Nasopharyngeal Airway (NPA) Insertion | ABCDE Emergency | OSCE Guide | UKMLA | CPSA
Summary
TLDRIn this instructional video, James discusses the nasopharyngeal airway (NPA), a crucial tool for managing patients with airway difficulties. He outlines its key indications, such as aiding semi-conscious patients and those with seizures or maxillofacial injuries, while highlighting contraindications like base of skull fractures. The video explains sizing options and demonstrates proper insertion techniques, ensuring the airway remains patent. James emphasizes the importance of reassessing the patient after insertion and provides guidance on safe removal. This comprehensive overview equips viewers with essential knowledge for effective airway management.
Takeaways
- 😀 The nasopharyngeal airway (NPA) is a tube designed to maintain airway patency, crucial for patients with airway difficulties.
- 😀 The NPA is particularly beneficial for patients who are semi-conscious, such as those recovering from anesthesia or under the influence of substances.
- 😀 It is an ideal airway device for patients experiencing seizures or those with jaw clenching, as it avoids gagging or vomiting.
- 😀 Significant maxillofacial injuries may require the use of an NPA, although caution is needed.
- 😀 A base of skull fracture is a relative contraindication for NPA insertion due to the risk of intracranial placement.
- 😀 The NPA comes in various sizes, with size 6 and size 8 being common for adults; selection is based on nostril size.
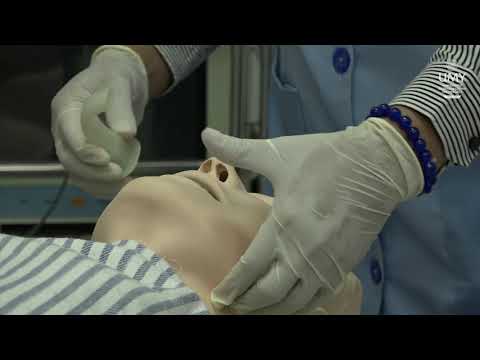
- 😀 The insertion technique involves lubricating the tube and gently twisting it into the nostril until the flange is positioned comfortably against the nostril.
- 😀 Care should be taken to avoid using a tube that is too long, which may cause the patient to gag or cough.
- 😀 After insertion, it's crucial to reassess the patient's airway and ensure they are ventilating adequately.
- 😀 The NPA is well-tolerated, allowing patients to potentially remove it themselves; it can also be easily removed by a healthcare provider.
Q & A
What is a nasopharyngeal airway?
-A nasopharyngeal airway is a flexible tube that is inserted into the nasal cavity and extends into the oropharynx to maintain an open airway.
When is a nasopharyngeal airway indicated?
-It is indicated for patients who are not fully unconscious, especially those recovering from anesthesia or intoxicated, as well as during seizures or in cases of significant maxillofacial injuries.
What are the contraindications for using a nasopharyngeal airway?
-A base of skull fracture is a relative contraindication due to the risk of the airway entering the cranial vault.
How do you determine the appropriate size for a nasopharyngeal airway?
-There is no reliable way to size the tube; instead, you should assess the patient's nostril size and select a tube that fits comfortably without causing extra pressure.
What sizes are commonly used for nasopharyngeal airways?
-Common sizes are typically size 6 and size 8.
What is the correct insertion technique for a nasopharyngeal airway?
-Gently insert the tube into the chosen nostril, twisting downwards until the flange rests comfortably against the nostril, ensuring the tip is positioned in the back of the oropharynx.
What should be done after inserting the nasopharyngeal airway?
-After insertion, it is important to reassess the patient's airway to confirm it is patent and to check if they are ventilating properly.
Can patients remove the nasopharyngeal airway themselves?
-Yes, the airway is often well-tolerated, and patients may be able to remove it themselves if they choose to.
What should be done if a patient starts to gag or cough after insertion?
-If the patient begins to gag or cough, it may indicate the tube is too long, and you should remove it and replace it with a smaller size.
How can additional support be provided to a patient after inserting a nasopharyngeal airway?
-Additional oxygen may be administered to support the patient after the airway is inserted.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Nasopharyngeal and Oropharyngeal Airway Insertion

Oropharyngeal Airway Insertion | Guedel | OPA | ABCDE Emergency | OSCE Guide | UKMLA | CPSA
MANAJEMEN AIRWAY-BREATHING

AHA Airway Management

DAS guidelines for the management of difficult airway; what should you know?

MENEMONICO AVALIAÇÃO PRIMARIA XABCDE - PARTE 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
