The Moving Layers of Earth and Plate Tectonics
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the layers of the Earth, breaking them down into four main parts: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. It explains the characteristics of each layer, such as the solid crust, molten magma in the mantle, and metal composition of the core. The video also introduces mantle convection, a process where warm magma rises and cools, which drives the movement of tectonic plates. These plates shape the Earth's surface and are responsible for geological phenomena like earthquakes and volcanoes. The video ends by highlighting how tectonic activity at plate boundaries affects the planet's surface.
Takeaways
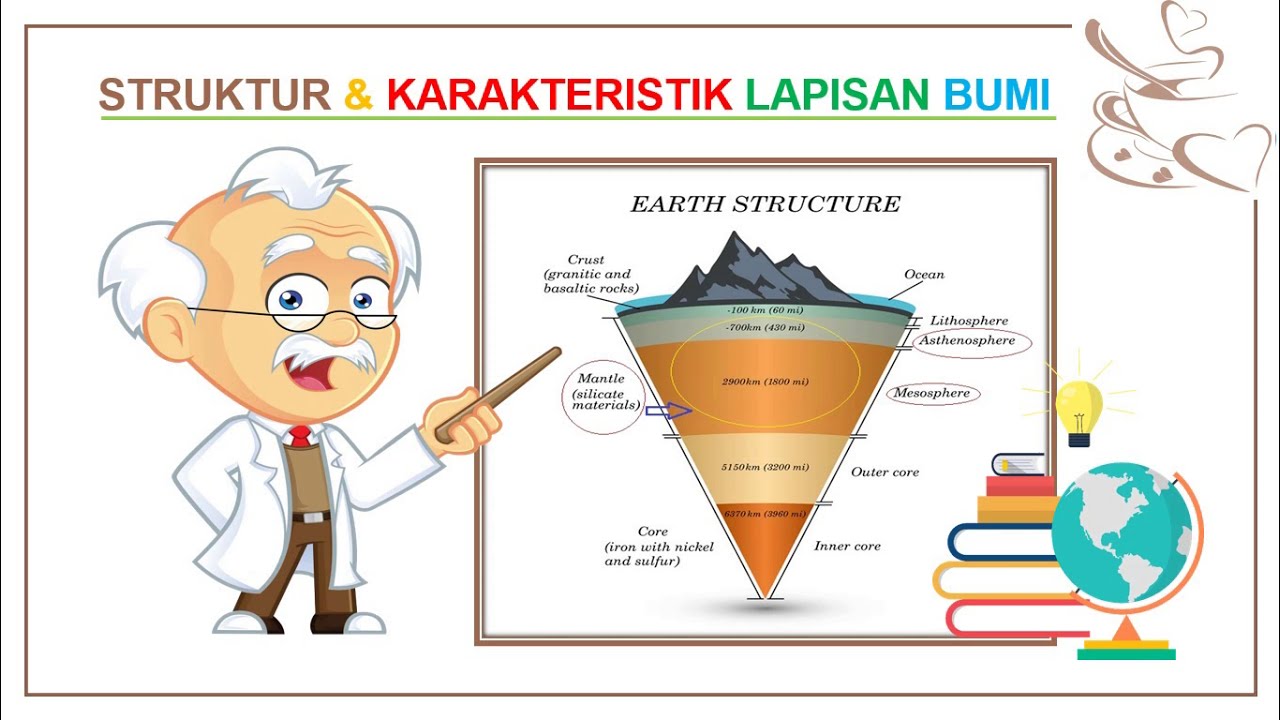
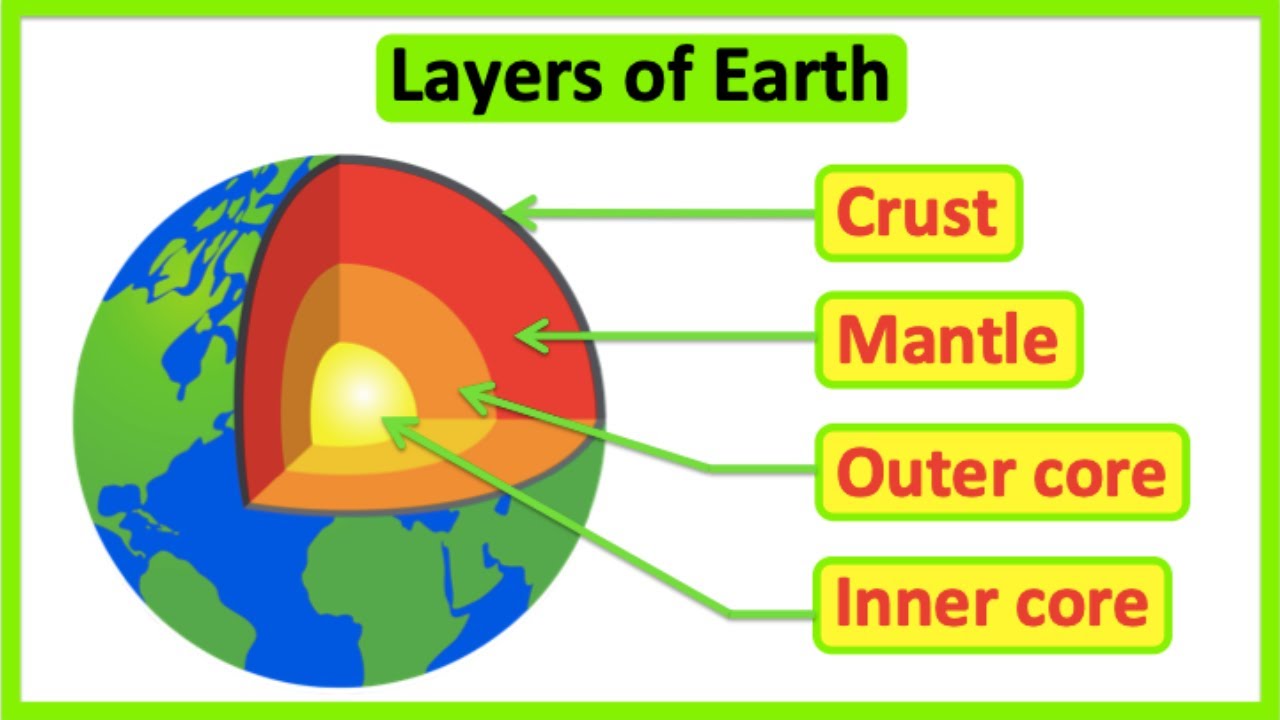
- 🌍 The Earth is divided into four main layers: crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
- 🗻 The crust is the outermost layer and is divided into oceanic crust (about 5 km thick) and continental crust (about 35 km thick).
- 🔥 The mantle is the thickest layer, extending to a depth of around 2,900 kilometers, and is composed of solid rock that behaves like a liquid due to high temperatures.
- 🌡️ The outer core is made of liquid metal (mostly iron and nickel) and reaches temperatures of up to 6,000 degrees Celsius.
- 🔩 The inner core, at the center of the Earth, is solid metal despite being hotter than the outer core.
- 🔁 Convection in the mantle is a key process where warm magma rises and cools, then sinks back down, creating a cycle.
- 🌋 The movement of the mantle affects the crust, causing the formation of new crust and the movement of tectonic plates.
- 🌏 Tectonic plates are constantly moving due to convection currents in the mantle, which can lead to the creation and destruction of crust.
- 🏔️ The interaction of tectonic plates is responsible for geological hazards such as earthquakes and volcanoes.
- 🌐 There are different types of tectonic plates, including large ones like the Pacific Plate and smaller ones like the Scotia Plate, with some being oceanic and others continental.
Q & A
What are the four main layers of the Earth?
-The four main layers of the Earth are the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core.
How thick is the oceanic crust?
-The oceanic crust is about five kilometers thick.
What is the average thickness of the continental crust?
