Demonstration of the Groundwater Flow Model
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Sawyer Trees, a water conservation assistant, demonstrates the groundwater flow model to explain the origin of water from precipitation. The video illustrates how groundwater is stored in the pore spaces of the aquifer and identifies the water table's position. It addresses the impact of pumping on the water table and the potential depletion of water resources. Sawyer emphasizes the importance of water conservation during a drought and discusses the risks of groundwater pollution from everyday activities. The video concludes with a demonstration of how pollutants can infiltrate the groundwater system, highlighting the need for sustainable water management.
Takeaways
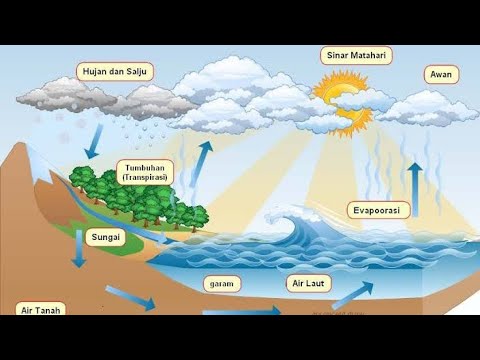
- 💧 Water originates from precipitation, such as rain and snow.
- 🌊 The water table is the topmost level where all pore spaces below it are filled with water.
- 🚰 Pumping groundwater can lower the water table and potentially deplete water resources.
- 🌍 Groundwater depletion can cause irreparable damage to aquifers and other negative consequences.
- 🌞 The city of Glendale has been experiencing a drought for 20 years, exacerbating water scarcity.
- 💦 Simple water conservation measures like turning off the faucet and shortening showers can help conserve water.
- 🔧 Fixing leaks promptly is an effective way to save water.
- 🚫 Pollution can unintentionally contaminate groundwater through oil leaks, litter, and pesticides.
- 🟣 Adding food coloring to the model demonstrates how pollution can seep into groundwater due to gravity.
- 💼 Treating polluted groundwater is costly in terms of energy and money.
Q & A
What is the primary source of water discussed in the video?
-The primary source of water discussed in the video is precipitation, which includes rain and snow.
How does the presenter simulate rainfall in the groundwater flow model?
-The presenter simulates rainfall by pouring water into the groundwater flow model.
What is the significance of porosity in the context of the groundwater flow model?
-Porosity is significant as it refers to the space between sand and gravel particles where water resides.
What is the water table and how is it represented in the model?
-The water table is the uppermost level of water in the aquifer where all pore spaces beneath it are filled with water. In the model, it is represented by the level where the water reaches.
Can the water table change, and if so, how?
-Yes, the water table can change, typically when water is pumped from the ground, causing it to lower.
What is the consequence of continuous groundwater pumping as shown in the video?
-Continuous groundwater pumping can deplete the water source to the point of no return, causing irreparable damage to aquifers.
How does the presenter demonstrate the impact of a long-term drought on water resources?
-The presenter mentions that they have been in a drought for 20 years, emphasizing the scarcity of water resources.
What are some ways the presenter suggests to conserve water?
-The presenter suggests conserving water by turning off the faucet while brushing teeth, shortening shower times, fixing leaks, and avoiding unnecessary water use like hosing down driveways.
Why is it important to consider water quality in addition to water conservation?
-Water quality is important because pollutants can seep into the groundwater, affecting the water we drink, which requires energy and money to treat.
How does the presenter demonstrate groundwater pollution in the model?
-The presenter demonstrates groundwater pollution by adding food coloring to the model, showing how pollutants can be pulled into the groundwater by gravity.
What is the final message of the video regarding groundwater and water resources?
-The final message is to understand the importance of groundwater and the need for conservation, especially in areas with scarce water resources like Arizona.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)