What Would REALLY Happen If You Cloned Yourself?
Summary
TLDRLife Noggin explores the possibility of human cloning, explaining the process of Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer used to clone animals like Dolly the Sheep. Despite recent advancements with primates, cloning humans faces low success rates and biological challenges. Even if successful, clones might differ in appearance, health, and personality due to environmental factors and life experiences, raising questions about the true nature of cloning.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Cloning is the process of creating a genetically identical copy of a living organism.
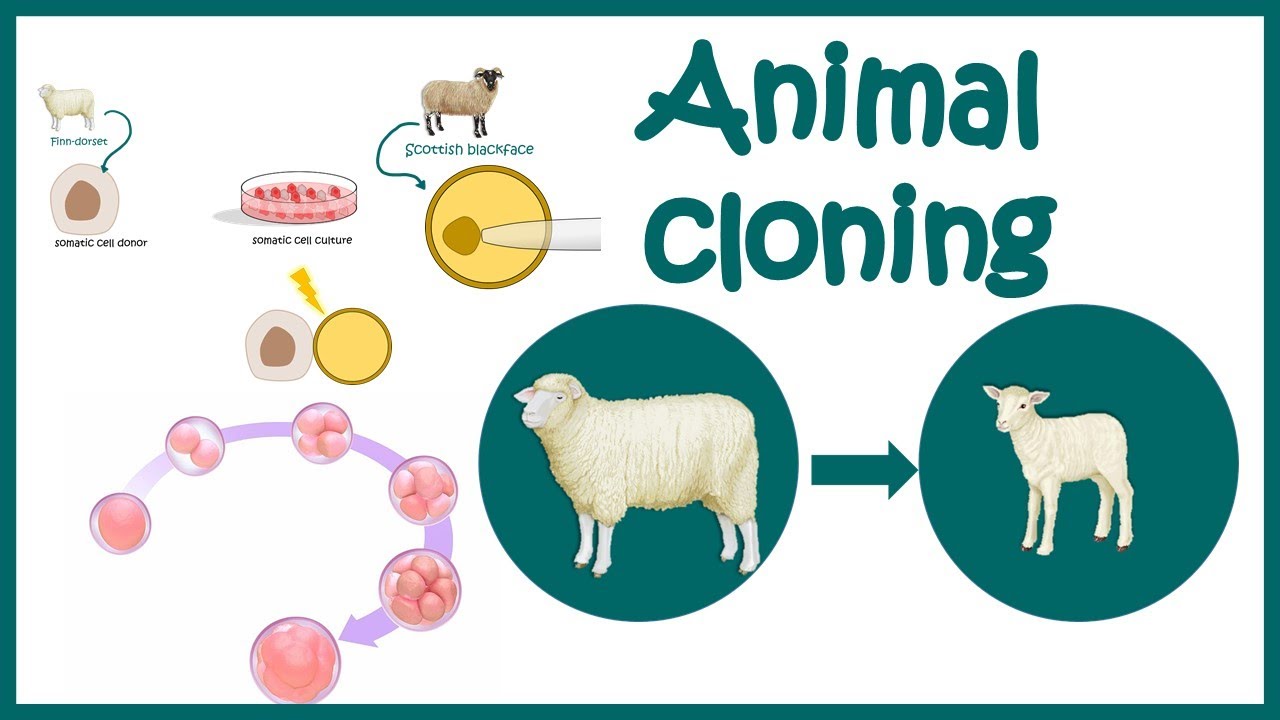
- 🐏 Scientists have cloned various animals, including Dolly the Sheep in 1996, and more recently, monkeys.
- 🔬 The most common method for cloning is Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT).
- 👶 In SCNT, scientists remove the DNA from an ovum and insert the nucleus from a somatic cell of the organism to be cloned.
- 🐒 Cloning primates like monkeys is challenging, with a success rate of only 1.6% in the case of the monkeys mentioned.
- 🧬 Spindle proteins are crucial for embryonic development and are difficult to manage in the cloning process.
- 🤔 Even if a human clone were created, it might not look or behave exactly like the original due to environmental factors and experiences.
- 🚫 Many cloned animals have health issues, including defects in vital organs and immune system problems.
- ⏳ Cellular aging in clones can occur faster than in non-clones, potentially leading to premature death.
- 🧠 A clone's personality could be very different from the original, as it is influenced by genetics and life experiences.
- 🦕 Cloning dinosaurs is not possible because DNA from dinosaurs has not survived long enough to be used.
Q & A
What is cloning?
-Cloning is the process of producing a genetically identical copy of a living organism, which can be done on various scales, from replicating basic DNA to creating a complete genetic copy of a living thing.
What is the most famous example of cloning in animals?
-The most famous example of cloning in animals is Dolly the Sheep, who was cloned in 1996. Since then, scientists have cloned cows, horses, cats, dogs, and more recently, monkeys.
What is the method used to clone full living things?
-The most successful and well-known method of cloning full living things is Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT), where the nucleus of a somatic cell is inserted into an enucleated ovum, and then implanted into a surrogate.
What is the current success rate of cloning primates?
-The success rate for cloning primates is quite low. For example, scientists started with 127 eggs and only ended up with 2 cloned monkeys, which means their success rate was only 1.6%.
What is the role of spindle proteins in cloning?
-Spindle proteins are crucial in cell division and development. They reside in the nucleus of an egg, and when the nucleus is removed for cloning, the spindle proteins are also removed, making embryonic development more difficult.
Could a human clone look completely different from the original person?
-Yes, a human clone could look completely different from the original person because appearance is based not only on genes but also on the fetal environment and which genes are turned off or on.
Can cloned animals suffer from health issues?
-Yes, many cloned animals suffer from health issues such as defective brains, hearts, livers, immune system problems, and faster cellular aging due to the quicker shrinking of the tips of their chromosomes.
Can a clone have a different personality from the original person?
-Yes, a clone can have a different personality from the original person because personality is formed not only through genetics but also through experiences and upbringing.
Why can't dinosaurs be cloned despite the interest?
-DNA from dinosaurs hasn't survived long enough to be used for cloning, so scientists cannot use genetic material to bring them back.
What is the ethical implication of human cloning?
-The ethical implications of human cloning include concerns about the welfare of the clone, the potential for exploitation, and the societal impact of creating genetically identical individuals.
Why might a clone die prematurely?
-A clone might die prematurely due to various health issues such as organ defects and immune system problems, as well as faster cellular aging compared to non-cloned individuals.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Do clones age faster? #InstanteBiotec 51
Animal cloning : Story of Dolly the sheep | The world of animal cloning | Animated biology

BIOTEKNOLOGI MODERN - KLONING

The Story of Dolly the cloned Sheep - Animal Cloning

#bioteknologi #kloning #transferinti #biologisma BIOTEKNOLOGI MODERN | KLONING (TRANSFER INTI)

Невероятная История Овечки Долли
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
