Rotational Motion
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the concept of rotational motion using a Ferris wheel as an example. It discusses how a Ferris wheel rotates around a fixed axis, with a constant change in its angular position. The script covers key concepts such as angular displacement, velocity, acceleration, and momentum. It introduces the right-hand rule to determine the direction of angular velocity and explains how the moment of inertia influences the force required to stop a rotating object. The principles of rotational motion help understand the dynamics of the Ferris wheel’s movement.
Takeaways
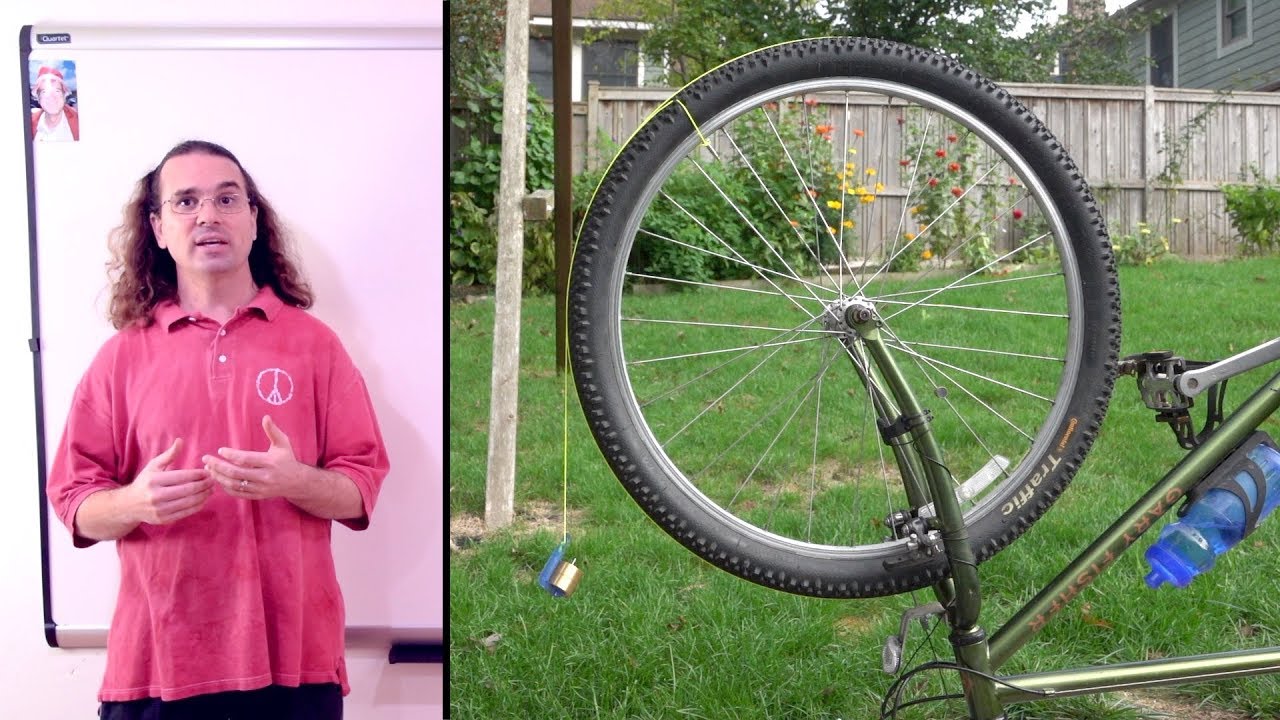
- 🎡 The Ferris wheel demonstrates rotational motion, rotating around a fixed axis in a circular manner.
- 🔄 In rotational motion, the axle at the center of the wheel remains stationary, and the wheel does not change its position.
