BTEC Applied Science - Unit 5 Chemistry - Enthalpy Changes
Summary
TLDRIn this BTEC Applied Science lesson, the focus is on enthalpy changes, covering key definitions and types such as enthalpy of combustion, formation, and hydration. The instructor explains that enthalpy, denoted as 'H', represents thermal energy within a chemical system. Students learn to differentiate between exothermic and endothermic reactions and how to interpret enthalpy changes through graphs. Specific examples illustrate how to balance combustion and formation equations. The lesson emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts in chemistry, preparing students for future calculations and applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Enthalpy (ΔH) is the thermal energy stored within a chemical system, represented by the equation H = U + PV.
- 😀 The change in enthalpy (ΔH) can be expressed as ΔH = ΔU + PΔV, indicating how energy is transformed during reactions.
- 🔥 Exothermic reactions release energy to the surroundings, resulting in an increase in temperature and a negative ΔH value.
- ❄️ Endothermic reactions absorb energy from the surroundings, leading to a decrease in temperature and a positive ΔH value.
- 📈 Enthalpy profile diagrams visually represent energy changes during reactions, showing the relationship between reactants and products.
- 🔥 The enthalpy of combustion (ΔH_c) is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance reacts completely with oxygen, always resulting in a negative ΔH.
- 🌱 The enthalpy of formation (ΔH_f) refers to the enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states.
- 💧 The enthalpy of hydration (ΔH_{hyd}) is the enthalpy change when gaseous ions are converted to aqueous ions, and it is also exothermic.
- ⚡ Activation energy is the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur, depicted as a peak in enthalpy diagrams.
- 🔄 The strength of bonds influences the exothermicity of a reaction; stronger bonds lead to more exothermic changes.
Q & A
What is the definition of enthalpy?
-Enthalpy, represented by the symbol H, is the thermal energy stored within a chemical system. It is defined as the sum of internal energy and the product of pressure and volume.
How can we measure enthalpy changes in a chemical reaction?
-We cannot directly measure enthalpy, but we can measure the energy released or absorbed during a reaction, which indicates the enthalpy change.
What is an exothermic reaction?
-An exothermic reaction is one that releases energy to the surroundings, resulting in an increase in the temperature of the surroundings and a negative enthalpy change (ΔH).
What is an endothermic reaction?
-An endothermic reaction absorbs energy from the surroundings, causing a decrease in the temperature of the surroundings and a positive enthalpy change (ΔH).
What do the axes represent in an enthalpy profile diagram?
-In an enthalpy profile diagram, the y-axis represents enthalpy, while the x-axis indicates the reaction pathway or progress of the reaction.
What is the enthalpy of combustion?
-The enthalpy of combustion is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance completely reacts with oxygen under standard conditions.
What are the standard conditions for measuring enthalpy changes?
-Standard conditions for enthalpy changes are defined as a temperature of 298 K, a pressure of 101 kPa, and solutions at 1 mole per decimeter cubed.
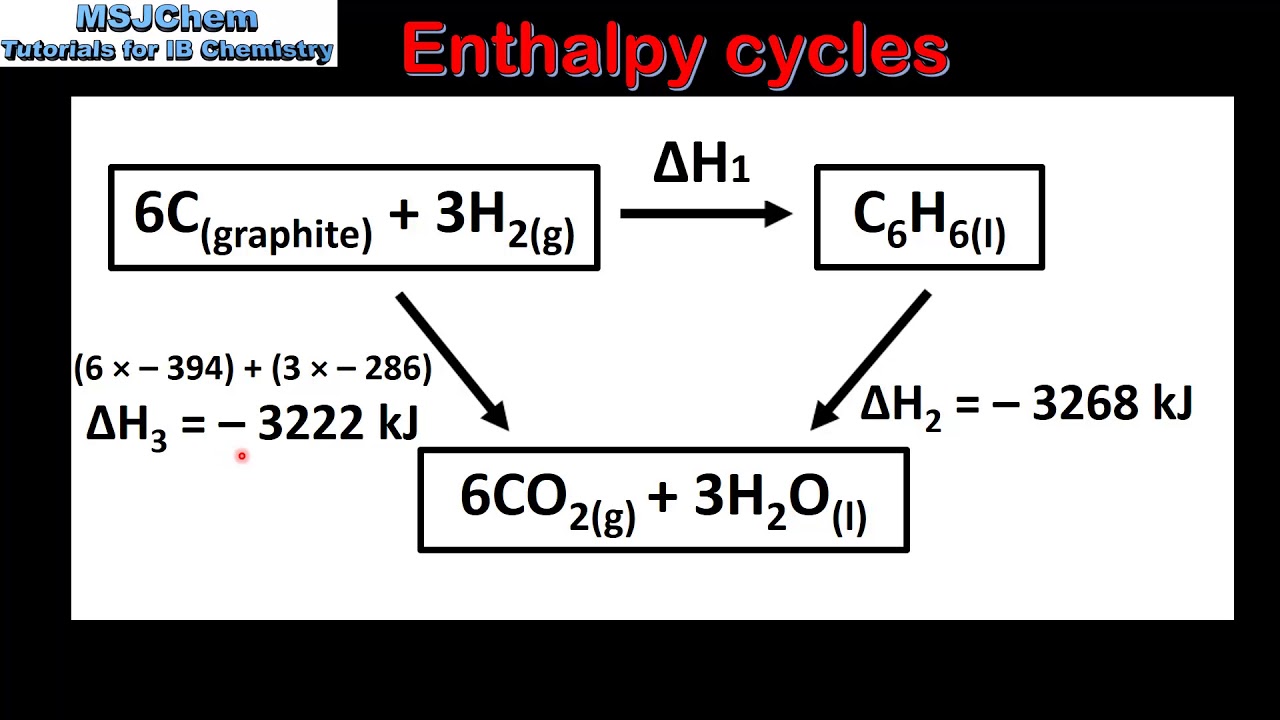
What is the significance of balancing chemical equations in enthalpy changes?
-Balancing chemical equations ensures that the law of conservation of mass is upheld, allowing accurate calculations of enthalpy changes for specific reactions.
What is the enthalpy of formation?
-The enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions.
What does the enthalpy change of hydration refer to?
-The enthalpy change of hydration refers to the enthalpy change when one mole of aqueous ions is formed from one mole of gaseous ions, typically resulting in an exothermic reaction.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)