Music Explained in 4 Minutes
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the origins and appeal of music, explaining how sound waves travel and how our brains interpret them through the cochlea. It delves into the role of the limbic system and dopamine in our enjoyment of music, and how patterns in music theory resonate with our natural inclination to recognize sequences. The script humorously suggests that music evolved from simple instruments like a bone flute and ties the emotional connection to music with our brain's ability to associate melodies and rhythms with memories and feelings.
Takeaways
- 🎶 Music works by sound waves, which are vibrations that hit our ears and are processed by our brain.
- 🎧 Different sound frequencies create different pitches, measured in Hertz (Hz), with humans hearing between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz.
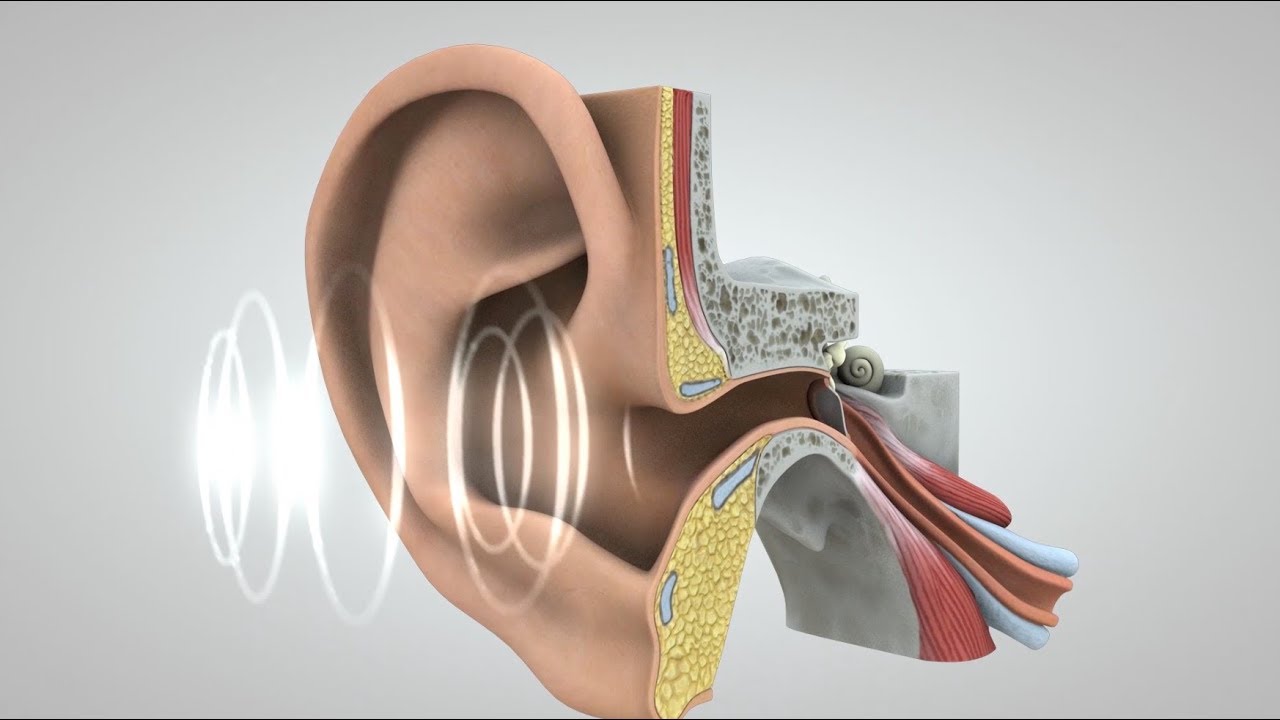
- 🧠 Vibrations are converted into electrical signals in the cochlea, which then travel to the brain to create the sensation of sound.
- 😊 Listening to music triggers the release of dopamine in the brain, which is linked to pleasure and emotions.
- 🔁 Familiar sounds or songs can release dopamine faster, similar to how a dog associates a bell with food.
- 🎵 Rhythms and patterns in music play a major role in why we enjoy it, as humans are naturally drawn to recognizing patterns.
- 📻 The brain associates music with emotions, memories, and experiences, which is why certain songs can evoke strong feelings.
- 🎼 Different genres of music have familiar patterns of melody, rhythm, and chords, influencing our emotional responses.
- ⛏️ The origins of music may have come from accidental discoveries, like primitive instruments made from rocks, bones, and flutes.
- 🎸 As simple melodies evolved over time, they gradually became the complex music we have today.
Q & A
How does sound travel and how does it relate to music?
-Sound travels in waves, which are vibrations that reach our ears and are perceived as sound. In music, different sounds are produced by waves with different frequencies, which determine the pitch of the sound.
What is the role of frequency in sound waves and how is it measured?
-Frequency determines how often a sound wave repeats per second and is measured in hertz. A higher frequency corresponds to a higher pitch.
What is the range of frequencies that humans can hear?
-Humans can hear frequencies from about 20 hertz to 20,000 hertz.
How do our ears convert sound vibrations into something our brain can understand?
-The cochlea in our inner ear is filled with fluid that converts sound vibrations into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain.
Why do we enjoy listening to music?
-Listening to music increases blood flow to the limbic system in the brain, which is associated with emotions and produces dopamine, a chemical that makes us feel good.
How does our brain's familiarity with a song trigger a dopamine response?
-When our brain recognizes a familiar song, it releases dopamine within the first few seconds of hearing it, similar to how dogs can associate food with a bell.
What is the significance of rhythm in music and how does it affect our brains?
-Rhythm provides a pattern of chords or notes that our brains recognize and enjoy because humans are naturally inclined to appreciate patterns.
What is music theory and why is it important?
-Music theory is a set of ideas that help us understand the structure and composition of music. It's important because it provides a framework for recognizing and creating patterns in music.
How does our brain associate emotions with certain songs or types of music?
-Our brain associates emotions with songs or music genres based on the patterns, melodies, and rhythms it detects, as well as the context in which we hear the music.
Why do we associate certain feelings with music?
-Our brains associate feelings with music because of the emotional responses triggered by the limbic system and the dopamine released when we recognize familiar patterns or melodies.
How did the simple act of making sounds with a rock and a bone lead to the development of music?
-The act of making sounds with a rock and a bone likely led to the discovery of the first flute, which initiated a progression towards more complex musical instruments and the music we know today.
What is the role of patterns in our enjoyment of music?
-Patterns play a crucial role in our enjoyment of music because our brains are wired to detect and appreciate patterns, which is part of our innate nature and prediction system.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)