Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs in the Workplace
Summary
TLDRThis video explores Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, a motivational theory by psychologist Abraham Maslow. The hierarchy consists of five levels: physiological needs, safety needs, belongingness and love needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization. Maslow asserts that individuals must satisfy lower-level needs before addressing higher ones. The framework is relevant in organizational settings, where meeting employee needs can enhance motivation and productivity. By ensuring basic needs are fulfilled, organizations can foster a supportive environment that encourages personal growth and success, illustrating the lasting impact of Maslow's theories in both psychology and management.
Takeaways
- 😀 Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a psychological theory that outlines five basic levels of human needs.
- 📚 Abraham Maslow introduced his ideas in a 1943 article and a 1954 book titled 'Motivation and Personality.'
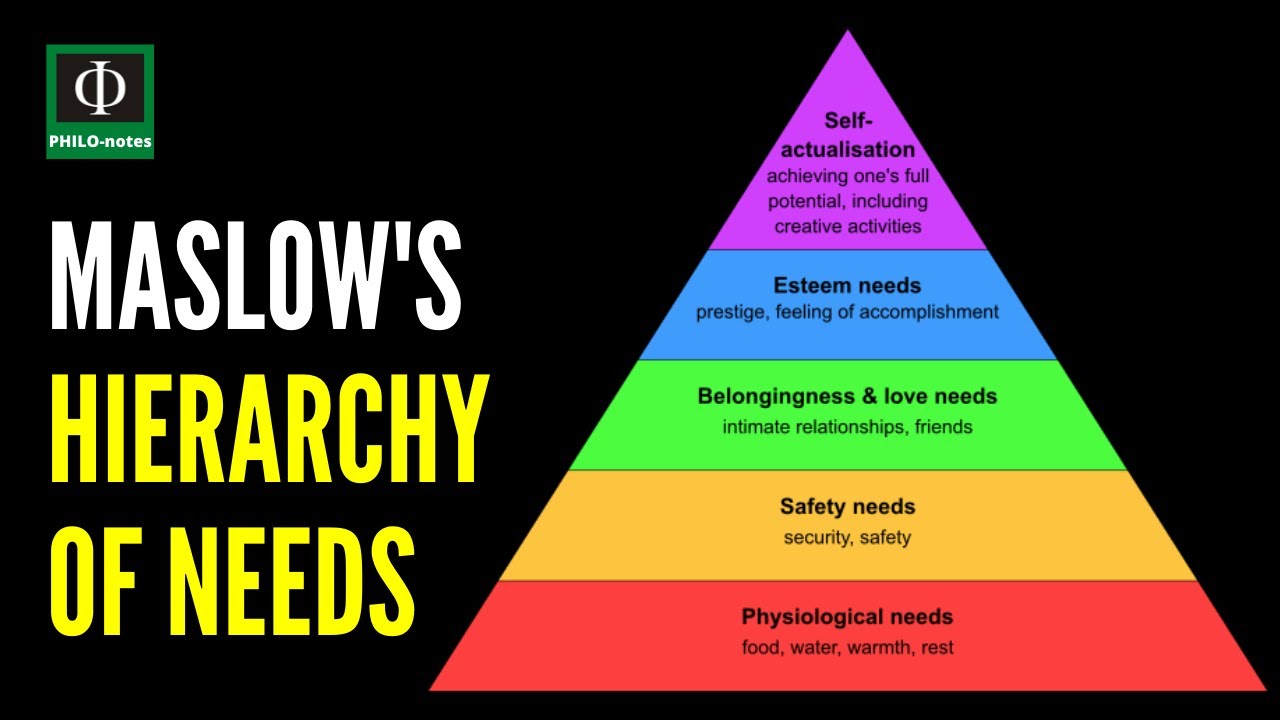
- 🔑 The first three levels of Maslow's pyramid—physiological needs, safety needs, and belonging—are considered lower-level needs.
- 🥗 Physiological needs include essentials like food, water, shelter, and clothing, which must be prioritized for survival.
- 🔒 Safety needs encompass job security, personal safety, health, and well-being in modern society.
- ❤️ Belonging needs involve interpersonal relationships, including friendships and family connections.
- 🌟 Esteem needs consist of both external respect from others and internal self-esteem, shaping one's self-worth.
- 🚀 Self-actualization, the highest level, refers to reaching one's full potential and personal fulfillment.
- 👥 Organizations can help employees meet their needs by ensuring fair pay, job security, and opportunities for socializing.
- 📈 Maslow's framework is still relevant today in organizational behavior, guiding management practices to enhance employee success.
Q & A
Who was Abraham Maslow and what were his contributions?
-Abraham Maslow was a psychologist and professor known for developing the Hierarchy of Needs, presented in his 1943 article in Psychological Review and his 1954 book 'Motivation and Personality'. His work has significantly influenced the human relations school of thought.
What are the five levels of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
-The five levels are: 1) Physiological needs (food, water, shelter), 2) Safety needs (personal security, health), 3) Belongingness and love needs (friendships, family), 4) Esteem needs (respect, self-esteem), and 5) Self-actualization (reaching one's full potential).
What is the significance of lower-level needs in Maslow's theory?
-Maslow believed that lower-level needs must be satisfied before individuals can focus on higher-level needs. For example, if physiological needs are unmet, an individual will prioritize meeting those needs before seeking social connections or esteem.
Can you explain the physiological needs in Maslow's pyramid?
-Physiological needs are the most basic human requirements, including food, water, sleep, air, shelter, and clothing. These needs must be met first for individuals to function effectively.
How do safety needs manifest in modern society?
-In modern society, safety needs relate to job security, personal security, and health. They encompass protections like workplace safety measures and health insurance.
What does Maslow mean by esteem needs?
-Esteem needs consist of two components: the respect and esteem from others (external) and self-respect and self-confidence (internal). Both are crucial for personal development and self-worth.
What is self-actualization according to Maslow?
-Self-actualization is the realization of one's full potential, creativity, and capabilities. It reflects an individual's desire to become everything they are capable of becoming.
How does the organization support employees' needs according to Maslow's theory?
-Organizations can support employees by ensuring basic needs are met (e.g., good pay, healthy work environment), providing security (e.g., safety measures, health coverage), fostering belongingness (e.g., team activities), recognizing achievements (e.g., praise, bonuses), and offering opportunities for self-actualization (e.g., training and innovative projects).
What role does socializing play in meeting belongingness needs?
-Socializing helps fulfill belongingness needs by creating friendships and fostering relationships within the workplace, which is essential for emotional well-being and job satisfaction.
Why is Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs still relevant today?
-Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs remains relevant because it provides a framework for understanding human motivation and behavior, which is applied in organizational settings to enhance employee satisfaction and productivity.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)