Oxidizing Agents and Reducing Agents
Summary
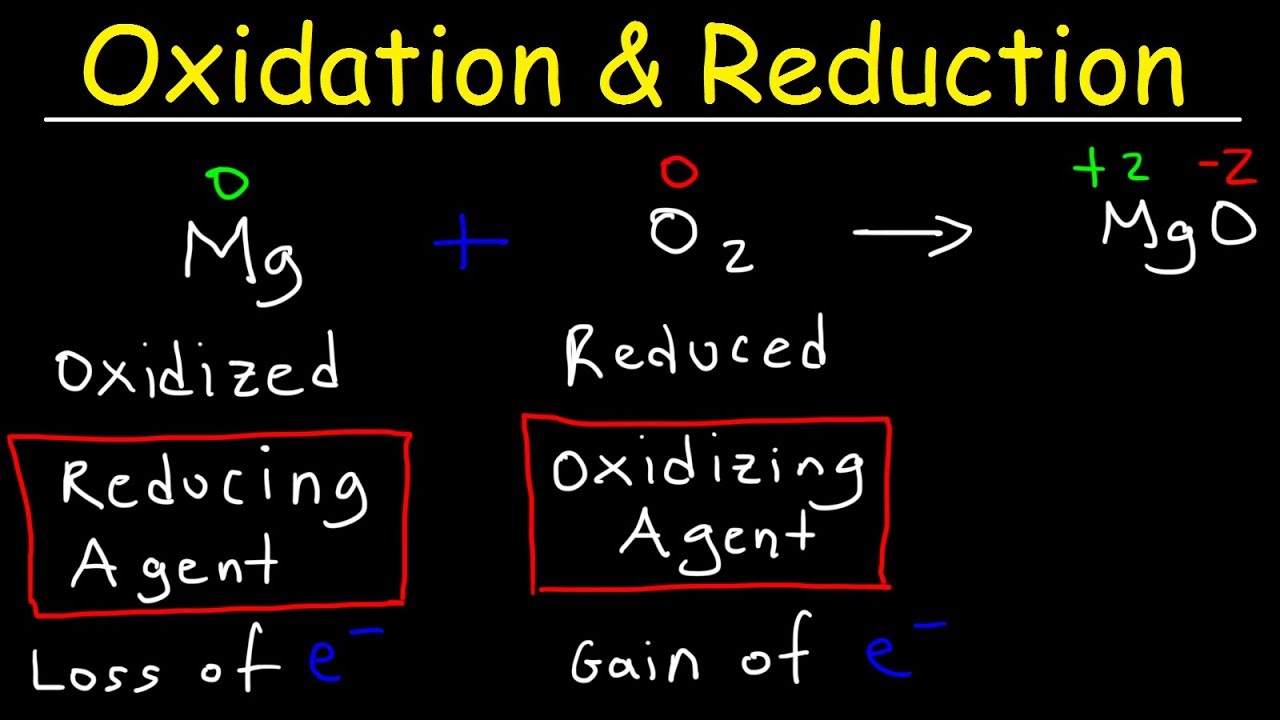
TLDRThis educational video delves into the concepts of oxidizing and reducing agents, essential in chemistry for understanding chemical reactions. It explains oxidation as the loss of electrons and reduction as the gain, using a diagram to illustrate electron transfer between two entities, A and B. The video clarifies that an oxidizing agent facilitates oxidation by accepting electrons, while a reducing agent enables reduction by donating electrons. It further discusses how to identify these agents in chemical equations by examining changes in oxidation numbers, providing examples to demonstrate the process clearly. The video also touches on the nuance of identifying agents within compounds, emphasizing the importance of considering the whole compound rather than just the individual atoms.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Oxidation is the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons.
- 🔄 An oxidizing agent is a substance that causes another substance to be oxidized by accepting electrons.
- 🔄 A reducing agent is a substance that causes another substance to be reduced by donating electrons.
- 🔄 In a chemical reaction, the substance that is oxidized is the reducing agent, and the substance that is reduced is the oxidizing agent.
- 📊 To identify oxidizing and reducing agents, one must look at the changes in oxidation numbers of the elements involved in the reaction.
- 📈 An increase in oxidation number indicates oxidation, while a decrease indicates reduction.
- 🧪 In complex chemical equations, it's common to refer to the whole compound rather than just the individual atom when discussing oxidizing and reducing agents.
- 🌐 The oxidizing agent gains electrons and is reduced, while the reducing agent loses electrons and is oxidized.
- 🔬 The process of identifying oxidizing and reducing agents involves understanding the transfer of electrons between substances.
- 📚 The script provides a methodical approach to determining oxidizing and reducing agents by examining oxidation numbers and the nature of electron transfer in chemical reactions.
Q & A
What is an oxidizing agent?
-An oxidizing agent is a substance that causes another substance to lose electrons, thereby causing oxidation. It facilitates the oxidation process by accepting electrons from the substance being oxidized.
What is a reducing agent?
-A reducing agent is a substance that causes another substance to gain electrons, thereby causing reduction. It facilitates the reduction process by donating electrons to the substance being reduced.
How can you identify an oxidizing agent in a chemical equation?
-In a chemical equation, an oxidizing agent can be identified by looking at the changes in oxidation numbers. If a substance gains electrons and its oxidation number decreases, it is being reduced and is the oxidizing agent.
How can you identify a reducing agent in a chemical equation?
-In a chemical equation, a reducing agent can be identified by looking at the changes in oxidation numbers. If a substance loses electrons and its oxidation number increases, it is being oxidized and is the reducing agent.
