How Electricity Gets to You
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the intricacies of electricity generation and distribution, highlighting the challenges of matching supply to demand in real-time. It explains the role of various power sources like nuclear, coal, natural gas, and renewables, and how they address base-load and peak demands. The script also explores the economic and technical aspects of energy storage, the evolution of the electric grid with renewable integration, and the importance of efficient long-distance power transmission. It concludes with a look at how electric vehicles could contribute to the grid's storage needs, offering a glimpse into a greener, more efficient energy future.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Electricity is generated from various energy sources like water, gas, wind, and is transmitted over long distances to power everyday devices.
- 🌐 Electric grids are vast, complex machines that must balance supply and demand with zero slack, unlike water systems which have some buffer.
- 🔆 Demand for electricity varies greatly depending on the time of day and season, with peaks typically in the morning and evening, and higher overall demand in winter and summer months.
- 🏠 The public library in Glenwood Springs, Colorado, illustrates the process of electricity generation and distribution, highlighting the variability in demand.
- 🌡️ Base-load power, provided by nuclear and coal power plants, operates continuously to meet the minimum demand, while natural gas plants are used for peak demand.
- 🌿 The integration of renewable energy sources like wind and solar is changing the electricity generation landscape, offering free power but with variable supply.
- 🔋 Energy storage is crucial for balancing supply and demand, but current battery technology is expensive and not yet practical for widespread grid storage.
- 🚗 The potential for electric vehicles (EVs) to act as mobile energy storage units, providing power back to the grid, is an emerging concept.
- 💧 Hydroelectric power offers a reliable and green energy source, with the ability to start and stop production quickly, and even store energy by pumping water uphill.
- 🌉 Efficient long-distance transmission of electricity is key, with high-voltage lines reducing power loss, and the use of direct current (DC) for very long distances.
- 🏢 The final step in electricity delivery involves stepping down high voltages to levels suitable for residential and commercial use, such as those in Glenwood Springs.
Q & A
What is the significance of electric grids in terms of their size and function?
-Electric grids are considered some of the single largest machines in existence, stretching across entire continents. They are responsible for delivering electricity from power sources to consumers, with zero slack, meaning supply must match demand in real-time.
How does the variability in electricity demand affect the operation of electric grids?
-The variability in electricity demand from minute-to-minute and month-to-month makes the task of converting natural fuels or phenomena into electric power difficult. Utilities must forecast demand based on trends, such as seasonal peaks and daily usage patterns, to match supply with demand.
What are the typical daily demand trends for electricity in the US during different months?
-In January, there is a two-peak daily demand trend, with spikes around 7:00 AM and in the evening. In July, energy use is highest in the late-afternoon or early-evening, but this varies by region, with the Southwest peaking around 4:00 pm and the northwest around 6:00 pm.
How do special events like holidays impact electricity demand?
-Special events, such as the Superbowl, can cause a temporary drop in electricity demand as people turn off lights and stop cooking to watch the event, illustrating the need for utilities to factor in such events when forecasting demand.
What role does nuclear power play in the electricity supply, and why is it not used to match demand?
-Nuclear power provides a stable supply of electricity 24/7 and is not designed to be turned off and on easily. It is impractical to operate nuclear power stations in response to demand fluctuations due to the time and cost required to shutdown and start up again.
Why are coal power stations also run continuously, and what is their role in the energy mix?
-Coal power stations, like nuclear, are not designed to be fired up quickly and are economically inefficient to run idle. They typically fulfill the base-load, producing the minimum amount of power needed at the lowest point in daily demand.
How do natural gas fired plants contribute to meeting peak electricity demand?
-Natural gas fired plants, particularly those with simple cycle combustion turbines, can reach full power within 15 minutes, making them effective for responding to short peaks in demand, such as during hot summer afternoons.
What challenges do renewable energy sources like wind and solar present to the electric grid?
-Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are variable and uncontrollable, which means they can't match supply to demand as reliably as traditional power sources. This variability requires the grid to adapt with storage solutions or other flexible generation methods.
How does battery storage help balance electricity supply and demand, and what are its limitations?
-Battery storage systems can store excess electricity when demand is low and release it when demand is high. However, they are currently limited by high costs and the need for significant infrastructure, making widespread grid storage economically impractical.
What is the concept of vehicle-to-grid and how could it potentially help with grid storage?
-Vehicle-to-grid is a concept where electric vehicles (EVs) could charge during off-peak hours and return electricity to the grid during peak demand. This could help balance supply and demand, but the real-world economics and technical feasibility are still being explored.
How does hydroelectric power contribute to the grid's ability to respond to variable electricity demand?
-Hydroelectric power is a reliable and low-carbon source of electricity that can start and stop making power quickly, allowing it to respond to demand fluctuations. Additionally, facilities like pumped-storage hydroelectricity can store energy by pumping water uphill when demand is low and generate power when demand is high.
Why is high-voltage transmission important for long-distance electricity transport, and what are its benefits?
-High-voltage transmission is crucial for efficiently transporting electricity over long distances because higher voltages result in less power loss during transmission. This allows for more centralized and cost-effective electricity production and distribution.
How do transformers play a role in the efficient distribution of electricity?
-Transformers allow for the conversion of electricity between higher and lower voltages, which is essential for efficient distribution. Higher voltages reduce power loss during transmission, while lower voltages are necessary for safe use by consumers.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Market design for electricity – Comparing the US and EU | Fabien Roques

