. perceptions of the war, revealing that the Viet Cong were not on the verge of defeat as claimed by U.S. leaders.
- 😀 The My Lai Massacre highlighted the brutal realities of the war, causing public outrage and questioning the U.S. military's moral standing.
- 😀 The Pentagon Papers, leaked in 1971, exposed governmental deception regarding the war's conduct and the extent of U.S. operations in Southeast Asia.
- 😀 The Vietnam War concluded with the fall of Saigon in 1975, resulting in significant loss of life and ultimately undermining U.S. credibility in global affairs.
Q & A
What was the historical context leading to the Vietnam War?
-The Vietnam War's origins lie in the late 1800s when France colonized Southeast Asia, creating French Indochina. This colonial rule continued until World War II, when Japan occupied Vietnam, leading to a desire for Vietnamese independence.
Who led the Vietnamese liberation movement?
-The Vietnamese liberation movement was primarily led by the Viet Minh, under the leadership of Ho Chi Minh, who sought to free Vietnam from colonial rule.
What was the significance of the Geneva Conference of 1954?
-The Geneva Conference of 1954 resulted in the partition of Vietnam along the 17th parallel into North Vietnam and South Vietnam, intended to be a temporary measure to allow for cooling off and eventual elections.
How did the United States become involved in the Vietnam War?
-The U.S. became involved by supporting the anti-communist government of Ngo Dinh Diem in South Vietnam, fearing the spread of communism and adopting the containment strategy.
What were the Gulf of Tonkin incidents?
-The Gulf of Tonkin incidents in 1964 involved reported attacks on U.S. naval vessels by North Vietnamese boats, leading to the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, which granted President Johnson authority to escalate U.S. military involvement.
What was the impact of the Tet Offensive in 1968?
-The Tet Offensive was a significant surprise attack by the Viet Cong that undermined U.S. claims of progress in the war and heightened public skepticism about the war's conduct and U.S. military leadership.
What was the My Lai Massacre, and why was it important?
-The My Lai Massacre involved the killing of hundreds of Vietnamese civilians by U.S. soldiers. It shocked the American public and highlighted the moral failures of the U.S. military during the war.
What were the Pentagon Papers, and what did they reveal?
-The Pentagon Papers were classified documents leaked in 1971, revealing that U.S. leaders had misled Congress and the public about the war's progress and the extent of U.S. military operations in Southeast Asia.
What led to the end of U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War?
-The Paris Peace Accords in 1973 marked the official end of U.S. involvement, but the North eventually overran the South in 1975, leading to the fall of Saigon.
What were the human costs of the Vietnam War?
-The war resulted in an estimated 1 to 3 million Vietnamese deaths, along with 58,000 American military casualties, and caused extensive suffering in Cambodia and Laos due to U.S. military actions.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)