2. F5 Big IP LTM (Local Traffic Manager) || Load Balancer Explained
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial introduces load balancers, explaining their role in distributing tasks for efficiency and preventing server overload. It contrasts DNS-based load balancing with modern load balancers, which actively monitor server health and service availability. The video also covers load balancer types, including Layer 4 and Layer 7, and their benefits like improved performance, security, and reliability. The next tutorial will focus on installing an F5 load balancer in VMware.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Load balancing is a method of distributing tasks across resources to optimize processing efficiency.
- 🔄 Before load balancers, DNS servers were used for redundancy and load balancing by mapping domain names to IP addresses.
- 🚫 DNS servers have limitations as load balancers because they don't check for network errors or server outages.
- 👀 Load balancers provide visibility into server health and can direct traffic away from inaccessible or down servers.
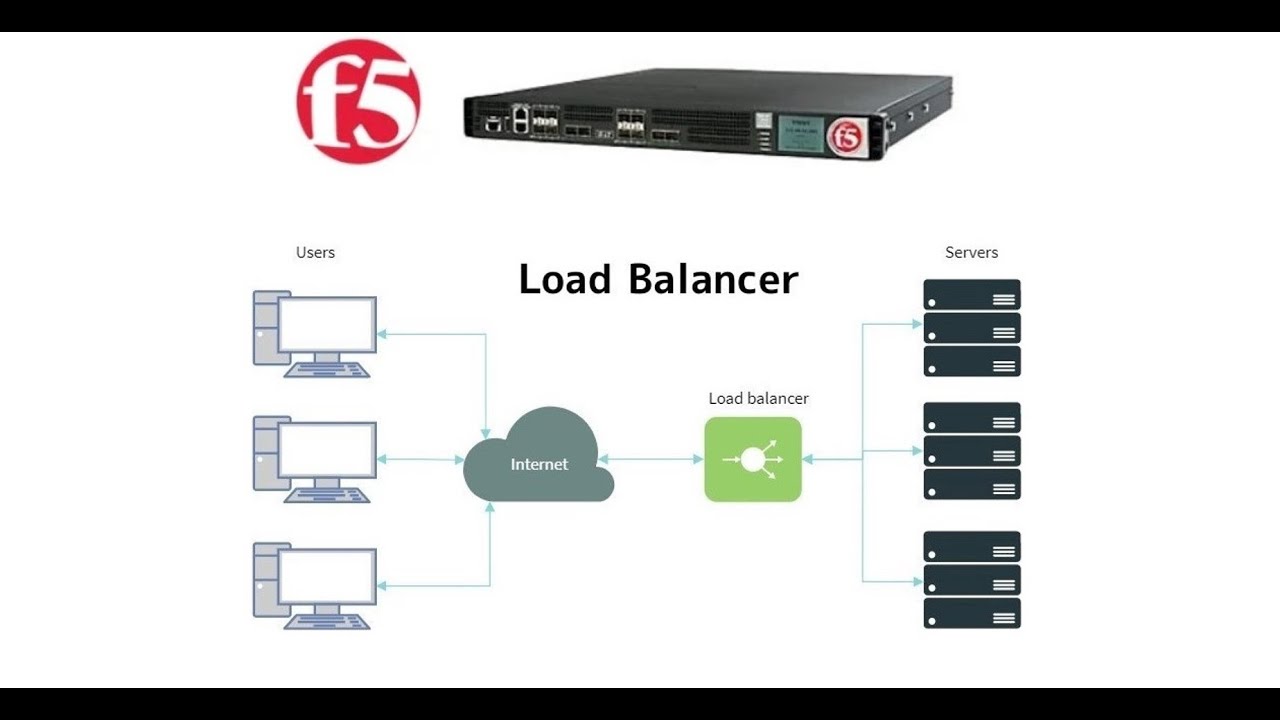
- 🛡️ A load balancer acts as a reverse proxy, distributing traffic based on various parameters across multiple servers.
- 🔒 Load balancers add a layer of security by sitting between external clients and internal services, preventing direct access to applications.
- 🚦 Load balancers improve performance, security, and reliability by efficiently managing web traffic and server load.
- 🌟 Benefits of load balancers include increased scalability, reduced downtime, improved performance, and enhanced application capacity and reliability.
- 📈 Layer 4 load balancers distribute connections based on network and transport layer protocols like IP, TCP, UDP, FTP.
- 🌐 Layer 7 load balancers distribute connections based on application layer protocols such as HTTP.
Q & A
What is a load balancer?
-A load balancer is a device that distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers based on various parameters to ensure maximum speed and capacity utilization while preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed.
What is the purpose of load balancing?
-The purpose of load balancing is to optimize response time, maximize throughput, minimize response time, and avoid overloading any single server, which can lead to decreased performance.
How was load balancing handled before load balancers?
-Before load balancers, DNS servers were used for redundancy and load balancing by directing multiple DNS records for one hostname to various IP addresses.
What are the limitations of using DNS for load balancing?
-DNS servers have limitations as load balancers because they do not check for network or server errors or outages, and they always return the same set of IP addresses for a domain.
Why is it problematic if DNS directs traffic to a server that is down?
-If DNS directs traffic to a server that is down, it can cause errors or outages, leading to a poor user experience and potential loss of service.
How does a load balancer differ from a DNS server?
-A load balancer actively monitors server health and service availability, ensuring that traffic is only sent to servers that are up and running properly.
What is a reverse proxy and how does it relate to a load balancer?
-A reverse proxy is a type of proxy server that retrieves resources on behalf of a client from one or more servers. A load balancer often acts as a reverse proxy, distributing client requests across servers to improve performance and security.
What security benefits does a load balancer provide?
-A load balancer provides security by sitting between external clients and internal services, preventing direct access to applications and protecting against web vulnerabilities.
What are the benefits of using a load balancer?
-Benefits of using a load balancer include increased scalability, redundancy, reduced downtime, improved performance, efficient failure management, increased flexibility, and enhanced application capacity and reliability.
What are the two categories of load balancers mentioned in the script?
-The two categories of load balancers mentioned are Layer 4 and Layer 7 load balancers, which distribute connections based on data found in the network/transport layer protocols and application layer protocols, respectively.
What will be covered in the next tutorial of the series?
-The next tutorial will cover the installation of F5 load balancer in VMware.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)