TOPIC 2: ELECTRICAL GENERATION AND TRANSMISSION
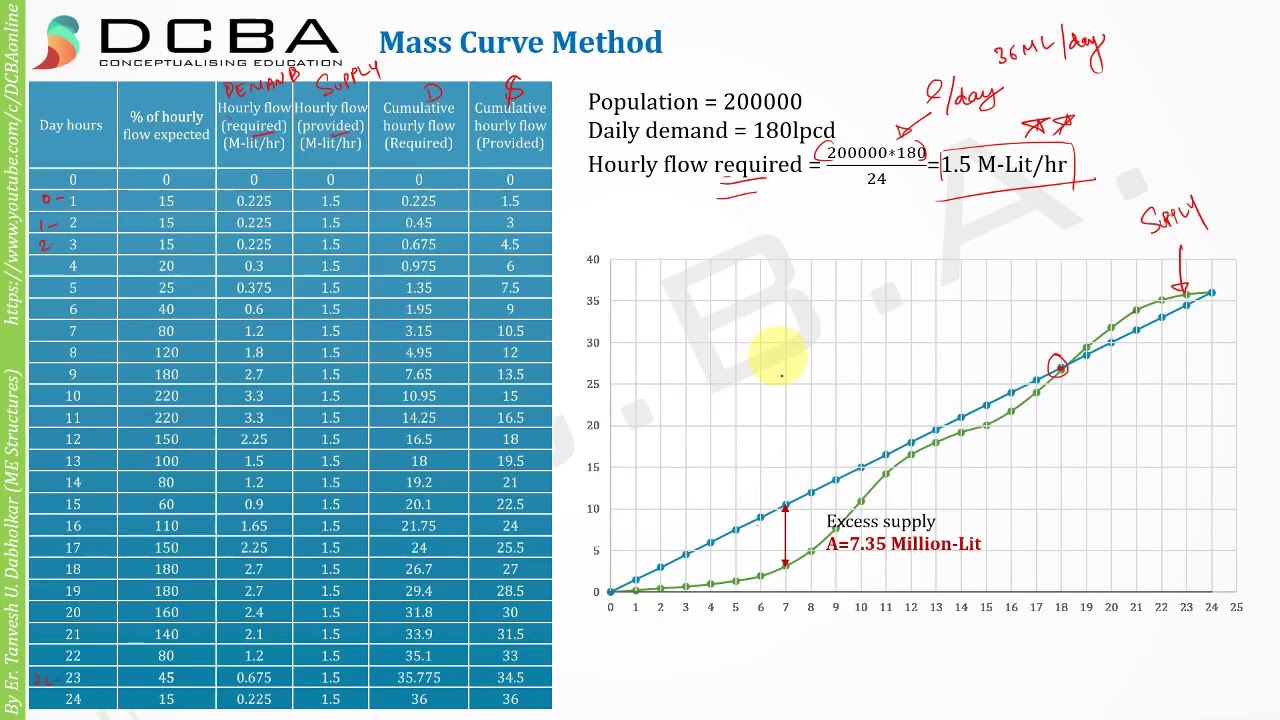
Storage capacity of Distribution Reservoir | Mass Curve Method

2ª Temporada - Episódio 3 - A transmissão da energia elétrica

ERDF : SMART GRIDS, la nécessaire mutation du réseau électrique

Map Matching @ Uber
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
