Signal detection theory - part 2 | Processing the Environment | MCAT | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into signal detection theory, explaining key concepts such as noise and signal distributions, represented graphically. It introduces the concept of d-prime, which measures the separation between these distributions, influencing task difficulty. The video outlines different decision-making strategies (B, D, C, and beta), illustrating how threshold choices affect the probability of hits and false alarms. The ideal observer strategy minimizes misses and false alarms, and the C variable indicates a participant's conservativeness or liberality in decision-making. Finally, the relationship between beta and d-prime is explored through an equation, providing a comprehensive overview of signal detection dynamics.
Takeaways
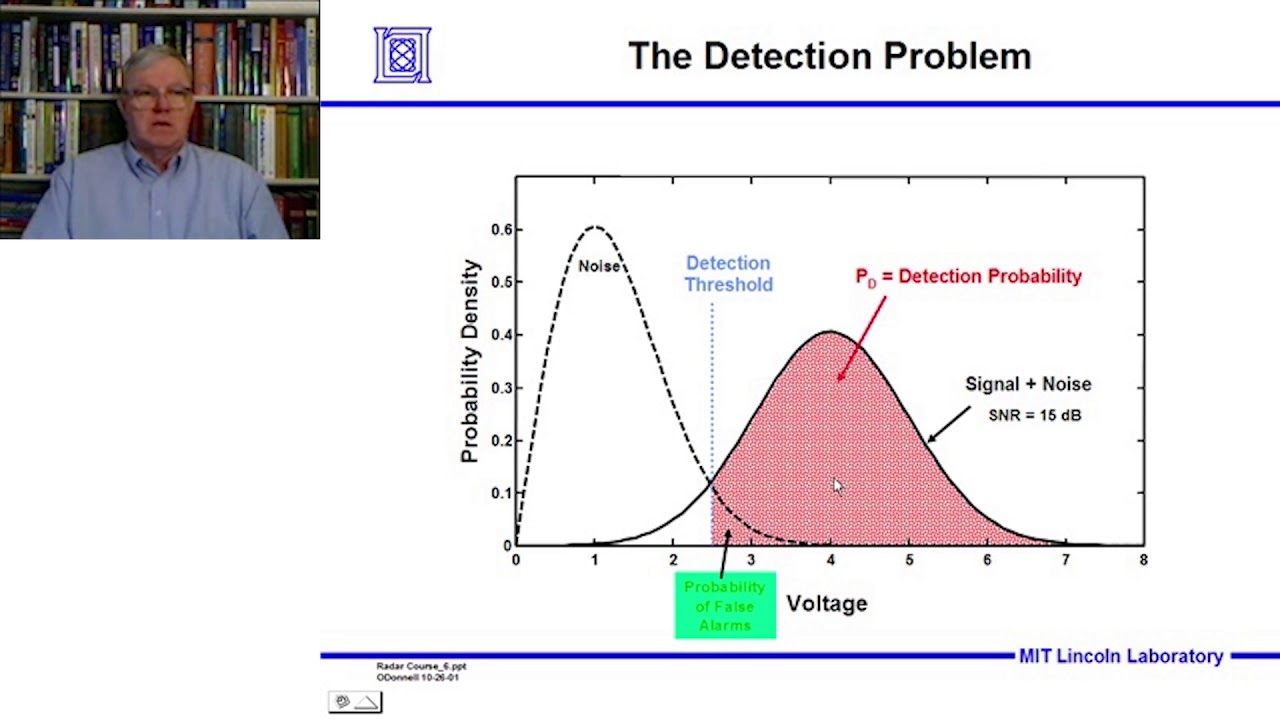
- 😀 The noise distribution represents background noise in signal detection theory.
- 😀 The signal distribution is shifted to the right of the noise distribution, indicating the presence of a signal.
- 😀 The distance between the means of the noise and signal distributions is known as d-prime (d').
- 😀 A larger d-prime indicates a task that is easier, as it suggests the signal is more distinguishable from the noise.
- 😀 The B strategy involves setting a specific threshold for responses, where anything above the threshold is a 'yes'.
- 😀 The D strategy adjusts the threshold relative to the signal distribution using the formula d' - B.
- 😀 The C strategy represents the ideal observer approach, minimizing both misses and false alarms, calculated as (B - d')/2.
- 😀 A C value of 0 indicates an ideal observer, while C values below or above 1 indicate liberal and conservative strategies, respectively.
- 😀 The beta (β) variable reflects the threshold based on the ratio of the heights of the signal and noise distributions.
- 😀 The equation ln(β) = d' × C helps quantify the decision-making strategy in signal detection.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of signal detection theory?
-Signal detection theory (SDT) aims to understand how individuals distinguish between a signal and background noise during tasks.
What does the noise distribution represent in SDT?
-The noise distribution represents the variability in responses when no actual signal is present, effectively illustrating background interference.
How is the signal distribution defined in the context of SDT?
-The signal distribution reflects the presence of a signal and may be shifted relative to the noise distribution, with the degree of shift quantified by d-prime.
What is d-prime, and why is it important?
-D-prime (d') is a measure of sensitivity in detecting a signal, indicating the difference between the means of the signal and noise distributions. A larger d' suggests easier detection of the signal.
What are the different strategies for setting thresholds in signal detection?
-The strategies include B strategy (fixed threshold), D strategy (threshold relative to signal distribution), and C strategy (ideal observer aiming to minimize errors).
How is the threshold determined in the B strategy?
-In the B strategy, an individual sets a specific threshold value; for example, if the threshold is 2, then any stimulus above this value is deemed a 'yes' response.
What does the C strategy represent in signal detection?
-The C strategy represents the approach of an ideal observer, calculated as C = (B - d') / 2, and aims to minimize both false alarms and misses.
How does the value of C classify an observer's strategy?
-C values classify strategies as follows: C = 0 indicates an ideal observer, C < 1 denotes a liberal strategy (more 'yes' responses), and C > 1 signifies a conservative strategy (more 'no' responses).
What is beta (β) in the context of signal detection theory?
-Beta (β) represents the ratio of the heights of the signal distribution to the noise distribution, providing insight into decision thresholds based on the relative strengths of signals and noise.
How is beta mathematically expressed in relation to d-prime and C?
-Beta is expressed as ln(β) = d' * C, linking the sensitivity measure (d') with the strategy (C) employed by the observer.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Human Information Processing
Introduction to Radar Systems – Lecture 5 – Detection of Signals; Part 1
Radar Signal Processing | Basic Concepts | Radar Systems And Engineering

SS1: Signals & Systems Syllabus | B.Tech 2nd Year Electrical & Electronics AKTU Syllabus

Signal detection theory - part 1 | Processing the Environment | MCAT | Khan Academy

Differential Instrumentation Amplifier | Bioinstrumentation Design
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
