Introduction to the Muscular System - Animated Tutorial | Complete Anatomy
Summary
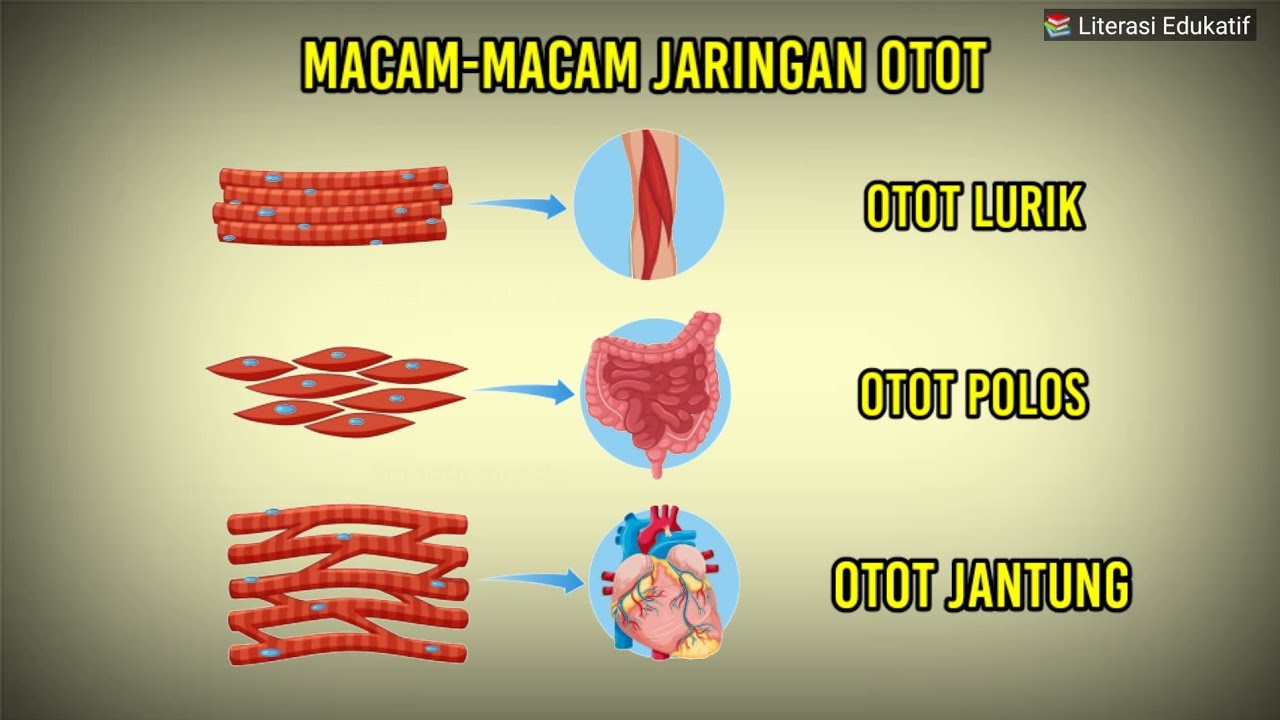
TLDRThe human body contains three types of muscles: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal. Smooth muscles, found in organs like the stomach and blood vessels, contract involuntarily with a non-serrated appearance. Cardiac muscles, located in the heart, also involuntarily contract but are striated. Skeletal muscles, which attach to bones and move them, contract voluntarily and come in pairs. They are categorized into parallel, convergent, circular, and pennate based on fiber orientation and arrangement, with subcategories like quadrilateral, strap-like, fusiform, and multi-pinnate.
Takeaways
- 💪 There are three types of muscles in the human body: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal.
- 🔍 Smooth muscles are found in the walls of organs like the stomach and blood vessels, and they contract involuntarily.
- 🫀 Cardiac muscles are located in the heart, also contracting involuntarily, but they have a striated appearance.
- 🏋️♂️ Skeletal muscles are attached to bones, move them, and contract voluntarily.
- 🔄 Skeletal muscles are categorized into four groups based on the orientation and arrangement of their fibers: parallel, convergent, circular, and pennate.
- 📏 Parallel skeletal muscles have fibers arranged in line with the pull during contraction and are further categorized by shape: quadrilateral, strap-like, and fusiform.
- 🌀 Convergent muscles have fibers that start wide and converge to attach to a narrow tendon.
- 🔄 Circular skeletal muscles have fibers arranged in a circular pattern, typically found around openings like the eye and mouth.
- 🪶 Pennate muscles have fibers attached to the sides of a tendon, resembling a feather, and are further categorized into unipennate, bipennate, and multipennate based on fiber arrangement.
- 🧬 Each muscle type plays a distinct role in the body, from involuntary actions like digestion to voluntary movements like walking.
Q & A
What are the three types of muscles found in the human body?
-The three types of muscles found in the human body are smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles.
In which organs are smooth muscles typically found?
-Smooth muscles are typically found in the walls of organs such as the stomach and in blood vessels.
How do smooth muscles differ in appearance from other muscle types?
-Smooth muscles have a non-serrated appearance.
What is the primary function of cardiac muscles?
-Cardiac muscles are found in the walls of the heart and are responsible for the heart's contractions.
How do cardiac muscles differ from smooth muscles in terms of appearance?
-Cardiac muscles have a striated appearance, unlike smooth muscles which are non-serrated.
What is the role of skeletal muscles in the body?
-Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and are responsible for their movement.
How do skeletal muscles differ from smooth and cardiac muscles in terms of control?
-Skeletal muscles contract voluntarily, unlike smooth and cardiac muscles which contract involuntarily.
What are the four distinct groups that skeletal muscles are subcategorized into based on the orientation and arrangement of their muscle fibers?
-Skeletal muscles are subcategorized into parallel, convergent, circular, and pennate groups.
What is the characteristic arrangement of fibers in parallel skeletal muscles?
-In parallel skeletal muscles, fibers are arranged in parallel to the line of pull during contraction.
How are convergent skeletal muscles defined in terms of their fiber arrangement?
-Convergent skeletal muscles contain fibers that have a wide origin but converge to attach to a narrow tendon.
What is the arrangement of fibers in circular skeletal muscles?
-Circular skeletal muscles are made up of fibers that are arranged in a circular manner.
What is the unique feature of pennate skeletal muscles regarding their attachment to tendons?
-Pennate skeletal muscles consist of muscle fibers that are attached to the sides of a tendon in a manner similar to a feather.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)