Modelleren 1: iteratief proces
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces numerical modeling in physics education, focusing on its application in common scenarios. It contrasts numerical methods with analytical methods, highlighting the former's ability to handle complex situations unsolvable by the latter. The tutorial walks through creating a simple numerical model for an object's motion, demonstrating iterative calculations over time steps to predict movement. It compares this approach with analytical solutions, showing how numerical models can provide precise answers even when direct formulas are inapplicable.
Takeaways
- 📚 Numerical modeling is an essential part of physics education for students.
- 🔍 It is important for exams as it helps solve physics problems using numerical methods.
- 🌐 Numerical modeling is used when analytical methods are too complex or inapplicable.
- 🕒 It involves breaking time into small steps to understand changes over time.
- 🔢 Numerical models use iterative processes to calculate what happens at each time step.
- 📈 The method can be applied to complex situations where analytical solutions are not feasible.
- 📝 Two approaches to numerical modeling in physics education are graphical and textual methods.
- 📋 The script focuses on the textual method, which is more straightforward for beginners.
- 🚗 An example is given using a car moving at a constant speed to demonstrate numerical modeling.
- 📉 The model starts with initial values, calculates displacement for each time step, and stops when a condition is met.
- 📊 The numerical model provides values at each second, which can be connected to form a line similar to the analytical solution.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video series?
-The main topic of the video series is numerical modeling for physics students, focusing on how to apply it in various common situations and what one must be able to do and know when numerically modeling in exams.
What are the two different ways a physicist can approach a situation?
-A physicist can approach a situation either analytically using formulas that perfectly describe the situation, or numerically using a numerical model to simulate what happens in the situation through an iterative process.
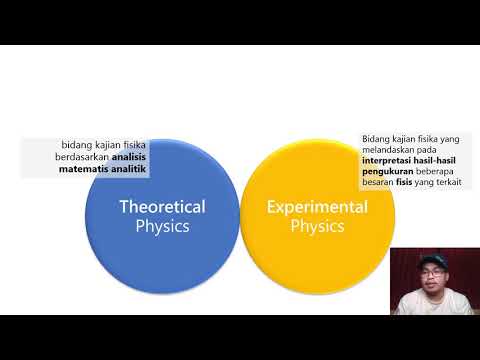
What is the advantage of using an analytical method?
-The advantage of using an analytical method is that once you have the correct formula and start with clear, precise measurement values as input, you can formulate a fairly accurate answer.
What is the main concept behind numerical modeling?
-The main concept behind numerical modeling is to divide the time you want to investigate into small time steps, called time increments, and during each time increment, you look at what happens to the variables of interest in a simplified environment.
Why is numerical modeling necessary for complex situations?
-Numerical modeling is necessary for complex situations because they can be so complex that there are no good analytical solution methods available. Numerical models can provide accurate answers when analytical models cannot perfectly describe the situation.
What are the two types of modeling approaches in physics education?
-The two types of modeling approaches in physics education are the graphical method and the textual method. The video focuses on the textual method, but acknowledges that the graphical method is equally valid.
How does the iterative process in numerical models work?
-The iterative process in numerical models works by repeating the calculation of the variables of interest after each time increment, updating their values, and storing them for later retrieval until a stopping condition is met.
What is the first step in creating a numerical model according to the script?
-The first step in creating a numerical model is to define the initial values for each of the variables that the model will calculate, also known as start values.
How is the displacement calculated in the first time step in the example given?
-In the example, the displacement in the first time step is calculated using the same formula as in the analytical method, which is displacement equals velocity times the duration of the time step.
What is the stopping condition used in the example provided in the script?
-The stopping condition used in the example is that the model should stop when the time is greater or equal to five seconds, as the movement is to be examined over that duration.
How does the numerical model compare to the analytical method in terms of the values it provides?
-The numerical model provides values for x at every whole second, similar to the analytical method, but it also includes intermediate values between each second, creating a stepped line rather than a straight line when plotted.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
#01 Fisika Komputasi: Pendahuluan

GRANDEZAS FÍSICAS (ESCALARES E VETORIAIS) | Resumo de Física Enem. |Prof Marcus Rossetto

Discutindo os casos e os momentos em Modelagem Matemática

What is a DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION?? **Intro to my full ODE course**

Blender BEGINNER tutorial! - Roblox Development

Yuk, Berpetualang di Dunia Algoritma SMP Kelas 9! | Materi Informatika Elemen Berpikir Komputasional
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
