What Are Momentum and Impulse? | Physics in Motion
Summary
TLDRIn this segment of 'Physics in Motion,' the concepts of momentum and impulse are explored using the example of an egg's behavior when thrown against different surfaces. The video explains how momentum, defined as mass in motion, is calculated and how impulse, the product of force and time, affects an object's motion. The egg breaks against a wall due to a large force over a short time, while it remains intact on a sheet because the force is smaller and applied over a longer duration. Additionally, the video highlights the application of these principles in parkour, demonstrating their relevance in real-world scenarios.
Takeaways
- 😀 Momentum is defined as the quantity of motion an object possesses, calculated as mass multiplied by velocity.
- 🚀 The formula for momentum is P = m × v, where P is momentum, m is mass, and v is velocity.
- 🥚 An egg thrown against a hard surface (like a wall) experiences a large force over a short time, causing it to break.
- 🛏️ When an egg is thrown against a soft surface (like a sheet), it experiences a smaller force over a longer time, allowing it to remain intact.
- ⏱️ Impulse is the product of force applied to an object and the time during which that force acts.
- 📏 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem states that the impulse applied to an object is equal to the change in its momentum.
- ⚖️ In both the egg and the sheet scenario, the same impulse is involved, but the stopping time differs, affecting the force experienced by the egg.
- 🏃♂️ In parkour, athletes use momentum and impulse to redirect horizontal momentum into vertical momentum to climb walls.
- 📊 Momentum is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction, which is crucial for transferring momentum from horizontal to vertical.
- 💡 Understanding momentum and impulse can help in various physical activities and prevent potential accidents, like breaking an egg.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video segment?
-The main focus of the video segment is to explain the physics behind why an egg breaks against a hard surface, like a wall, but not against a soft surface, like a sheet, using concepts of impulse and momentum.
How is momentum defined in the context of the video?
-Momentum is defined as the quantity of motion an object has, which can be calculated by multiplying the mass of the object by its velocity.
What formula is used to calculate momentum?
-The formula to calculate momentum (P) is P = mass (m) multiplied by velocity (v).
What is the significance of using velocity instead of speed when calculating momentum?
-Velocity is used instead of speed because momentum is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
What is impulse and how is it related to momentum?
-Impulse is the product of the force acting on an object over the time during which that force acts. It is directly related to momentum because the impulse applied to an object equals the change in its momentum.
What happens to the egg when it hits a wall compared to when it hits a sheet?
-When the egg hits a wall, it experiences a large force over a short period of time, causing it to break. In contrast, when it hits a sheet, the force is weaker and applied over a longer time, preventing it from breaking.
How does increasing the stopping time affect the force experienced by the egg?
-Increasing the stopping time decreases the force required to stop the egg, which is why the egg does not break when it hits a soft surface like a sheet.
What real-world example is provided to illustrate the concepts of momentum and impulse?
-The real-world example provided is parkour, specifically the vertical wall run, where an athlete redirects their horizontal momentum into vertical momentum to climb a wall.
Why is understanding momentum and impulse important for athletes?
-Understanding momentum and impulse is important for athletes because it helps them maximize their performance, such as in executing jumps and maneuvers effectively while minimizing the risk of injury.
What does the Impulse-Momentum Theorem state?
-The Impulse-Momentum Theorem states that the impulse applied to an object is equal to the change in momentum of that object.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

FISIKA Kelas 10 - Momentum & Impuls | GIA Academy

Fisika SMA - Impuls & Momentum (1) - Pengenalan Impuls dan Momentum, Rumus Impuls dan Momentum (I)
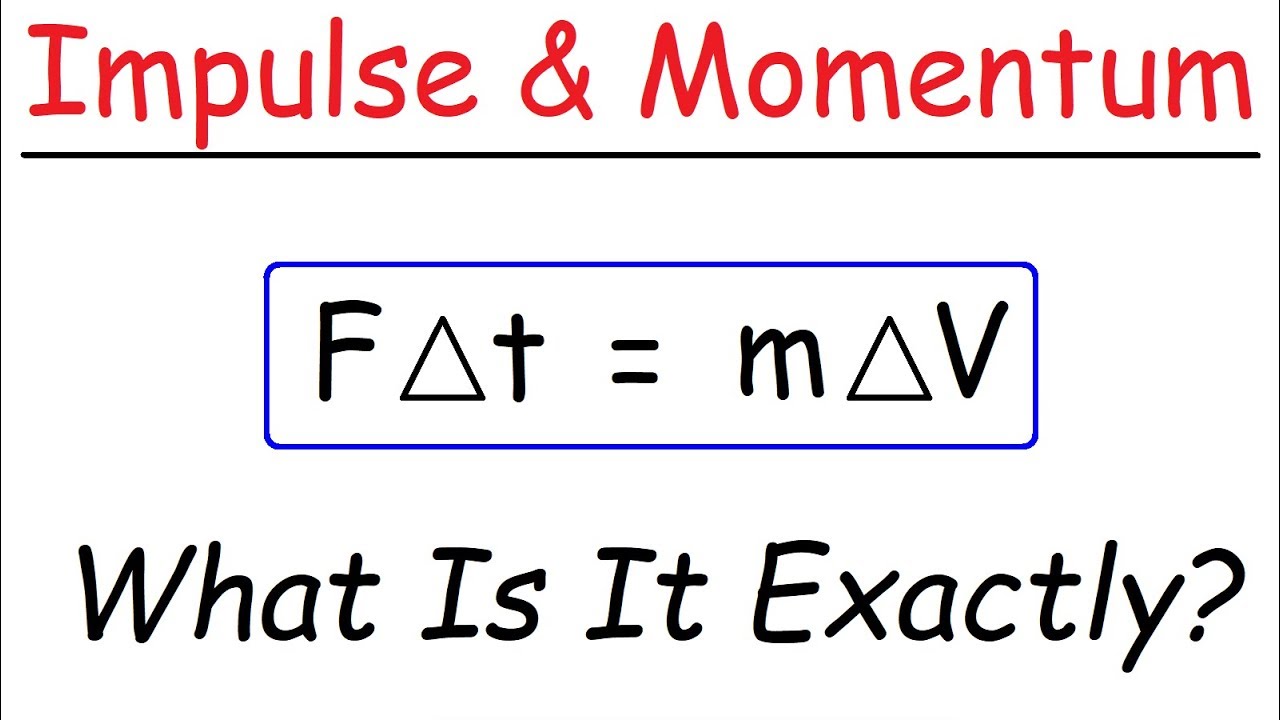
Introduction to Impulse & Momentum - Physics

UJIAN SEKOLAH FISIKA KELAS 12 - SOAL UJIAN SEKOLAH FISIKA KELAS 12 2022

08 01 Fisika Dasar 1- Momentum Dan Impuls

Fisika SMA - Impuls & Momentum (2) - Hubungan antara Impuls dan Momentum (I)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
