DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION OF CARBOHYDRATES
Summary
TLDRThis video covers the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, focusing on carbohydrate metabolism. It explains how carbohydrates are broken down into ATP, the body's energy source. The process starts in the mouth with salivary alpha-amylase and continues through the stomach and small intestine. Enzymes like maltase, sucrase, and lactase play key roles in converting disaccharides into monosaccharides, which are absorbed into the bloodstream via the intestinal lining. The breakdown products—glucose, fructose, and galactose—are transported through active transport into the blood, completing digestion.
Takeaways
- 📚 Carbohydrate metabolism refers to the process of converting carbohydrate-containing foods into ATP, the energy source for the body.
- 🍽️ Digestion is a biochemical process that breaks down food molecules through hydrolysis into simpler units for cellular metabolic needs.
- 💧 Hydrolysis is the breakdown of compounds using water, where larger units are split into simpler units, like monosaccharides.
- 🦷 Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with salivary alpha-amylase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates.
- 👄 Saliva, secreted by salivary glands, contains 99% water and small amounts of inorganic ions, aiding in the hydrolysis of carbohydrates.
- 🍲 Carbohydrate digestion in the stomach is minimal because the acidic environment inactivates salivary alpha-amylase, only softening the food.
- 💡 The primary site for carbohydrate digestion is the small intestine, where pancreatic enzymes further break down polysaccharides into disaccharides.
- ⚙️ Enzymes like maltase, sucrase, and lactase in the intestinal mucosal cells convert disaccharides into monosaccharides like glucose, galactose, and fructose.
- 🩸 Monosaccharides are absorbed into the bloodstream through the villi of the intestinal lining via active transport.
- 🔄 The three main monosaccharides produced from carbohydrate digestion are glucose, galactose, and fructose, which enter the bloodstream for energy use.
Q & A
What is carbohydrate metabolism?
-Carbohydrate metabolism is the process by which the body converts foods containing carbohydrates into ATP, which serves as the energy source for the body.
How is digestion defined in biochemistry?
-In biochemistry, digestion is defined as the biochemical process by which food molecules are broken down into simpler chemical units through hydrolysis, allowing them to be used by cells for their metabolic needs.
What role does hydrolysis play in digestion?
-Hydrolysis involves the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones by using water. In digestion, it breaks down carbohydrates into simpler chemical units like monosaccharides.
Where does the digestion of carbohydrates begin, and which enzyme is involved?
-Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth, where the enzyme salivary alpha-amylase catalyzes the hydrolysis of some alpha-glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates.
What is the role of salivary alpha-amylase in the digestion of carbohydrates?
-Salivary alpha-amylase breaks down alpha-glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates, facilitating the conversion of polysaccharides into simpler forms like disaccharides and oligosaccharides.
Why is only a small amount of carbohydrate digestion done in the mouth?
-Only a small amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth because food is swallowed quickly, often without sufficient chewing to fully break down the carbohydrates.
What happens to carbohydrate digestion in the stomach?
-Carbohydrate digestion does not continue in the stomach because the acidic gastric juices deactivate salivary alpha-amylase. However, the food is softened but not further broken down.
Where does the primary digestion of carbohydrates occur?
-The primary site of carbohydrate digestion is the small intestine, where pancreatic alpha-amylase continues the hydrolysis of polysaccharides into disaccharides.
Which enzymes are responsible for breaking down disaccharides into monosaccharides?
-The enzymes maltase, sucrase, and lactase break down disaccharides into monosaccharides. Maltase converts maltose into glucose, sucrase converts sucrose into glucose and fructose, and lactase breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose.
How are monosaccharides absorbed into the bloodstream?
-Monosaccharides like glucose, fructose, and galactose are absorbed into the bloodstream through the intestinal lining (villi) via active transport, aided by ions.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
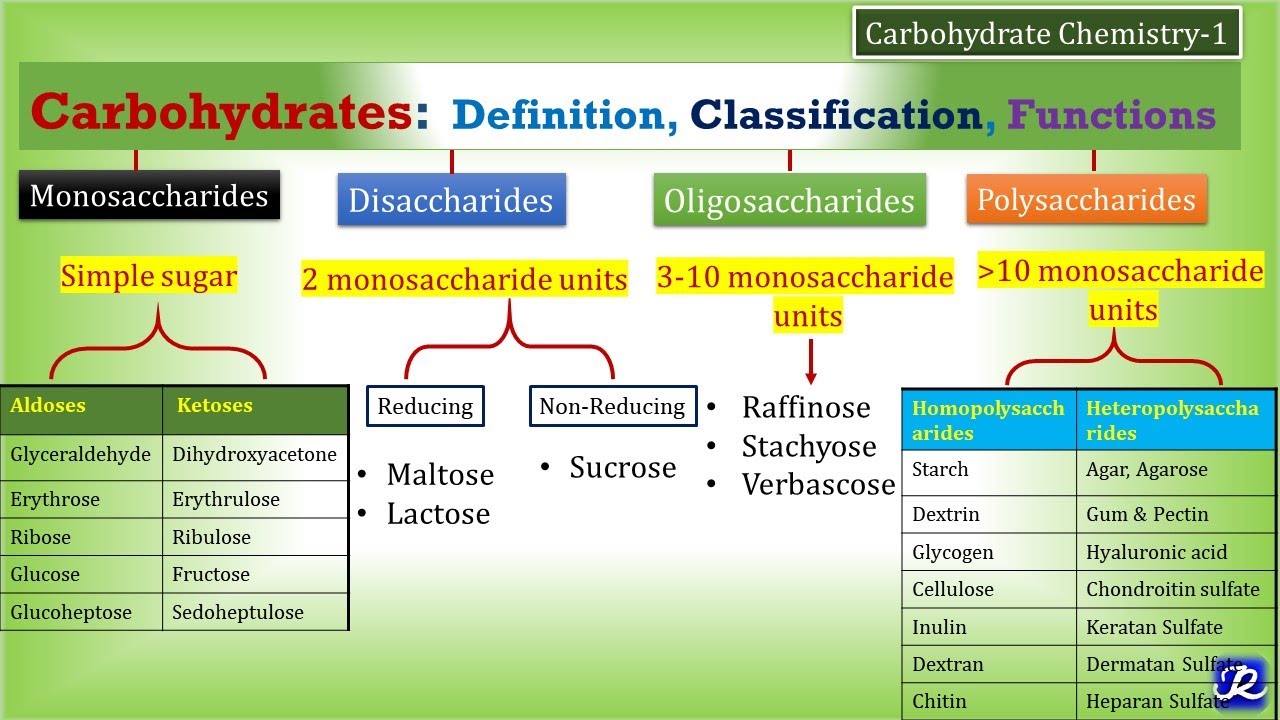
1:Carbohydrates-Definition, Classification, Functions | Carbohydrate Chemistry 1| Biochemistry

ITCS473 SQAT Practitioner's Interview#6 - Sarawut Sangaroon

METABOLISME KARBOHIDRAT PADA TERNAK RUMINANSIA - Oleh Haridsyah

Fungsi Dari Enzim Pencernaan

PENCERNAAN KARBOHIDRAT DALAM TUBUH MANUSIA (Lengkap dengan Skema)

Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
