Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Explained
Summary
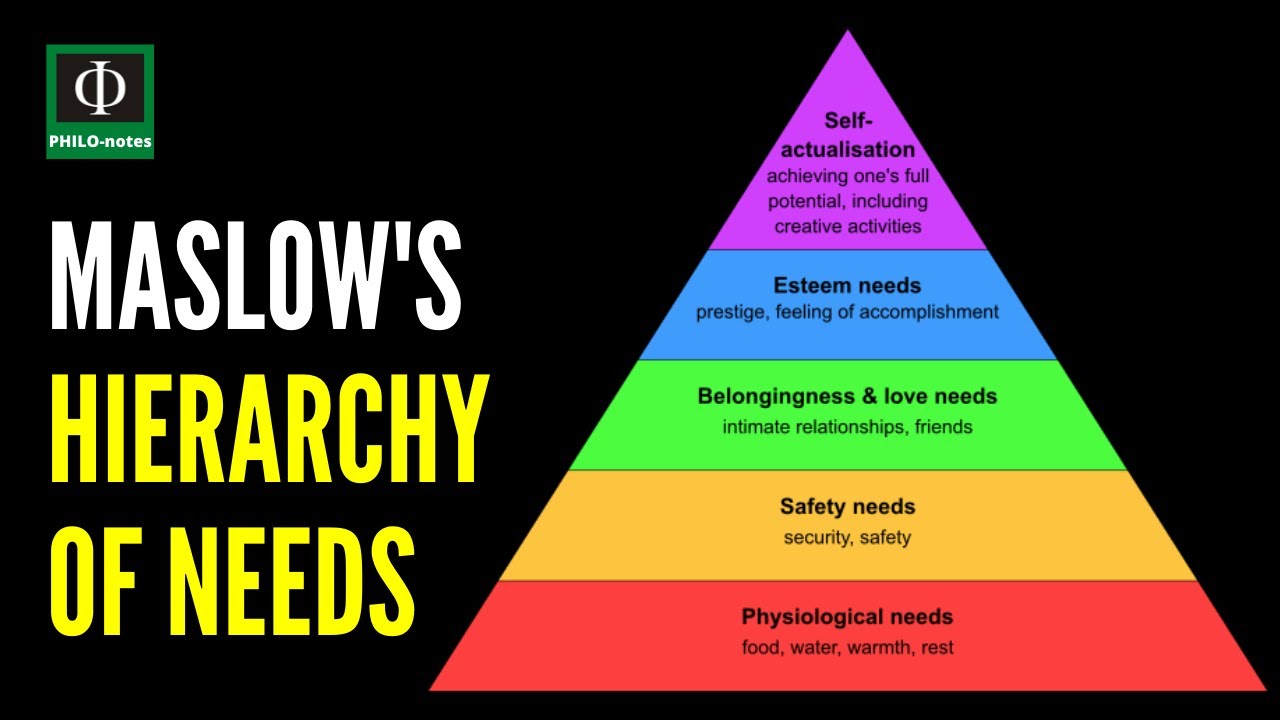
TLDRIn this lesson, we explore Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs, a motivational theory that outlines five levels of human needs: physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization. Initially presented as a strict hierarchy, Maslow later acknowledged that needs can overlap. The model categorizes needs into deficiency and growth, with the latter including cognitive, aesthetic, and transcendence needs. Despite its simplicity and holistic approach, the theory faces criticism for not accounting for cultural differences and the empirical challenge of measuring self-actualization.
Takeaways
- 📚 Abraham Maslow introduced the Hierarchy of Needs in his paper 'A Theory of Human Motivation', focusing on understanding what motivates human behavior.
- 🔑 The hierarchy is organized into five levels: physiological needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs, each building upon the other.
- 🌱 The model suggests that individuals are motivated to fulfill their most basic needs first (physiological) before moving up to more complex needs like self-actualization.
- 🔄 Maslow's theory was later modified to allow for some overlap between the levels, acknowledging that not everyone prioritizes needs in the same strict order.
- 💧 Physiological needs, the most basic level, include essentials like food, water, air, shelter, warmth, and sleep, which are crucial for survival.
- 🛡️ Safety needs encompass the desire for security and stability, such as job security, a safe environment, and health insurance, once physiological needs are met.
- 🤝 Social needs involve the desire for love, belonging, and acceptance, which become important after safety needs are satisfied.
- 🏆 Esteem needs are about achieving recognition, respect, and status. They can be divided into lower esteem (external respect) and higher esteem (self-respect).
- 🌟 Self-actualization is the pinnacle of the hierarchy, representing the drive to reach one's full potential and is unique to each individual.
- 🔍 Maslow later expanded the model to include cognitive and aesthetic needs, and transcendence needs, which are growth needs that motivate individuals to learn, appreciate beauty, and connect with something beyond themselves.
- ⚖️ While the model is easy to understand and holistic, it has limitations, including the difficulty in empirically testing self-actualization and not accounting for cultural differences in the prioritization of needs.
Q & A
Who introduced the concept of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
-Abraham Harold Maslow, an American psychologist, introduced the concept of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
In what paper did Maslow first introduce his theory of human motivation?
-Maslow first introduced his theory of human motivation in a paper entitled 'A Theory of Human Motivation.'
What are the five levels of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
-The five levels of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs are physiological needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs.
What are deficiency needs in the context of Maslow's theory?
-Deficiency needs, sometimes called D-needs, are needs that motivate people when they are unmet. They become stronger the longer they go unmet and are essential to avoid unpleasant feelings or even death.
How does the hierarchy of needs represent a person's motivation to meet their needs?
-The hierarchy represents a person's motivation by suggesting that only when a lower level of needs has been fully met would an individual then be motivated by the opportunity to meet the next level of their needs.
What are the physiological needs according to Maslow's theory?
-Physiological needs include basic physical requirements such as food, water, air, shelter, warmth, and sleep, which are vital to survival.
What are the safety needs that Maslow identified in his theory?
-Safety needs include being free from war, natural disasters, and violence, as well as having job security, a safe working environment, access to grievance procedures, savings, and health insurance.
Why are social needs important in Maslow's hierarchy?
-Social needs are important because they involve the desire to develop interpersonal relationships and feel a sense of belonging to a group, which helps avoid issues like loneliness, anxiety, and depression.
What are esteem needs and how do they differ from self-actualization needs in Maslow's theory?
-Esteem needs are related to the desire for recognition, achieving high status, respect, and feeling important. They differ from self-actualization needs, which are the drive to become the best one can be and achieving one's full potential as a human being.
How did Maslow modify his original hierarchy of needs later in his career?
-Maslow later modified his original hierarchy by including cognitive and aesthetic needs, and later transcendence needs, suggesting that the progression up the hierarchy doesn't have to be strict and that levels can overlap to some extent.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
-Advantages include its ease of understanding and application, expressing the human desire for achievement, and providing a holistic approach to motivation. Disadvantages include the inability to empirically test self-actualization, lack of cultural differences consideration, and the fact that individuals value needs differently.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)