History of X-rays
Summary
TLDRThis episode explores the accidental discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen in 1895, which revolutionized medicine, genetics, and manufacturing. The script delves into the history of X-rays, their initial use for entertainment, and the technological advancements that transformed them into an essential medical tool. It also discusses the physics behind X-ray production, their role in imaging, and Roentgen's decision not to patent his discovery, emphasizing his significant contribution to science and society.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The discovery of X-rays revolutionized medicine and other fields like genetics and manufacturing.
- 🏥 Halifax Medical Center houses the Halifax Radiology Museum, showcasing original radiology equipment from 1928.
- 📸 X-rays are now a common part of society, used in security, manufacturing, and medical diagnostics.
- 🧬 X-ray diffraction was key to understanding the DNA molecule's structure by scientists like Rosalind Franklin, Watson, and Crick.
- 🌟 The first American medical X-ray was performed at Dartmouth College in 1896, marking a significant milestone.
- 🎭 Early X-ray technology was used for entertainment, with 'bone portrait' studios offering X-ray images of body parts.
- 🏬 The inventor of X-rays, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, worked at the University of Würzburg, where he made his groundbreaking discovery.
- 🔋 The Crookes tube, an early experimental device, was used by Roentgen to produce X-rays and led to the first human radiograph.
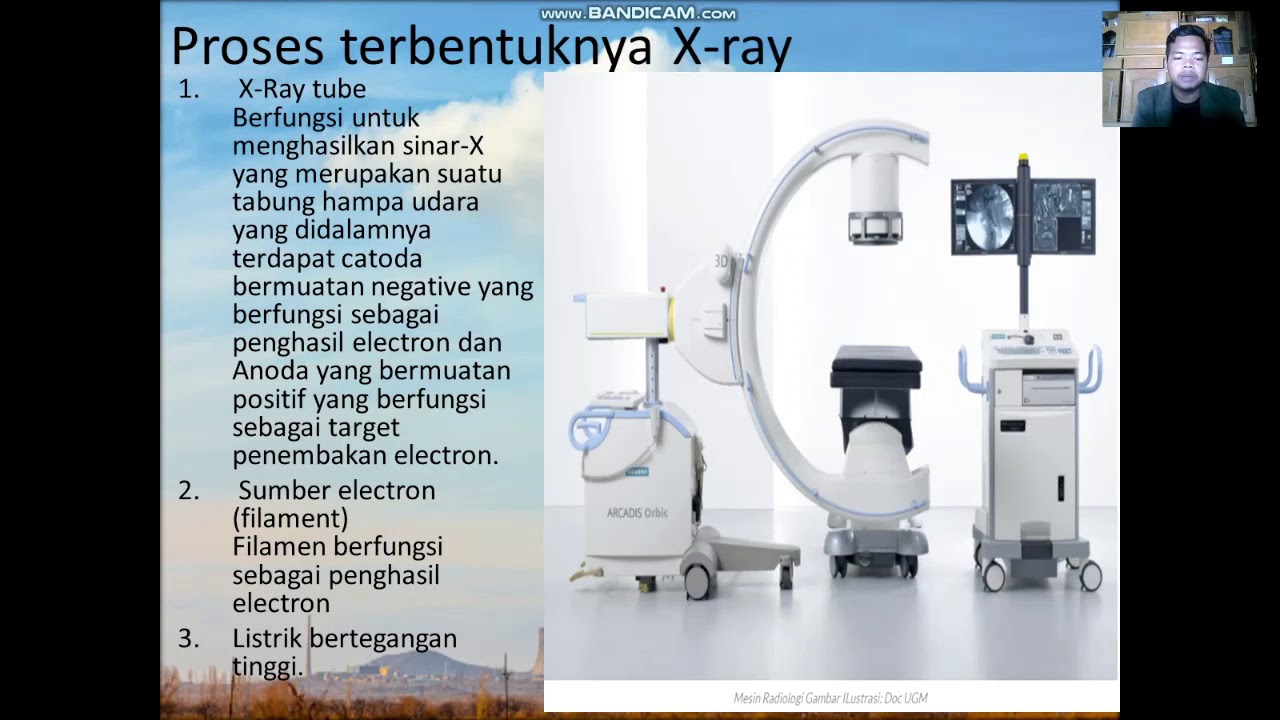
- ⚙️ Modern X-ray tubes have evolved with a rotating anode and improved cathode design for more efficient X-ray production.
- 🛠️ The voltage (kVp) and current (mA) settings on an X-ray machine are crucial for adjusting the image quality and penetrating power.
- 🌌 Roentgen's discovery has had a profound impact on our understanding of the world, from genetics to material science and beyond.
Q & A
What significant discovery is discussed in the video script?
-The video script discusses the discovery of X-rays, which revolutionized the field of medicine and transformed other fields such as genetics and manufacturing.
Where is the Halifax Medical Center located?
-The Halifax Medical Center is located in Daytona Beach, Florida, approximately 2 miles from the world's most famous beach and a half a mile from the Daytona International Speedway.
Who made the Halifax Radiology Museum possible?
-The Halifax Radiology Museum was made possible by Mr. Bud Hinkle, who was the Radiology manager from 1985 to 1995.
How did X-rays contribute to the understanding of DNA?
-X-rays contributed to the understanding of DNA through the work of PhD scientist Rosalyn Franklin, who used X-ray diffraction to examine the DNA molecule, and later Watson and Crick used this information to define the double helix structure of DNA in 1953.
What was the term used to describe the initial public fascination with X-rays?
-The initial public fascination with X-rays was termed 'X-ray Mania', where people were eager to get their hands on this new technology.
What was the first American Medical X-ray performed on?
-The first American Medical X-ray was performed at Dartmouth College on February 3rd, 1896, and it was an image of a student's hand with a fractured distal phalanx.
Who was responsible for the discovery of X-rays?
-Professor Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, a physics professor at the University of Würzburg in Germany, is credited with the discovery of X-rays.
What was the Crooks tube and how was it used in the discovery of X-rays?
-The Crooks tube was a device that produced cathode rays and was used by Roentgen in his experiments. It was a high-powered light bulb-like device evacuated of air with an anode and cathode connected to a high voltage DC power supply. Roentgen used it to discover X-rays when he noticed a faint glow from a piece of paper covered in phosphorescent material.
What was the purpose of the black box that Roentgen constructed during his experiments?
-Roentgen constructed a black box to cover the Crooks tube to block any light that might interfere with his experiment to detect other types of rays.
How did the early X-ray technology lead to misconceptions about its capabilities?
-Early X-ray technology led to misconceptions because people were afraid that it could be used for inappropriate purposes, such as seeing through clothing, due to its ability to see through walls and human bodies.
What was the first radiograph of a human taken by Roentgen?
-The first radiograph of a human, purportedly of Roentgen's wife's hand, was taken by Roentgen after six weeks of characterizing the new X-ray. This image showed her hand with a wedding ring and is considered the first radiograph of a human hand.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)