Measuring the Human Heart - Heartbeat, Blood Pressure, and Cardiac Output | Visible Body
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the mechanics of the human heart, focusing on heartbeat, blood pressure, and cardiac output. It explains the heart's size, weight, and the two phases of a heartbeat—systole and diastole. Viewers learn about how blood pressure is measured, the function of heart valves, and how cardiac output is calculated based on stroke volume and heart rate. The video emphasizes the importance of these metrics in understanding heart function and encourages using interactive 3D models to explore circulatory system anatomy.
Takeaways
- 💪 The human heart is a powerful organ, weighing around 300 grams, and is about the size of a fist.
- 🧔 Typically, an adult male's heart is larger than that of an adult female.
- 💓 The average resting heart rate is about 72 beats per minute.
- 🫀 The heartbeat results from the contraction and relaxation of the ventricles, the heart's lower chambers.
- 🔄 The heartbeat has two phases: systole (ventricles contract) and diastole (ventricles relax).
- 🔊 The sound of the heartbeat comes from the closing of the heart's valves during systole and diastole.
- 📊 Blood pressure is measured with two numbers: systolic pressure (when ventricles contract) and diastolic pressure (when ventricles relax).
- 🩸 The average systolic pressure is around 120 mmHg, while the average diastolic pressure is around 70 mmHg.
- 📏 Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) using a sphygmomanometer.
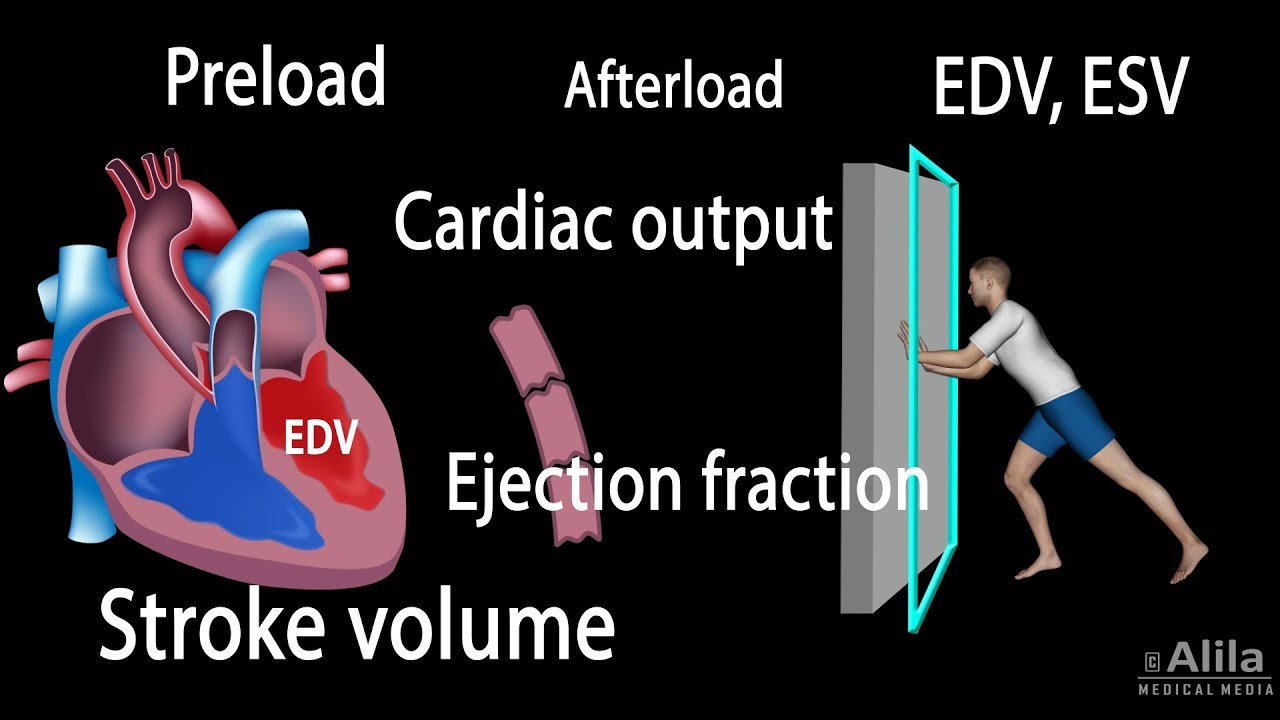
- 🚴 Cardiac output, the volume of blood the heart pumps per minute, is calculated by multiplying stroke volume (average 70 mL) by heart rate (average 72 beats per minute), resulting in 5.4 liters per minute.
Q & A
What is the average weight of an adult human heart?
-The average adult human heart weighs around 300 grams, which is less than a pound.
How does the size of a male's heart compare to a female's heart?
-Typically, the heart of an adult male is slightly larger than the heart of an adult female.
How many times does the average human heart beat per minute at rest?
-The average human heart beats around 72 times per minute at rest.
What are the two phases of the heartbeat?
-The two phases of the heartbeat are systole, when the ventricles contract and pump blood out, and diastole, when the ventricles relax and fill with blood.
What causes the heartbeat sound?
-The heartbeat sound is caused by the closing of the heart's valves. During systole, the mitral and tricuspid valves close, while during diastole, the semilunar valves close.
How is blood pressure measured and what do the two numbers represent?
-Blood pressure is measured using two numbers. The systolic pressure represents the highest pressure when the ventricles contract, while the diastolic pressure represents the lowest pressure when the ventricles relax.
What is the average systolic and diastolic blood pressure?
-The average systolic pressure is around 120 millimeters of mercury, and the average diastolic pressure is around 70 millimeters of mercury.
What unit is used to measure blood pressure?
-Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg), which is a manometric unit used to measure force applied by a liquid.
How is cardiac output calculated?
-Cardiac output is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (amount of blood pumped per beat) by the number of heartbeats per minute. For example, with a stroke volume of 70 milliliters and a heart rate of 72 beats per minute, the cardiac output would be 5040 milliliters, or 5.4 liters per minute.
How does cardiac output change with physical activity?
-Cardiac output increases with a higher heart rate, which is required during increased physical activity to supply more oxygenated blood to the body.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

CICLO CARDÍACO : Coração como bomba - Fisiologia ( capítulo 9) │Guyton e Hall

8-15 Cardiac Cycle (Cambridge AS & A Level Biology, 9700)

How the Heart Works (Animation)

Fisiologi Pengaturan Tekanan Darah
Cardiac Output, Stroke volume, EDV, ESV, Ejection Fraction

Cardiovascular System Physiology - Cardiac Output (stroke volume, heart rate, preload and afterload)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)