Digestive System, Part 1: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #33
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the digestive system through a fun analogy involving nachos. It highlights how food provides energy and materials for our bodies, breaking down complex molecules into simpler components like sugars, fatty acids, and amino acids. The process involves mechanical and chemical digestion, starting in the mouth and continuing through the stomach and intestines. Enzymes play a key role in breaking down macromolecules into monomers, which are absorbed by cells for energy and tissue-building. The video also emphasizes the importance of proper digestion and ends with a humorous nod to the elimination process.
Takeaways
- 🌮 The main reason we eat food, like nachos, is to obtain energy and raw materials needed for survival and body maintenance.
- ⚛️ Both food and the human body are made of matter (atoms) and contain stored energy in the bonds between those atoms.
- 🦠 The digestive system converts food into usable forms for the body through six main steps: ingestion, propulsion, mechanical digestion, chemical digestion, absorption, and defecation.
- 🧬 Enzymes play a crucial role in digestion by breaking down macromolecules (like lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids) into smaller monomers (fatty acids, sugars, amino acids, and nucleotides) that the body can use.
- 🚶 Your body’s cells use the absorbed nutrients to generate energy, build tissues, and maintain bodily functions, adapting to current needs.
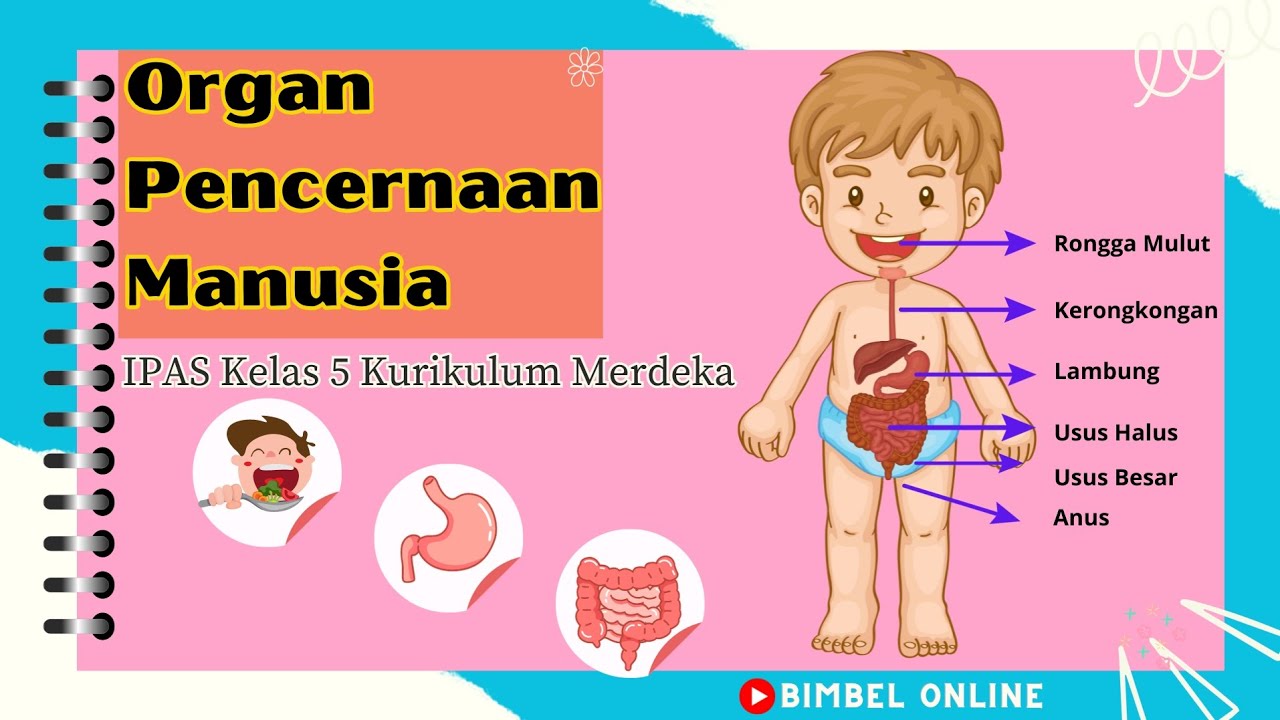
- 🍽️ The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a hollow tube that runs from the mouth to the anus, allowing for the movement, digestion, and absorption of food.
- 🧱 The digestive tract consists of various tissue layers, including mucosal, submucosal, and muscularis externa, each playing a role in food processing and nutrient absorption.
- 🧪 Mechanical digestion physically breaks down food, while chemical digestion uses enzymes to further decompose food into basic molecules.
- 🚽 After nutrient absorption, indigestible materials are excreted from the body through defecation, completing the digestive process.
- 👩🔬 The digestive process requires cooperation between multiple organs and accessory organs, such as the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder, which assist with enzyme production and digestion.
Q & A
Why do humans eat food like nachos?
-Humans eat food to obtain energy for staying alive and to acquire the raw materials required to build tissues. Food provides both matter and energy, which are essential for life.
What are the two main things that both humans and food have in common?
-Both humans and food are made of matter, which is composed of atoms, and both contain energy stored in the bonds between these atoms.
How does the body convert food like nachos into usable energy and raw materials?
-The digestive system breaks down food into smaller molecules that cells can absorb and use. The process involves mechanical and chemical digestion, with enzymes breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into monomers like sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids.
What are the four main types of biological molecules found in food?
-The four main types of biological molecules in food are lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Why does the digestive system need to break down food into its smallest components?
-Cells can only absorb and use the smallest building blocks, or monomers, from food. Polymers like carbohydrates and proteins must be broken down into sugars and amino acids so the body can use them for energy and tissue building.
What role do enzymes play in digestion?
-Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. In digestion, enzymes break down large biological molecules into smaller ones, such as breaking down carbohydrates into sugars and proteins into amino acids.
What happens to food once it enters the mouth?
-Food is broken down mechanically by chewing, and chemically by enzymes in saliva. This begins the process of breaking down the food into smaller, more usable forms.
What is peristalsis and why is it important?
-Peristalsis is the involuntary contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscles in the digestive organs, which moves food through the alimentary canal. It ensures that food is pushed along the digestive tract, even if someone is upside down.
What are the six main steps of human digestion?
-The six steps are ingestion (eating), propulsion (moving food through the digestive tract), mechanical digestion (breaking food down physically), chemical digestion (breaking food down with enzymes), absorption (cells absorbing nutrients), and defecation (removal of indigestible substances).
How does the body protect itself from digesting its own tissues during digestion?
-The inner lining of the digestive tract is protected by mucus, which is secreted by columnar epithelial cells. This mucus lubricates the tract and protects the tissue from being digested by the body’s own enzymes.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)