Customer Development - Steve Blank
Summary
TLDRThe script explores the concept of customer development in startups, emphasizing that initial business models are built on hypotheses, essentially guesses, which need to be tested with real customers. It highlights the four-step process: customer discovery, validation, creation, and company building. Founders are encouraged to personally engage with customers, iterate on feedback, and pivot strategies when necessary. The key is to learn through experimentation, build a minimum viable product, and ensure product-market fit before scaling. The process fosters agility, allowing businesses to adapt based on customer insights and refine their business models.
Takeaways
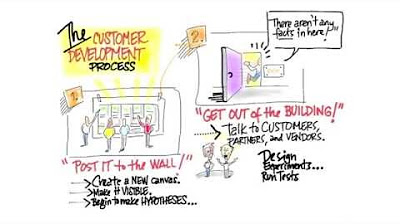
- 📝 The term 'hypotheses' is used to describe educated guesses in business planning, particularly when filling out a business model canvas.
- 🧩 The business model canvas helps organize initial thoughts about customers, products, pricing, and other business aspects.
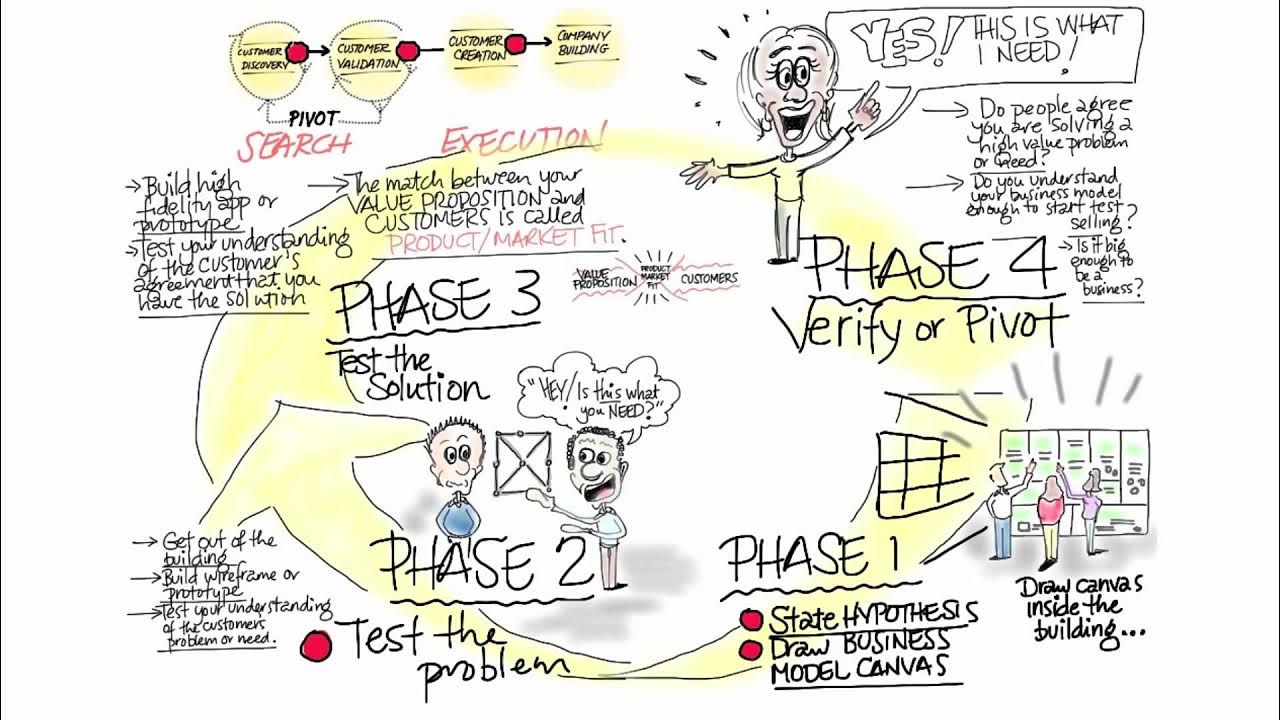
- 🔄 The customer development process involves four steps: customer discovery, customer validation, customer creation, and company building.
- 🏗️ Customer discovery is about testing assumptions about customer problems or needs and finding a product-market fit.
- 🤝 Customer validation involves testing if the proposed solution matches the customer's problem and is ready for market.
- 💡 The concept of a 'pivot' is crucial; it allows for changes in business strategy when hypotheses do not align with reality.
- 🚀 Customer creation is about generating demand and preparing for scaling the business.
- 👥 Founders play a critical role in customer development due to their deep understanding and ability to make strategic changes quickly.
- 🔬 The process emphasizes getting out of the building to gather insights from real customers, not just relying on internal assumptions.
- 📈 The minimum viable product (MVP) approach is recommended for startups to gather feedback and make informed decisions before fully developing a product.
- 🔄 Iterations and pivots are part of the normal cycle in startups, allowing for continuous improvement and adaptation to customer feedback.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the business model canvas mentioned in the script?
-The business model canvas helps organize thoughts around hypotheses or guesses about customers, products, pricing, and more, rather than focusing on functional organizations like sales or marketing. It's a starting point to structure initial assumptions about a business model.
Why does the script refer to 'hypotheses' as 'guesses'?
-The script emphasizes that hypotheses are essentially guesses because when filling out the business model canvas, there are no facts yet, just assumptions about customers, products, and business strategies.
What is the customer development process, and why is it important?
-The customer development process is a method for testing and validating the hypotheses made on the business model canvas. It involves going outside the building to gather insights by talking to customers, partners, and vendors, and running experiments to validate these guesses and turn them into facts.
What are the four steps in the customer development process?
-The four steps in the customer development process are: 1) Customer discovery, 2) Customer validation, 3) Customer creation, and 4) Company building.
Why is it essential for founders, not employees, to engage in customer development?
-Founders are essential in customer development because they have the vision and authority to make strategic changes to the company's direction. Employees, such as sales executives, only execute the founder's vision but don't have the power to pivot the strategy based on customer feedback.
What is a pivot, and how is it different from an iteration?
-A pivot is a substantive change to one or more components of the business model, such as changing the customer segment or pricing strategy. An iteration is a smaller adjustment, like changing the price of a product from $9.99 to $6.99, without altering the overall strategy.
What does the script suggest about building products in startups versus established companies?
-In startups, building products involves a lot of guessing, and it's crucial to create a minimum viable product (MVP) to gather feedback before fully committing to the product's development. In established companies, the customer needs are better understood, so more accurate feature sets can be developed.
How does the concept of the minimum viable product (MVP) help startups?
-The MVP allows startups to build only the core features necessary to test their product with customers, thus saving time and money. It helps startups validate their ideas before fully committing resources to the development process.
What is the significance of testing product-market fit during customer discovery?
-Testing product-market fit is crucial because it determines whether the solution the startup is building matches the customers' needs. Achieving product-market fit means that customers value the product enough to pay for it, making it the key validation point for the startup.
What should a startup do when initial customer feedback is negative?
-If the initial feedback is negative, the startup should understand why their hypotheses were wrong and pivot or iterate based on those insights. The goal is to keep refining the product until it meets the needs of the target customers.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)