Respiratory Examination | OSCE Guide (Latest) | UKMLA | CPSA
Summary
TLDRThe transcript outlines a medical student's interaction with a patient named James during a respiratory examination. Andrew, the medical student, conducts a thorough chest exam by inspecting, palpating, and listening to the chest with a stethoscope. He checks for any abnormalities in James' hands, arms, face, and neck while also assessing chest expansion and breath sounds. James cooperates fully, and the exam reveals no signs of respiratory disease. The exam concludes with Andrew recommending further tests, such as measuring oxygen saturations and sending off a sputum sample, to complete the assessment.
Takeaways
- 😀 The doctor introduces himself as Andrew, a final-year medical student, and confirms the patient's name and date of birth (James Alexander, 30th December 1989).
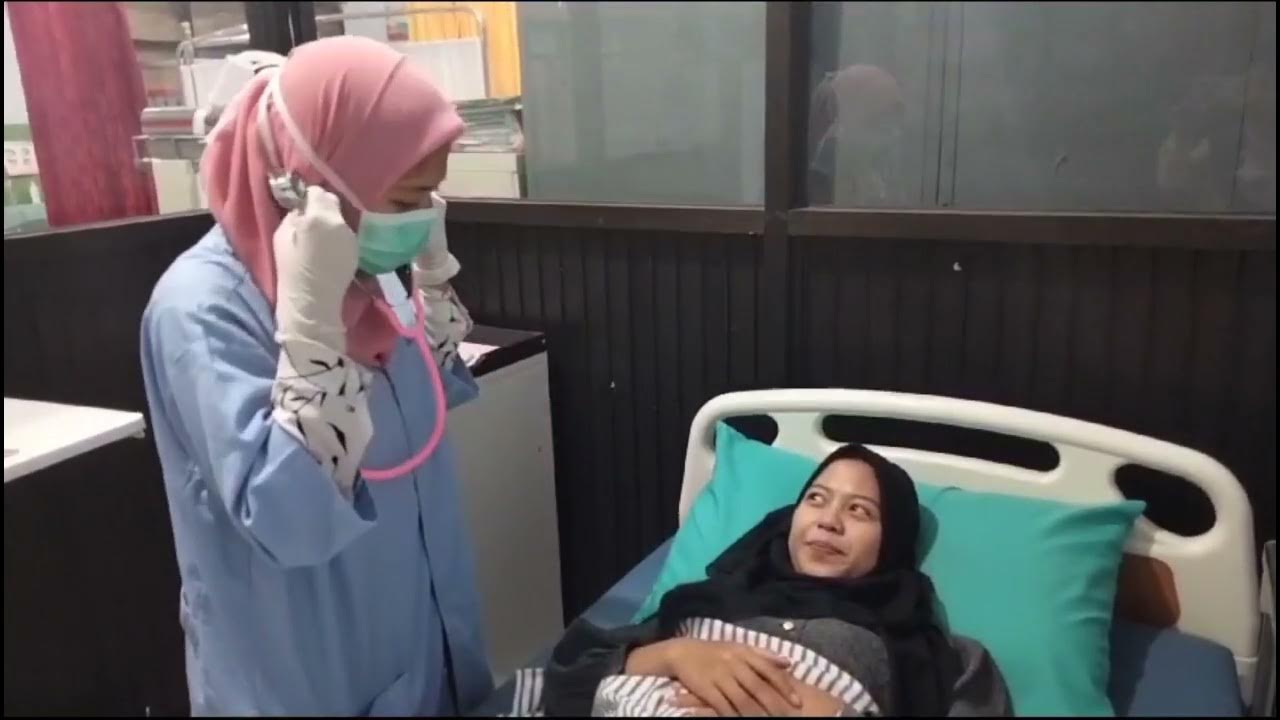
- 🩺 The examination involves a chest assessment through inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation using a stethoscope.
- 🤝 James gives consent for the chest examination and denies having any pain or questions about the procedure.
- 👋 The doctor starts by inspecting James's hands, checking for any abnormalities such as clubbing by asking him to bring his fingernails together.
- 🔥 Temperature and pulse are assessed by touching James's arms and wrists, followed by an examination of his face, eyes, and mouth.
- 🫁 The doctor examines the position of the windpipe and assesses chest expansion by placing hands around the chest and asking James to take deep breaths.
- 🛠 Percussion is performed on the chest to assess for any abnormal sounds, followed by auscultation, where James is asked to say 'ninety nine' while the doctor listens with the stethoscope.
- 🧠 The examination proceeds to the back, where chest expansion is checked again, percussion is done, and auscultation is repeated with the same instructions.
- 💡 The doctor checks for any pain in James's lower back and calves, indicating attention to potential signs of deep vein thrombosis.
- ✅ The respiratory exam concludes with no abnormal findings, but the doctor recommends measuring oxygen saturations and possibly sending off a sputum sample to complete the assessment.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the examination performed on James?
-The purpose of the examination is to assess James's respiratory health by inspecting, palpating, percussing, and auscultating his chest.
What specific observations are made during the hand inspection in the examination?
-During the hand inspection, the doctor checks for any signs of clubbing (by bringing fingernails together), temperature differences, and tremors in the arms.
What is the significance of asking James to say 'ninety-nine' during the chest auscultation?
-The 'ninety-nine' test is used to assess vocal resonance, helping to detect areas of increased or decreased lung density by amplifying sound transmission through the chest.
Why does the doctor assess the position of James's windpipe during the exam?
-The windpipe (trachea) is assessed to ensure it is in the midline, which indicates there is no deviation, a sign of possible underlying conditions like lung collapse or pneumothorax.
What are the findings of James’s respiratory exam?
-The findings indicate that James had no signs of respiratory disease, his pulse and respiratory rate were normal, and both the percussion notes and breath sounds were normal and symmetrical.
What additional tests does the doctor suggest after completing the respiratory exam?
-The doctor suggests measuring James's oxygen saturations and sending off a sputum sample to complete the respiratory exam.
Why is the doctor feeling James’s chest and back during the exam?
-The doctor feels James’s chest and back to assess chest expansion and symmetry, which helps evaluate how well his lungs are inflating.
What does the doctor mean by 'normal vesicular breathing'?
-Normal vesicular breathing refers to the normal breath sounds heard during auscultation, which are soft and low-pitched, indicating healthy lung function without abnormal sounds like wheezing or crackles.
Why does the doctor check for glands in James's neck?
-The doctor checks for enlarged glands (lymph nodes) in the neck, which can be a sign of infection or other medical conditions affecting the respiratory system.
What does the doctor check for when pressing on James’s lower back?
-Pressing on James’s lower back allows the doctor to check for tenderness or pain, which could indicate underlying issues such as muscle strain or referred pain from respiratory problems.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)