Acid-Base Titrations & Standard Solutions | A-level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel
Summary
TLDRThis video series educates viewers on titrations, a volumetric analysis technique to determine chemical unknowns like concentration and molar mass. It covers the titration process, using standard solutions, and calculations involved. The script guides through preparing standard solutions, conducting titrations, and analyzing results. It also includes practical examples, such as making a sodium hydroxide solution and calculating unknown concentrations or molar masses, enhancing understanding of titration applications.
Takeaways
- 🔬 **Titrations Defined**: Titrations are a form of volumetric analysis used to determine unknown chemical properties by reacting a known volume and concentration of one solution with a measured volume of another.
- 📊 **Standard Solutions**: Standard solutions, with known concentrations, are crucial in titrations for calculating unknowns such as concentration, molar mass, and chemical formulas.
- 🧪 **Titration Process**: The process involves adding a measured volume of substance X to a flask, adding an indicator, and then adding substance Y from a burette until the endpoint is reached, allowing for the calculation of unknowns.
- 💧 **Indicator Role**: Indicators, chosen based on the chemicals involved, are added to the flask to signal the endpoint of a titration.
- 🔋 **Burette Usage**: A burette is used to add the solution Y into the flask containing X, with careful control over the addition until the endpoint is reached.
- 🔎 **Calculating Unknowns**: By analyzing titration results, one can calculate various unknown chemical properties, guided by the principles of stoichiometry.
- ⚖️ **Making Standard Solutions**: The creation of a standard solution involves dissolving a weighed amount of solute in a solvent, transferring to a volumetric flask, and making up to the mark with solvent.
- 📐 **Concentration Concept**: Concentration measures how much solute is dissolved in a given volume of solvent, which is fundamental to understanding titration calculations.
- 🔄 **Solution Mixing**: After preparing a standard solution, it is thoroughly mixed by inverting the flask to ensure homogeneity.
- 📚 **Titration Calculations**: Calculations in titration involve determining the concentration of unknown solutions, molar masses, and other properties using the reaction stoichiometry and volumes measured.
- 📉 **Error Identification**: The script highlights common errors in preparing standard solutions and suggests improvements, such as using a weighing boat and a volumetric flask for accuracy.
Q & A
What is a titration?
-A titration is a form of volumetric analysis where a known volume and concentration of one solution reacts with a measured volume of another solution to determine chemical unknowns such as concentration, molar mass, formula, and water crystallization.
What is a standard solution?
-A standard solution is a solution with a known concentration used in titrations to calculate chemical unknowns.
How do you make a standard solution?
-To make a standard solution, you first weigh the required mass of the solute, dissolve it in a solvent in a beaker, then transfer the solution into a volumetric flask. Rinse the beaker and add the washings to the flask. Add solvent to the flask without exceeding the graduation line, then adjust the volume by adding solvent drop by drop until the meniscus is at the graduation line. Finally, mix the solution thoroughly by inverting the flask.
What is the purpose of an indicator in titration?
-An indicator in titration is used to signal the endpoint of the reaction, indicating when the titration is complete.
How do you calculate the number of moles required for a standard solution?
-The number of moles required is calculated by multiplying the desired concentration by the volume in decimeters cubed.
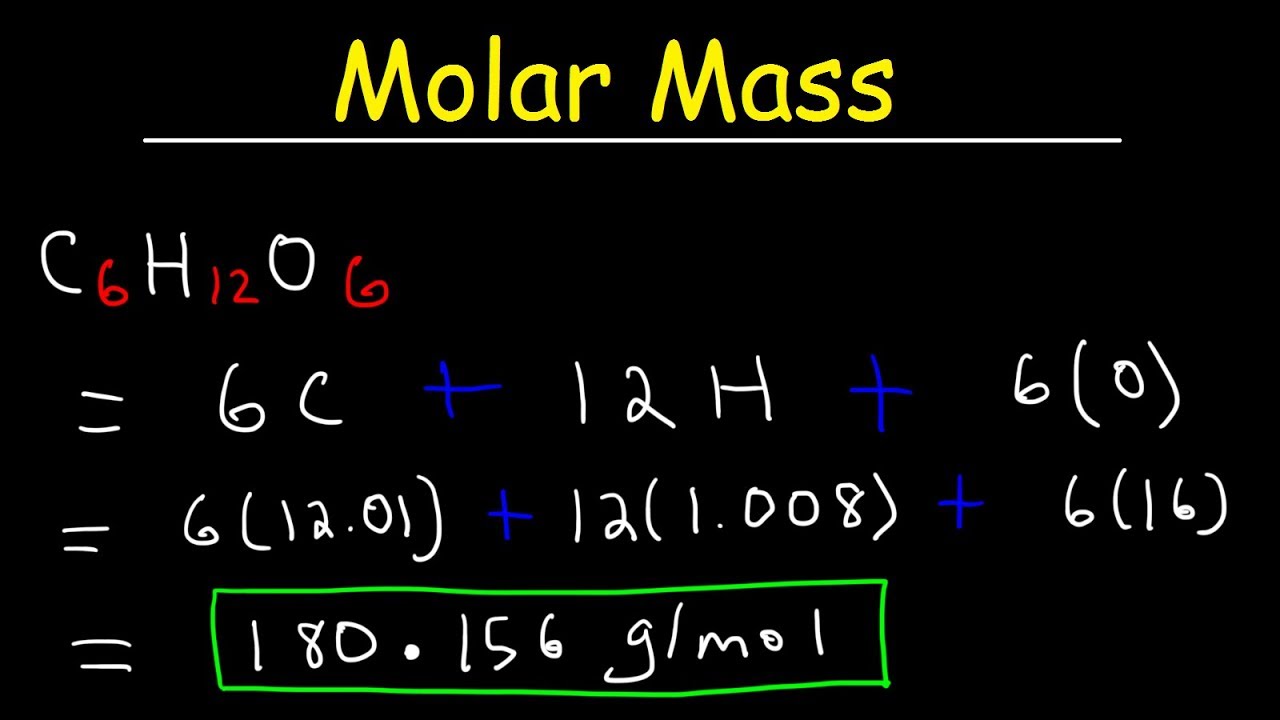
What is the molar mass of sodium hydroxide?
-The molar mass of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is approximately 40 grams per mole, calculated by adding the atomic masses of sodium (23), oxygen (16), and hydrogen (1).
How do you calculate the mass of a solute needed for a standard solution?
-The mass of the solute needed is calculated by multiplying the number of moles by the molar mass of the substance.
What is the reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide?
-The reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) produces sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O).
How do you find the concentration of an acid using titration?
-To find the concentration of an acid using titration, you calculate the moles of the base that reacted, use the reaction stoichiometry to find the moles of acid, and then divide the moles of acid by the volume of acid used to get the concentration.
What is the significance of the meniscus in making a standard solution?
-The meniscus is significant in making a standard solution because it indicates the correct volume of solution in the volumetric flask. The bottom of the meniscus should align with the graduation line to ensure the accurate volume.
Why is it important to mix the solution thoroughly after making a standard solution?
-It is important to mix the solution thoroughly after making a standard solution to ensure homogeneity and that the concentration of the solute is uniform throughout the solution.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Lab Experiment #5: Volumetric Analysis by RedOx Titration.

Precipitation Titration: Mohr's & Volhard's Method // HSC Chemistry

Concentración molar

Video 2 Preparation of solid solution
How To Calculate The Molar Mass of a Compound - Quick & Easy!

Padronização (parte 2 - cálculos e conceitos envolvidos): titulação de hidróxido de sódio (NaOH)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
