Rapid, structured ECG interpretation: A visual guide FOR REVISION!! #electrocardiogram
Summary
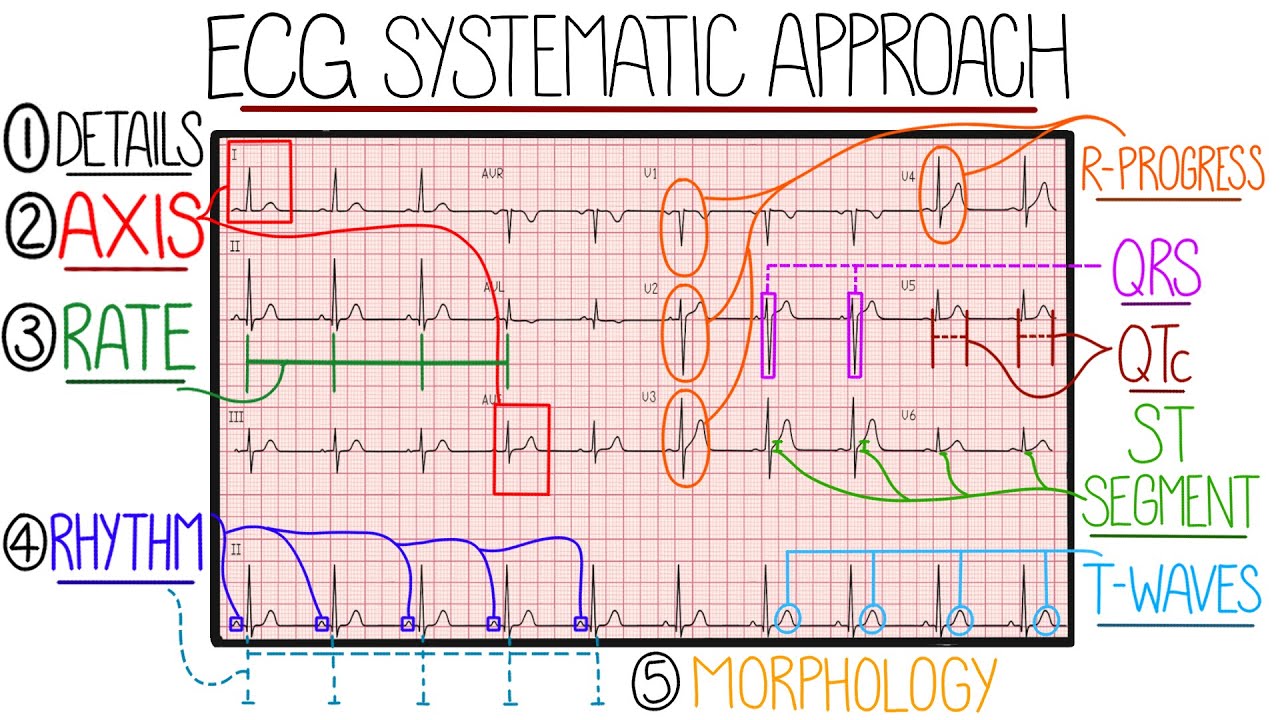
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive guide to the rapid clinical assessment of a 12-lead ECG, detailing the steps for accurate interpretation. It covers essential concepts such as heart rate, rhythm analysis, and the significance of bradycardias and tachycardias. Viewers will learn to identify various arrhythmias, understand cardiac axis deviations, and assess key waveforms and intervals, including P waves, PR intervals, QRS complexes, and QT intervals. With practical examples and clear definitions, this resource is invaluable for anyone looking to enhance their ECG interpretation skills.
Takeaways
- 😀 Always verify patient details and previous ECGs for accurate interpretation.
- 😀 Confirm the ECG is set to 25 mm/second, as it is crucial for rate calculations.
- 😀 Determine heart rate by counting R waves and multiplying by six; normal rates are between 60-100 bpm.
- 😀 Bradycardia is defined as a heart rate below 60 bpm, while tachycardia exceeds 100 bpm.
- 😀 Regular rhythm with positive P waves indicates sinus bradycardia; absence of P waves suggests junctional escape rhythm.
- 😀 Tachycardias can be classified based on QRS shape: narrow (<3 small squares) or broad (≥3 small squares).
- 😀 Atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation are common irregular rhythms characterized by specific wave patterns.
- 😀 The cardiac axis helps determine the overall electrical activity direction; deviations provide diagnostic clues.
- 😀 Assess the PR interval for heart block; a fixed prolonged interval suggests first-degree heart block.
- 😀 T wave inversions and tall waves can indicate serious conditions like myocardial infarction or hyperkalemia.
Q & A
What is the initial step in ECG assessment?
-Always start by checking the patient's name, age, and gender, and review previous ECGs and clinical history.
Why is it important to set the ECG to 25 mm/second?
-The interpretation of the ECG relies on this setting for accurate rate and rhythm analysis.
How do you calculate the heart rate from an ECG?
-Locate the rhythm strip, count the number of R waves, and multiply by six to determine the rate in beats per minute.
What defines a normal heart rate?
-A normal heart rate typically ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute.
What distinguishes sinus bradycardia from other forms of bradycardia?
-Sinus bradycardia is characterized by a regular rhythm with positive P waves preceding each QRS complex at a rate of less than 60 bpm.
What is the significance of the QRS complex width in tachycardias?
-Narrow complex tachycardias have a QRS duration of less than 3 small squares and typically originate from the atria, while broad complex tachycardias, greater than 3 small squares, usually originate from the ventricles.
What are the key features of atrial fibrillation?
-Atrial fibrillation is characterized by an irregularly irregular rhythm and the presence of fibrillatory waves without obvious P waves.
How can you identify left ventricular hypertrophy on an ECG?
-Left ventricular hypertrophy can be suspected if the depth of the S wave in V1 added to the height of the R wave in V5 or V6 is greater than 7 large squares.
What does a prolonged QT interval indicate?
-A prolonged QT interval, especially above 500 ms, can predispose patients to dangerous arrhythmias like Torsades de Pointes.
What is the significance of T wave inversion?
-T wave inversion can indicate ischemia or other cardiac issues, and its significance increases if present in two anatomically grouped leads.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)