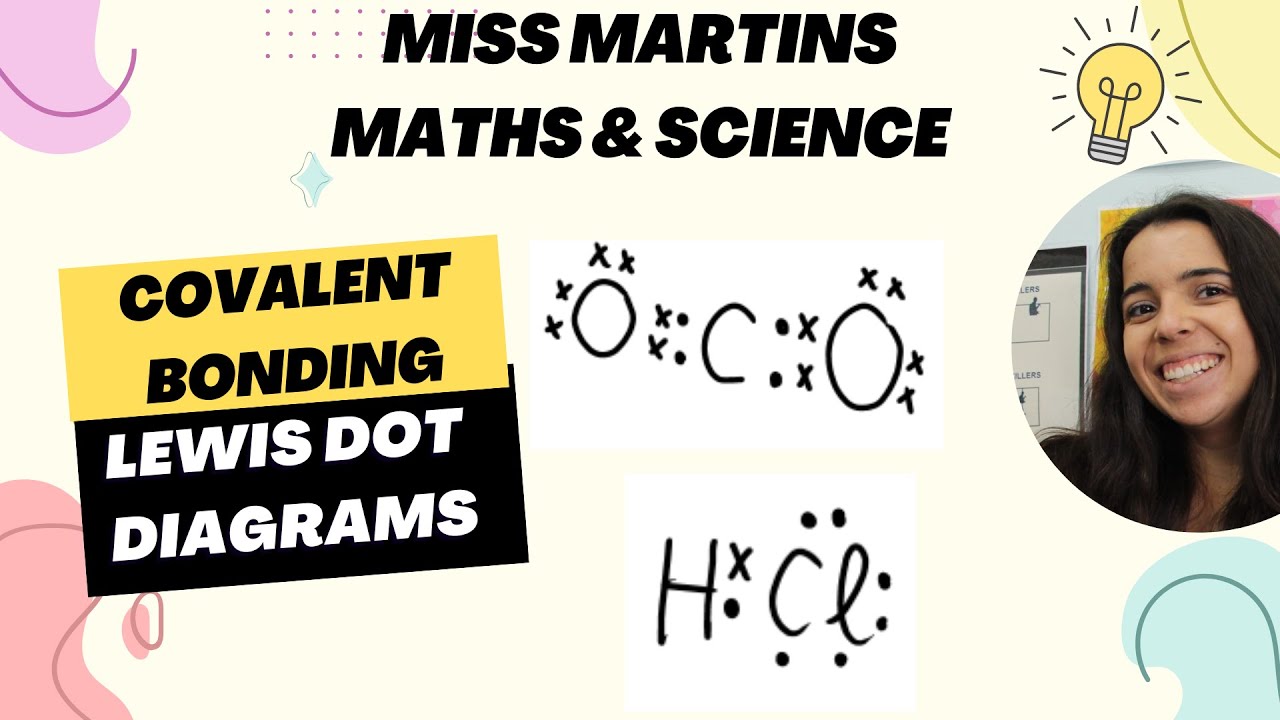What Are Covalent Bonds | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains covalent bonding, where atoms share electrons to form bonds, commonly seen between non-metals. It distinguishes covalent bonds from ionic bonds and highlights their directional nature. The script also covers single, double, and triple bonds, and contrasts small covalent molecules with giant covalent structures like diamond. It concludes with a challenge to identify covalent compounds based on their physical properties and periodic table positions.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons, typically between non-metal elements.
- 🌐 Non-metals, found on the right and upper part of the periodic table, prefer sharing electrons due to their partially filled valence shells.
- 🔗 Covalent bonds can be single, double, or triple, depending on the space available in the outer shell of the atom.
- 📐 Covalent bonds are directional, unlike ionic bonds which are formed by electrostatic attraction between charged particles.
- 👥 Non-metal atoms share electrons by overlapping orbitals, creating a bonding orbital that contains two electrons.
- 📚 Covalent bonds are represented in chemical formulas with straight lines or dot and cross diagrams, which show only the valence electrons.
- 💧 Small molecules like water and giant compounds like diamond are examples of covalent structures.
- 🔥 Compounds with covalent bonds have low melting and boiling points and are non-conductive because the electrons are evenly shared.
- 💎 Diamond is an example of a giant covalent structure where each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds.
- 🌐 Allotropes of non-metals, like carbon and silicon, bond covalently and can form different structures of the same element.
Q & A
What is a covalent bond?
-A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond formed between non-metal atoms where electrons are shared rather than transferred.
How do atoms form covalent bonds?
-Atoms form covalent bonds by overlapping their orbitals to share electrons, creating a bonding orbital that contains two electrons.
Why do non-metals typically form covalent bonds?
-Non-metals form covalent bonds because they have a strong attraction for a few additional electrons and it is energetically unfavorable for them to lose electrons.
Where on the periodic table are non-metals found?
-Non-metals are found on the right-hand side and upper part of the periodic table.
What are some common non-metal elements that form covalent bonds?
-Some common non-metal elements that form covalent bonds include carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halides.
How are covalent bonds represented in chemical formulas?
-Covalent bonds are represented in chemical formulas with straight lines, where each line represents a pair of shared electrons.
What is a dot and cross diagram?
-A dot and cross diagram is a way to represent covalent bonds that shows only the valence electrons of the atoms involved in the bond.
Are covalent bonds directional?
-Yes, covalent bonds are directional, meaning they have a fixed position and orientation, unlike ionic bonds which are formed through electrostatic attraction.
What is the difference between small covalent molecules and giant covalent compounds?
-Small covalent molecules are individual molecules like water, while giant covalent compounds form extensive lattices or chains, like diamond, where each atom is covalently bonded to many others.
Why do compounds made from small covalent molecules have low melting and boiling points?
-Compounds made from small covalent molecules have low melting and boiling points because the forces holding them together are weak intermolecular forces, not the stronger covalent bonds.
How does the structure of a giant covalent compound like diamond affect its properties?
-The structure of a giant covalent compound like diamond results in very high melting and boiling points because the atoms are held rigidly in place by strong covalent bonds throughout a large lattice.
What are allotropes and how are they related to covalent bonding?
-Allotropes are different structural forms of the same element. They bond covalently, and examples include different forms of carbon like graphite and diamond.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)