Introduction to Geostatistics Part III Module 1
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial delves into spatial interpolation and inference, focusing on kriging methods to transform discrete data into predictive models for natural resource management. By illustrating key examples, such as the correlation between air quality and health, the lecture emphasizes the importance of spatial models in understanding environmental issues. It discusses various deterministic interpolation techniques, including nearest neighbor and inverse distance weighting, highlighting the need for structural proximity and clustering effects in effective estimation. Ultimately, the session underscores the significance of statistical tools in managing resources and enhancing decision-making processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Spatial interpolation is essential for understanding and visualizing natural resource phenomena.
- 😀 Models help visualize spatial dispersion and manage critical resources, like contaminated soil and air quality.
- 😀 A significant relationship exists between environmental variables, as demonstrated by studies on biodiversity and lung cancer.
- 😀 Deterministic interpolation methods are commonly used in computer graphics and scientific visualization.
- 😀 Linear interpolation estimates unknown values based on a weighted average of known sample data.
- 😀 The simplest interpolation method involves using the nearest neighbor to assign sample values.
- 😀 Triangulation can provide a more complex interpolation method by considering three neighborhood samples.
- 😀 The inverse square distance method is a popular interpolation technique but can lead to clustering issues.
- 😀 Effective interpolation should account for structural proximity and clustering effects of samples.
- 😀 Understanding statistical tools is vital for transforming sparse sample data into comprehensive models.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the tutorial discussed in the transcript?
-The tutorial focuses on spatial interpolation and spatial inference, specifically using kriging methods to analyze spatial patterns of natural resources.
Why is modeling reality important in the context of natural resource management?
-Modeling reality is important because it helps visualize and understand the spatial dispersion of characteristics in natural resources, allowing for better evaluation and management.
Can you provide an example of how modeling has been beneficial in scientific research?
-An example is the collaboration between biologists studying Lincoln's biodiversity and cancer researchers who discovered a strong correlation between air quality and lung cancer occurrences through their respective models.
What are some applications of spatial models mentioned in the transcript?
-Applications include managing air quality, controlling the abundance of migratory bird species, and assessing contamination levels in rivers.
What is the main difference between deterministic models and those used for natural phenomena?
-Deterministic models work under certainty and often do not account for uncertainty, while models for natural phenomena must deal with inherent uncertainties and variabilities.
What is the purpose of using a linear interpolator in spatial analysis?
-The linear interpolator aims to estimate values at unknown locations based on a linear combination of known sample values in the neighborhood.
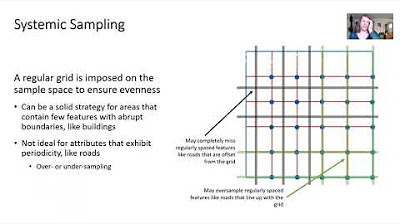
What are the drawbacks of using simple interpolation methods like polygons of influence?
-The drawbacks include discontinuities between polygons, which can result in areas receiving the same value despite different spatial characteristics.
How does the inverse square distance method of interpolation work?
-The inverse square distance method assigns weights to sample values based on the inverse of their squared distance to the point being estimated, allowing for contributions from all samples.
What properties should a spatial interpolator reflect according to the discussion?
-A spatial interpolator should reflect both the structural proximity of samples to the estimated point and a declustering effect to account for correlated samples.
What references are suggested for further reading on spatial modeling and interpolation?
-The transcript suggests classical references from authors like 'His' and 'Peoc', particularly for evaluations related to natural resources.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

A "Crash Course" to Spatial Interpolation
Spatial Sampling & Interpolation

Episode 80: What Mining Engineers Need to Know About Resource Estimation. Fresh Thinking Podcast

EDUC 201 A - Tutorial 3 (Chapter 2) - Fall 24/25

#1 Carga piezométrica e fluxo subterrâneo
MCMC Gibbs Sampler part 2 aproksimasi diskrit
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
