Pemeriksaan Tanda Rangsang Meningeal, Sensasi Radikuler, Refleks Patologis, dan Refleks Primitif
Summary
TLDRIn this detailed demonstration, Dr. Drial Sarf presents a comprehensive physical examination focused on assessing neck stiffness and neurological signs. The video outlines key techniques for evaluating conditions such as meningeal irritation and radicular sensations, including tests like the Kernig sign and Brudzinski sign. Each step is methodically explained, emphasizing patient positioning and observation of involuntary responses. Dr. Sarf also explores reflex testing and specific neurological assessments, ensuring thoroughness in diagnosing potential nerve involvement. This informative session is essential for medical students and healthcare professionals aiming to enhance their clinical skills.
Takeaways
- 😀 The demonstration involves physical examination techniques for assessing neck stiffness (kaku kuduk).
- 😀 The examination begins with the patient lying supine without a pillow, ensuring full neck rotation.
- 😀 Passive neck flexion is performed to check for resistance, which indicates possible stiffness.
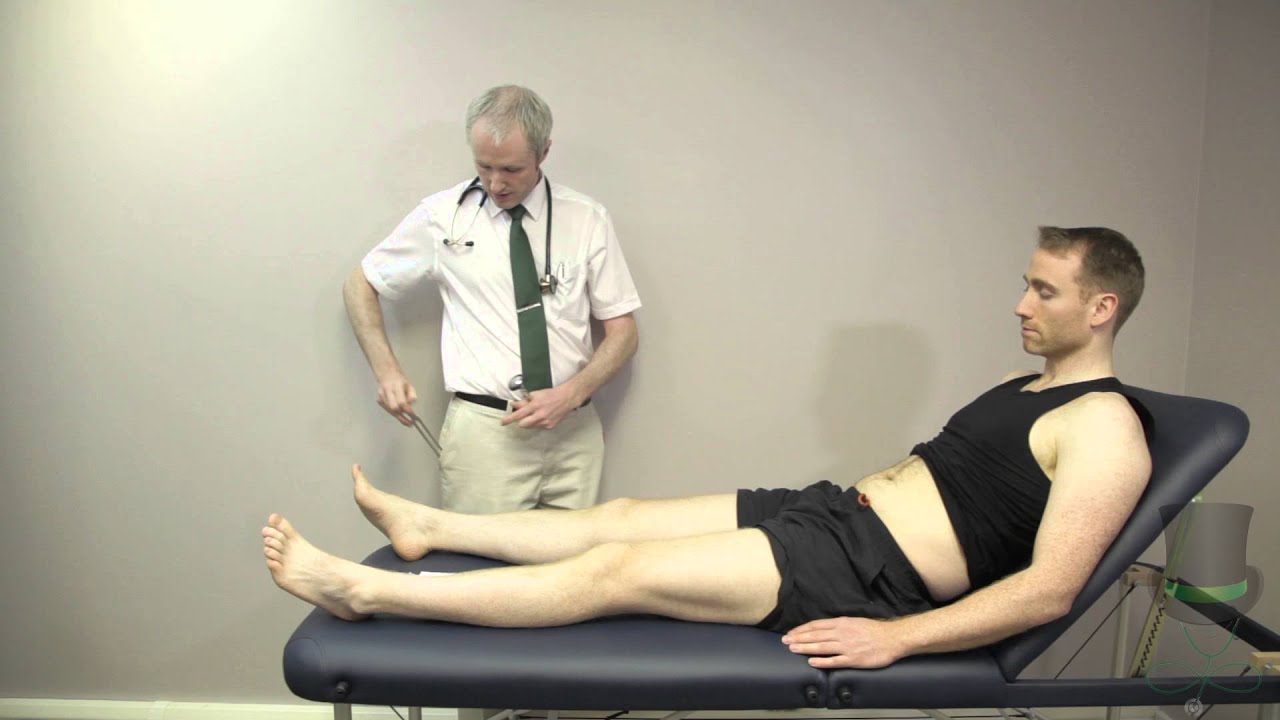
- 😀 Kernig's sign is assessed by flexing the hip and knee to 90 degrees, then extending the knee to check for resistance.
- 😀 Brudzinski's sign is observed by flexing the neck to see if the patient's knees involuntarily flex.
- 😀 The Chaddock sign and Sural reflexes are used to check for involuntary movements in response to stimuli.
- 😀 The Ulnar nerve test is performed by tapping the ulnar groove to observe any radicular pain.
- 😀 The Babinski reflex and its variants are tested to assess neurological function in the lower extremities.
- 😀 The examination includes testing for pathological reflexes such as the glabellar reflex and grasp reflex.
- 😀 Throughout the assessment, the examiner continuously communicates with the patient to gather feedback on sensations and pain responses.
Q & A
What is the main focus of Dr. Drial Sarf's demonstration?
-The main focus of Dr. Drial Sarf's demonstration is the physical examination techniques for detecting neck stiffness and various neurological signs.
How should the patient be positioned for the physical examination?
-The patient should be lying supine without a pillow, allowing for proper examination of neck mobility.
What does a positive neck stiffness test indicate?
-A positive neck stiffness test indicates the presence of neck stiffness (kaku kuduk) when there is resistance during passive flexion of the neck.
What procedure is performed to check for the Kernig sign?
-To check for the Kernig sign, the patient's hip and knee joints are flexed to 90 degrees, and the knee is extended passively. If there is resistance or pain, the sign is considered positive.
What does a positive Brudzinski sign indicate?
-A positive Brudzinski sign is indicated when there is involuntary flexion of the knees upon passive flexion of the patient's neck, suggesting possible meningeal irritation.
How is the Chaddock sign tested?
-The Chaddock sign is tested by applying pressure to the inferior aspect of the zygomatic arch and observing for involuntary flexion of the elbows.
What is the purpose of performing the Tinel's test at the wrist?
-The Tinel's test at the wrist is performed to detect median nerve irritation, where tapping over the carpal tunnel may elicit pain or tingling along the nerve's distribution.
What is the significance of the Babinski reflex?
-The Babinski reflex is significant as it indicates the integrity of the corticospinal tract; a positive response is shown by dorsiflexion of the big toe and fanning of the other toes.
What reflexes are assessed during the neurological examination?
-Reflexes assessed during the neurological examination include the Babinski reflex, the Hoffmann reflex, the glabella reflex, and the palmomental reflex, among others.
What does the presence of a pathological reflex suggest?
-The presence of a pathological reflex suggests possible central nervous system involvement, indicating conditions such as upper motor neuron lesions.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
The Diabetes Exam

Dermato Musculoskeletal: Pemeriksaan Anamnesis & Muskuloskeletal

Pemeriksaan Fisik Muskuloskeletal - dr. Mohammad Shahreza, Sp.OT

Epley Maneuver for Vertigo - Ask Doctor Jo

The Science of Soil Health: Nightcrawlers and Soil Water Flow

How to detect drift and resolve issues in you Machine Learning models?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
