Basic geometry: language and labels | Introduction to Euclidean geometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video serves as an introduction to geometry, exploring its fundamental concepts, such as points, line segments, rays, and dimensions. The instructor explains that 'geometry' derives from 'geo' (earth) and 'metry' (measurement), emphasizing its role in understanding shapes and spatial relationships. Key definitions are provided, including points (zero dimensions), line segments (one dimension), and rays, along with their notation. The video further discusses the concept of collinearity and midpoints, before expanding into two-dimensional (planes) and three-dimensional spaces, laying the groundwork for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Geometry is derived from the Greek words 'geo' (earth) and 'metry' (measurement), meaning 'earth measurement.'
- 🔺 Geometry encompasses the study of shapes, space, and their relationships.
- 📏 A point is a fundamental concept in geometry, representing a precise location with zero dimensions.
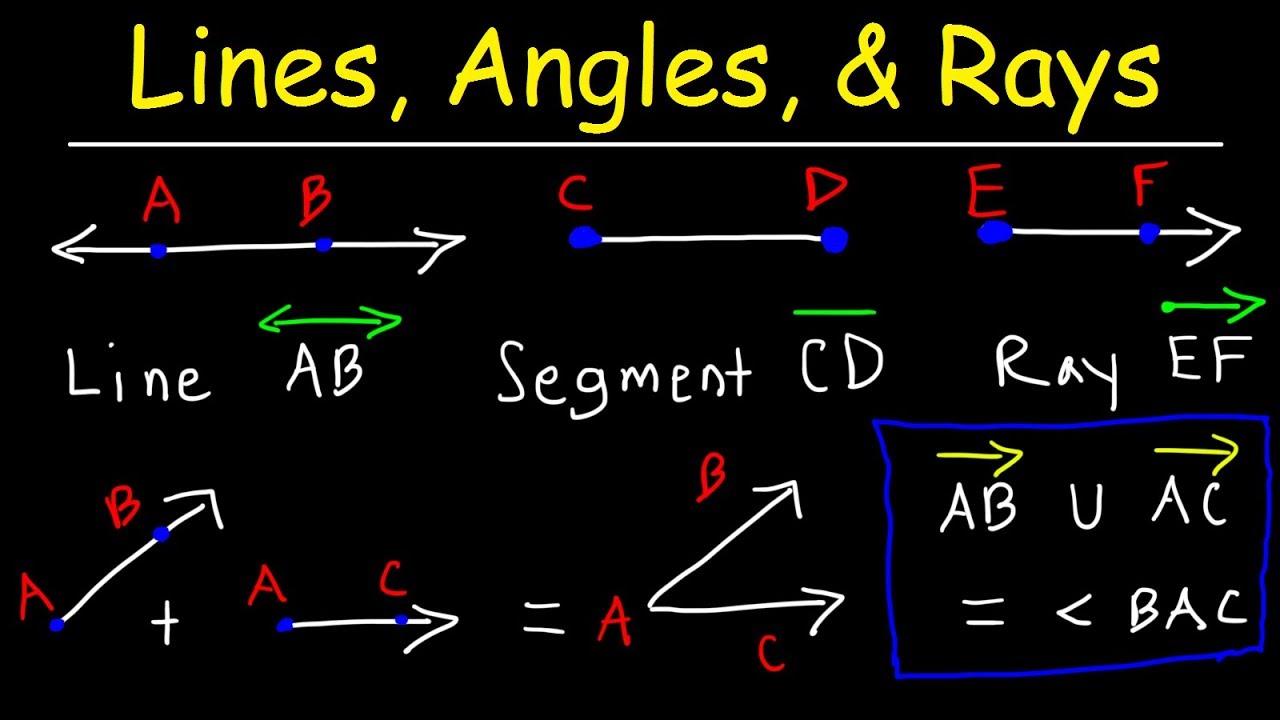
- 📏 A line segment connects two points and has a defined length, unlike a point.
- ➕ A ray is a one-dimensional figure that starts at a point (vertex) and extends infinitely in one direction.
- ↔️ A line extends infinitely in both directions and is defined by two points.
- 📐 Collinear points lie on the same straight line, demonstrating a relationship between distances.
- ⚖️ The midpoint of a line segment is the point that is exactly halfway between its endpoints.
- 📐 Two-dimensional objects can move in two directions, such as on a plane.
- 🔳 Three-dimensional space includes movement in three directions, adding depth to geometric concepts.
Q & A
What does the term 'geometry' mean?
-The term 'geometry' comes from the Greek words 'geo,' meaning 'earth,' and 'metry,' meaning 'measurement.' Thus, geometry refers to the measurement of the earth.
What is the primary focus of geometry?
-Geometry primarily focuses on the study of shapes, space, and the relationships between them.
What is a point in geometric terms?
-A point is defined as a specific position in space with no dimensions, meaning it cannot be moved without changing its identity.
How do we define a line segment?
-A line segment is defined as a straight path connecting two points, known as endpoints, and it has a finite length but no width.
What distinguishes a ray from a line segment?
-A ray starts at a point (the vertex) and extends infinitely in one direction, whereas a line segment has two endpoints and a finite length.
How is a line represented in geometry?
-A line is represented as extending infinitely in both directions and is denoted with arrows on both ends, such as line EF.
What does it mean for points to be collinear?
-Collinear points are points that lie on the same straight line.
What is a midpoint?
-A midpoint is the point that is exactly halfway between two endpoints on a line segment.
How many dimensions does a point have?
-A point has zero dimensions.
What defines a two-dimensional object?
-A two-dimensional object can be measured in two different directions, typically length and width, such as a plane or surface.
What are the characteristics of three-dimensional space?
-Three-dimensional space includes length, width, and height, allowing movement in and out of a plane, providing a full spatial representation.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Math Antics - Points, Lines, & Planes

GARIS DAN SUDUT
Lines, Rays, Line Segments, Points, Angles, Union & Intersection - Geometry Basic Introduction

Garis dan Sudut Kelas 7 SMP Semester 2

Definisi Titik, Garis dan Bidang dalam Ruang | Geometri Ruang | Matematika

Equation of Lines (Standard and General) - Analytic Geometry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