What is the relationship between oxidation and reduction in a chemical reaction?
-Oxidation and reduction are complementary processes that occur simultaneously in a chemical reaction. Oxidation is the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons. One substance is oxidized (loses electrons) while another is reduced (gains electrons).
Can you provide an example of how to determine if a substance is being oxidized or reduced?
-Yes, in the script, calcium (Ca) is used as an example. It starts with an oxidation number of 0 and ends with +2, indicating it has lost electrons and is being oxidized. Conversely, chlorine (Cl2) starts with an oxidation number of 0 and ends with -1, indicating it has gained electrons and is being reduced.
What does it mean when a substance's oxidation number increases?
-When a substance's oxidation number increases, it means the substance is losing electrons and is being oxidized. This is indicative of the substance acting as a reducing agent in the reaction.
What does it mean when a substance's oxidation number decreases?
-When a substance's oxidation number decreases, it means the substance is gaining electrons and is being reduced. This is indicative of the substance acting as an oxidizing agent in the reaction.
How do you determine the oxidizing and reducing agents in a reaction involving compounds?
-In reactions involving compounds, you look at the changes in oxidation numbers of the elements within the compounds. The compound that loses electrons (and thus has an element with an increased oxidation number) is the reducing agent, and the compound that gains electrons (with an element having a decreased oxidation number) is the oxidizing agent.
Can you explain the concept of oxidation numbers and their importance in identifying oxidizing and reducing agents?
-Oxidation numbers are a way of keeping track of the distribution of electrons in a chemical reaction. They are used to determine if a substance is being oxidized (loses electrons, oxidation number increases) or reduced (gains electrons, oxidation number decreases). By analyzing changes in oxidation numbers, you can identify the oxidizing and reducing agents in a reaction.
Why is it important to understand the difference between oxidizing and reducing agents?
-Understanding the difference between oxidizing and reducing agents is crucial for predicting the outcome of chemical reactions, especially in redox reactions. It helps in determining the changes in oxidation states, which is essential for balancing equations and understanding the electron transfer process.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Oxidação e redução

REAKSI REDOKS - SIMPLE KONSEP - KIMIA (Kursus Online Rp8.000 per BULAN : cek deskripsi)

19.3 Oxidizing and Reducing Agents

ELETROQUÍMICA: PILHAS e BATERIAS | Química para ENEM e Vestibulares | Prof. Paulo Valim

Oxidation Reduction Ch 13
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions - Basic Introduction
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
