BAB 4 GERAK DAN GAYA || Gerak – Materi Kelas 7 Kurikulum Merdeka
Summary
TLDRThis educational video introduces key concepts of motion, focusing on the differences between distance and displacement, as well as speed and velocity. It explains how motion is relative and emphasizes the importance of reference points in determining displacement. The video outlines the formulas for calculating speed and velocity, distinguishing between scalar and vector quantities. By engaging with real-life examples, viewers learn how these concepts apply to their everyday experiences, fostering a deeper understanding of the physical world. Overall, it serves as a foundational lesson in the principles of motion for seventh-grade students.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding motion begins with recognizing how we travel to school and the distances involved.
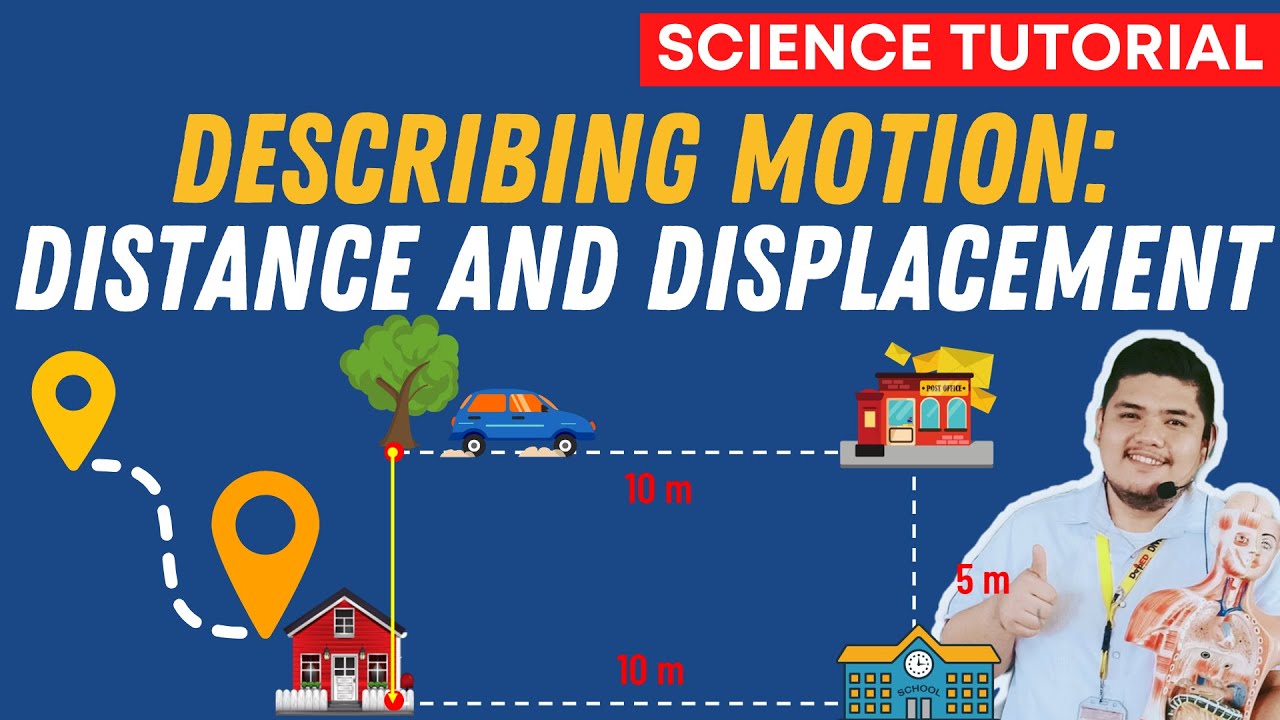
- 📏 Position is defined as a reference point, and displacement is the difference between final and initial positions.
- 🚶♂️ Distance is the total path traveled, which can differ from displacement when returning to the starting point.
- ⚖️ Motion is relative; how we perceive movement depends on the observer's frame of reference.
- 🌳 Apparent motion occurs when stationary objects seem to move due to the observer's movement (e.g., trees appearing to pass by when in a bus).
- ⏱️ Speed is a scalar quantity that indicates how fast something is moving, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes direction.
- 📊 Average speed can be calculated by dividing distance by time, while instantaneous speed refers to speed at a specific moment.
- 🧮 The formula for calculating velocity is displacement divided by time, emphasizing the importance of direction in motion.
- 🚦 Real-life examples can illustrate how speed and velocity are applied in daily activities, enhancing understanding of these concepts.
- 🔍 Grasping the differences between speed and velocity is crucial for interpreting various motion scenarios correctly.
Q & A
What is the difference between distance and displacement?
-Distance is the total path traveled by an object, regardless of direction, while displacement is the change in position measured from the starting point to the final position.
How is displacement calculated?
-Displacement is calculated by subtracting the initial position from the final position, using the formula: Displacement = Final Position - Initial Position.
What is meant by 'relative motion'?
-Relative motion refers to how the movement of an object can be perceived differently based on the observer's point of view or reference frame.
Can you give an example of relative motion?
-An example of relative motion is when a person in a moving car sees a stationary tree as moving backward, while the tree itself is not moving.
What is the formula for calculating speed?
-Speed is calculated using the formula: Speed = Distance / Time.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
-Speed is a scalar quantity that measures how fast an object is moving without considering its direction, whereas velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and the direction of motion.
What are scalar and vector quantities?
-Scalar quantities are defined only by their magnitude (e.g., distance, speed), while vector quantities are defined by both magnitude and direction (e.g., displacement, velocity).
What does it mean when we say an object is in motion?
-An object is in motion when its position changes relative to a reference point over time.
What is average speed?
-Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken, and it may not be constant throughout the motion.
How does the concept of 'zero displacement' apply?
-Zero displacement occurs when an object returns to its initial position after moving, resulting in no overall change in position despite any distance traveled.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Linear Motion - Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity, Acceleration - SPM & IGSCE Physics
DESCRIBING MOTION: DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT | SCIENCE 7 QUARTER 3 MODULE 1

Gerak Benda dan Makhluk Hidup di Lingkungan Sekitar

BAB 4 : GERAK DAN GAYA | Part 1 : GERAK BENDA | IPA SMP Kelas 7 Kurikulum Merdeka

DESCRIBING MOTION: SPEED AND VELOCITY| SCIENCE 7 QUARTER 3 MODULE 1

Kinematics in 1 dimension part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