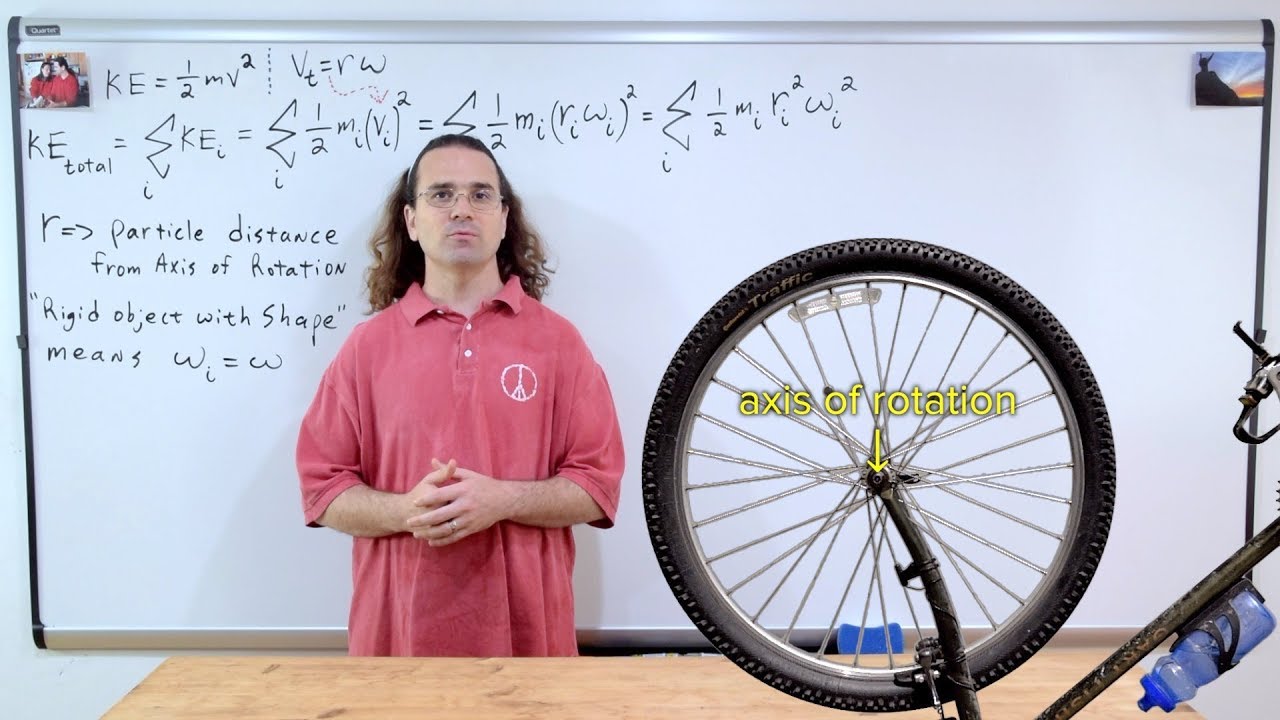
- 📍 A point (O) on the rim of the wheel serves as the reference orientation for measuring angular displacement.
- 🌀 Angular displacement measures how far the wheel rotates from its reference orientation, forming an angle between the point (P) and the reference orientation (O).
- ⚙️ Angular velocity, also known as rotational velocity, gives the speed of the wheel and the axis about which it rotates.
- ⬆️ The direction of angular velocity can be determined using the right-hand rule: if the fingers curl in the direction of rotation, the thumb points in the direction of angular velocity.
- ↕️ Angular acceleration occurs when the angular velocity changes, and it is directly proportional to the change in angular velocity.
- 💫 The force needed to stop a wheel in motion is called the moment of inertia, calculated as the product of the mass and the square of the distance from the axis to the wheel's particles.
- 🔄 Angular momentum is the product of an object's moment of inertia and its angular velocity, indicating its tendency to spin.
- 🎢 A Ferris wheel operates based on these principles of rotational motion, allowing for the calculation of its angular velocity, angular acceleration, angular momentum, and moment of inertia.
Q & A
What type of motion does a Ferris wheel demonstrate?
-A Ferris wheel demonstrates rotational motion, which occurs when an object rotates around a fixed axis in a circular motion.
What remains stationary in rotational motion, such as in the case of a Ferris wheel?
-In rotational motion, the axle at the center of the wheel remains stationary while the wheel rotates around it.
What is angular displacement, and how is it measured?
-Angular displacement measures how far the wheel is rotated from its reference orientation. It is the angle formed between a point on the wheel's rim and the reference orientation.
How is angular velocity or rotational velocity defined?
-Angular velocity, or rotational velocity, refers to the angular speed of an object and the axis around which the object is rotating.
What happens when angular velocity keeps changing in rotational motion?
-When angular velocity changes in rotational motion, angular acceleration occurs. It is directly proportional to the change in angular velocity.
How can the direction of angular velocity be determined?
-The direction of angular velocity can be determined using the right-hand rule: if you curl your fingers in the direction of rotation, your thumb will point in the direction of the angular velocity.
What happens to the angular velocity when a wheel rotates in an anti-clockwise direction?
-When a wheel rotates in an anti-clockwise direction, the angular velocity points upwards, as indicated by the right-hand rule.
What is the moment of inertia, and how is it calculated?
-The moment of inertia is the force required to stop a rotating object. It is calculated as the product of the object's mass and the square of the distance from the axis to the particles that make up the object (I = M * r^2).
What is angular momentum, and how is it related to moment of inertia and angular velocity?
-Angular momentum measures an object's tendency to spin. It is the product of the object's moment of inertia and its angular velocity.
How do the principles of rotational motion apply to a Ferris wheel?
-A Ferris wheel operates based on the principles of rotational motion. Its angular velocity is affected by the rate of rotation, and it is possible to determine angular acceleration, angular momentum, and moment of inertia during its motion.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)