-The continental crust is about 35 kilometers thick on average.
What is the mantle made of and what is its temperature?
-The mantle is made of rock that has melted into magma due to temperatures around 4000 degrees Celsius.
How deep does the mantle extend?
-The mantle extends to a depth of approximately 2,900 kilometers.
What are the main components of the outer core?
-The outer core is made primarily of liquid metal, mostly iron and nickel.
How deep does the outer core extend?
-The outer core extends to a depth of about 5,200 kilometers.
What is unique about the inner core despite being hotter than the outer core?
-Despite being hotter than the outer core, the inner core is solid metal, mainly composed of iron and nickel.
What is convection and how does it relate to the Earth's mantle?
-Convection is the process where warm materials rise and cold materials sink. In the Earth's mantle, warm magma rises towards the surface, cools, and then sinks back down, creating a convection cell.
How does convection in the mantle affect the Earth's crust?
-Convection in the mantle causes the formation of new crust as magma solidifies, and the movement of tectonic plates due to the forces generated by the rising and sinking of the mantle material.
What is a tectonic plate and how many are there?
-A tectonic plate is a piece of the Earth's lithosphere that is constantly moving due to convection currents. There are several different tectonic plates, including both oceanic and continental plates.
What is the process called when old and dense crust is pulled back into the mantle?
-The process where old and dense crust is pulled back into the mantle is called slab pull.
How do the movements of tectonic plates contribute to geological hazards?
-The movements of tectonic plates contribute to geological hazards such as earthquakes and volcanoes, as these activities often occur along the boundaries where plates interact.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Penjelasan Lengkap Struktur Lapisan Bumi dan Karakteristiknya

Layers of the Earth based on chemical composition and physical properties
STRUKTUR DAN KARAKTERISTIK LAPISAN BUMI
Layers of the Earth | Structure of the Earth | Educational Science Lesson

BAB 5 - Lapisan Bumi | IPA SMP/MTs Kelas 7 Semester 2

Materi Dinamika Litosfer (Lapisan Bumi) : Materi Geografi SMA dan SIMAK UI | Part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
