Macroscopic Characteristics of Minerals Part 1: Luster and Color
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial expands on previous lessons about minerals, focusing on identifying minerals through their luster and color. Luster describes how light reflects off a mineral's surface, classified as metallic or non-metallic. Non-metallic minerals can exhibit various lusters, including adamantine, vitreous, pearly, silky, resinous, greasy, and dull. The tutorial also explains the influence of transition metals on a mineral's color and the use of a streak test for identification. By understanding these key properties, geologists can accurately identify minerals in nature.
Takeaways
- 💡 Luster is a key property used by geologists to identify minerals, with two main categories: metallic and non-metallic.
- 🔎 Metallic luster minerals are opaque with a mirror-like shine, while non-metallic minerals can range from opaque to transparent and are less shiny.
- 🌟 There are seven types of non-metallic lusters: adamantine, vitreous, pearly, silky, resinous, greasy, and dull.
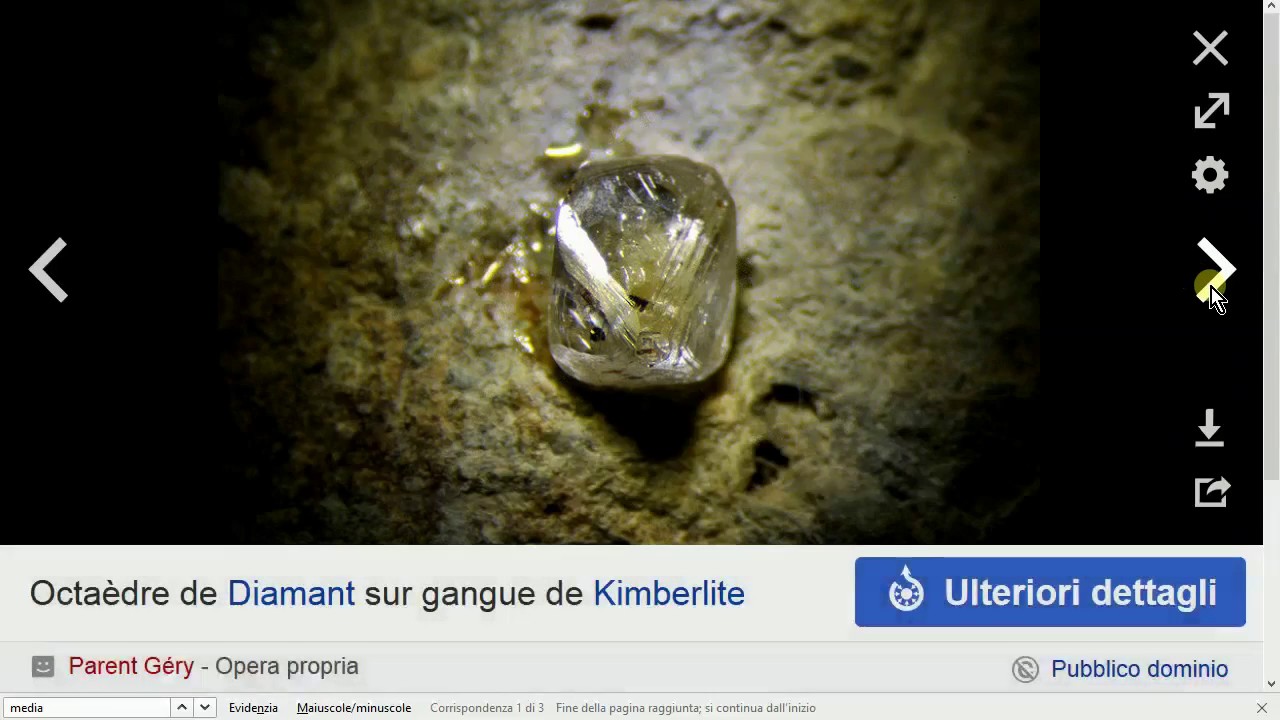
- 💎 Adamantine luster minerals are the shiniest non-metallics, like diamonds and Herkimer quartz.
- 🔮 Vitreous luster resembles clean glass, found in minerals like quartz and calcite.
- ✨ Pearly luster is iridescent, seen in minerals with layered structures like muscovite.
- 🧵 Silky luster is found in minerals with parallel fibers, such as ulexite and satin spar.
- 🌳 Resinous luster looks like hardened resin, as seen in sphalerite, which can have different lusters.
- 🖤 Greasy luster, like graphite, appears and feels oily due to its atomic structure.
- 🎨 Color is influenced by transition metals in a mineral, but streak tests provide more consistent identification than visible color.
Q & A
What is the primary property geologists use to identify minerals by eye?
-Geologists primarily use the property of luster to identify minerals by eye. Luster describes the way light reflects off a mineral’s surface.
What are the two main categories of luster?
-The two main categories of luster are metallic and non-metallic. Metallic minerals have a shiny, mirror-like appearance, while non-metallic minerals can range from opaque to transparent and tend to be less shiny.
How is luster related to a mineral’s refractive index?
-Luster is related to the speed that light travels through a mineral, which is determined by its refractive index. Minerals with a refractive index greater than 3 generally have a metallic luster.
What are the seven types of non-metallic lusters?
-The seven types of non-metallic lusters are adamantine, vitreous, pearly, silky, resinous, greasy, and dull.
Which mineral is commonly known for having an adamantine luster?
-Diamonds are commonly known for having an adamantine luster, which is the shiniest of the non-metallic lusters.
What causes the pearly luster in minerals?
-Pearly luster is caused by the iridescence that occurs when light reflects and refracts off different crystallographic planes in a mineral, creating a shifting rainbow effect based on the angle of observation.
What is the difference between a silky luster and a fibrous luster?
-A silky luster is caused by thin, parallel fibers in the mineral that resemble silk, while a fibrous luster occurs when these fibers are coarser, more like twine.
How do transition metals affect the color of minerals?
-Transition metals affect the color of minerals due to their ability to absorb specific wavelengths of visible light through their partially filled d-orbitals, which influences the color reflected off the mineral's surface.
What is the difference between allochromatic and idiochromatic minerals?
-Allochromatic minerals get their color from trace amounts of transition metals, while idiochromatic minerals are 'self-colored' due to the presence of a transition metal in their standard chemical formula.
What is the purpose of a streak test in mineral identification?
-A streak test helps identify minerals by observing their powdered form, as the streak color is more consistent than the mineral's surface color. It is especially useful for distinguishing between minerals with similar appearances.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Earth and Life Science Rewind 3 Physical and Chemical Properties of Minerals

Macroscopic Characteristics of Minerals Part 2: Cleavage and Hardness

Properties of Rock-forming Minerals
I minerali

SHS Earth and Life Science | Lesson 3: MINERALS

Rocks and Minerals for Kids - Compilation Video - Science for Kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
