10 The Cardiac Cycle Video
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed explanation of the cardiac cycle, highlighting the sequential phases associated with one heartbeat. It defines systole as the contraction phase and diastole as the relaxation phase, illustrating the processes of atrial systole, ventricular systole, and the relaxation period. The video emphasizes that during the cardiac cycle, the heart spends more time in relaxation than contraction, with specific timings for each phase. It also notes how the heart's function changes during exercise, leading to a faster heartbeat and shorter relaxation periods, ultimately demonstrating the heart's efficiency and adaptability.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cardiac cycle encompasses all events associated with one heartbeat, involving both atrial and ventricular activities.
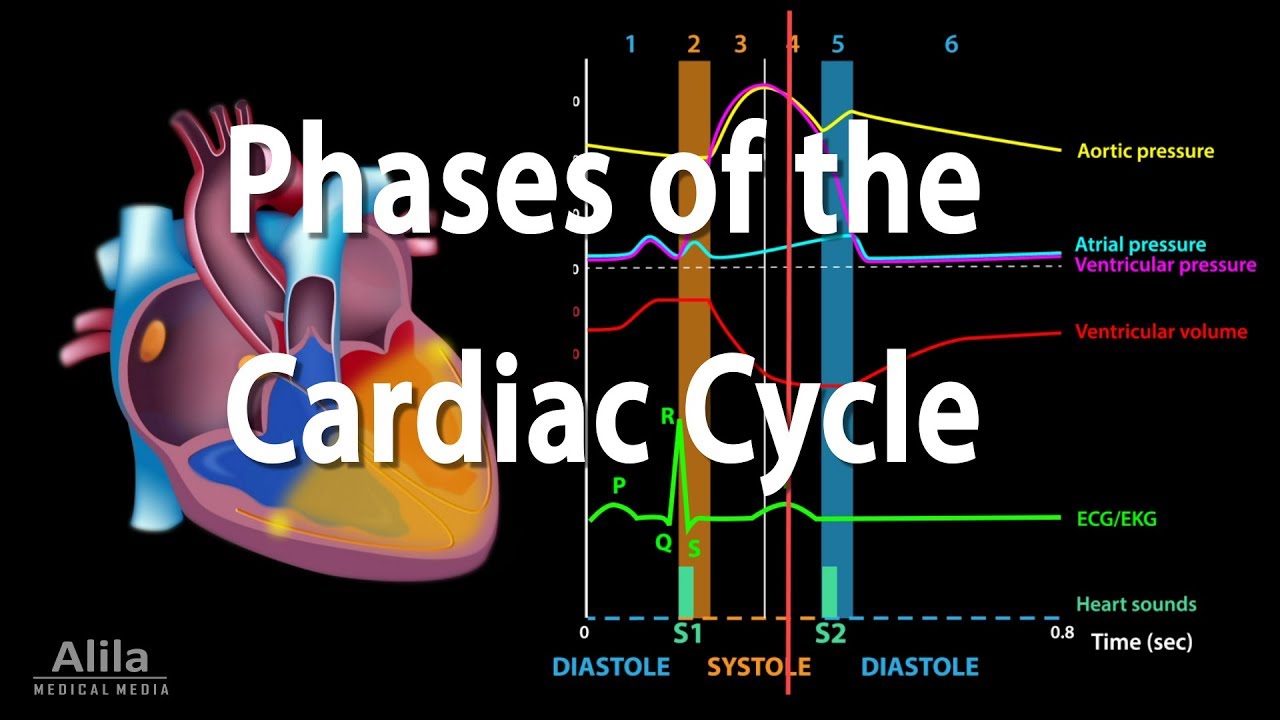
- ❤️ The terms 'systole' and 'diastole' refer to the contraction and relaxation phases of the heart, respectively.
- 📉 Atrial systole occurs first, where the atria contract and push blood into the ventricles, contributing 25% of ventricular filling.
- 🩸 During ventricular systole, the ventricles contract and eject about 70 mL of blood into the arteries.
- 🔄 The relaxation period allows all chambers of the heart to relax and fill with blood, which constitutes about 75% of ventricular filling.
- 📊 The entire cardiac cycle takes approximately 0.8 seconds, with the majority of this time spent in relaxation.
- ⚖️ Pressure dynamics are crucial: AV valves open when atrial pressure exceeds ventricular pressure, while semilunar valves open when ventricular pressure exceeds arterial pressure.
- 🧠 The SA node initiates atrial contraction, which is represented by the P wave in an ECG.
- 🔗 Each contraction of the heart is associated with specific electrical events, as seen in the ECG wave patterns.
- 🏃♂️ During exercise, the duration of the relaxation period shortens, leading to an increased heart rate and more rapid cycles.
Q & A
What is a cardiac cycle?
-A cardiac cycle includes all the events associated with one heartbeat, involving the contraction and relaxation of the heart's chambers.
What happens during atrial systole?
-During atrial systole, the atria contract while the ventricles are relaxed, causing blood to flow from the atria into the ventricles.
What are the phases of contraction and relaxation in the heart?
-The phases are termed systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation). Atrial systole and diastole refer to the atria, while ventricular systole and diastole refer to the ventricles.
What triggers the contraction of the atria?
-The contraction of the atria is triggered by an action potential generated at the SA node, which causes depolarization and the appearance of the P wave on an ECG.
How much blood is ejected into the ventricles during atrial systole?
-Approximately 25% of the blood fills the ventricles during atrial systole.
What occurs during ventricular systole?
-During ventricular systole, the ventricles contract, increasing pressure and causing the AV valves to close and the semilunar valves to open, allowing blood to be ejected into the arteries.
What is the significance of the relaxation period in the cardiac cycle?
-The relaxation period allows the heart chambers to fill with blood, and it is when 75% of ventricular filling occurs before contraction.
What role do the semilunar valves play during the cardiac cycle?
-The semilunar valves prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles once the blood is ejected into the pulmonary trunk and aorta.
How long does a complete cardiac cycle take at rest?
-A complete cardiac cycle at rest takes approximately 0.8 seconds.
How does exercise affect the cardiac cycle?
-During exercise, the relaxation period of the cardiac cycle becomes shorter, resulting in a faster heart rate.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Cardiac Cycle || Systole, Diastole, Blood flow in heart, Movement of Valves

The Cardiac Cycle is SO EASY! Stop Making it Hard!

Measuring the Human Heart - Heartbeat, Blood Pressure, and Cardiac Output | Visible Body

How the Heart Works (Animation)
The Cardiac Cycle, Animation

8-15 Cardiac Cycle (Cambridge AS & A Level Biology, 9700)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
