Earth and Compasses | Magnetism | Physics | FuseSchool
Summary
TLDRThis video explores Earth's magnetic field, explaining how it functions as a giant magnet influencing compasses. It clarifies the distinction between geographic and magnetic poles and discusses the phenomenon of pole reversal, which has occurred multiple times in Earth's history. The video also highlights the crucial role of Earth's magnetism in protecting its atmosphere from solar wind, drawing a connection to Mars' thin atmosphere possibly due to a weakened magnetic field.
Takeaways
- 🧲 The Earth functions like a giant magnet, which is why compasses work.
- 🧭 Compasses use a freely spinning needle, which is a magnet attracted to the Earth's magnetic field.
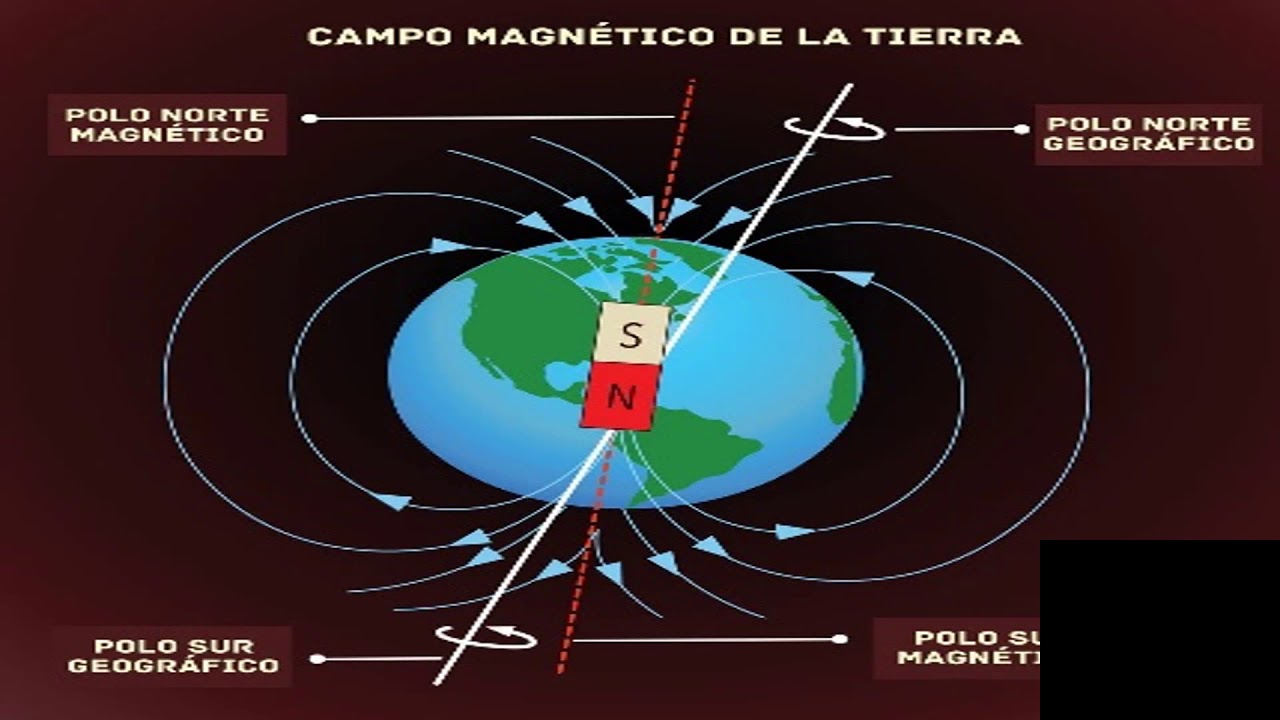
- 🌍 The Earth's geographic north pole is actually near the magnetic south pole.
- 🔄 Earth's magnetic poles can switch, meaning the magnetic north becomes the south and vice versa.
- 🌊 Evidence of magnetic pole reversals is found at the bottom of the ocean through solidified lava.
- 🔥 Geophysicists think Earth's magnetic field is generated by electric currents in its hot liquid metal core.
- 💨 Earth's magnetic field protects the planet from harmful solar wind, shielding the atmosphere.
- 🌌 Solar wind particles that penetrate the magnetic field create auroras, like the Northern Lights.
- 🚫 Without a magnetic field, Earth's atmosphere could be stripped away by solar wind, exposing the surface to harmful UV rays.
- 🪐 Mars might have lost its atmosphere due to a failure in its magnetic field, allowing solar wind to break it down.
Q & A
What is the primary reason compasses can show us the direction of north?
-Compasses can show us the direction of north because the Earth is a giant magnet, and the compass needle, which is also a magnet, aligns with the Earth's magnetic field.
How does the magnetic field of a magnet look like?
-The magnetic field of a magnet is shaped like lines extending from the magnet's north pole to the south pole, forming a loop that continues outside the magnet.
What is the relationship between the north pole of a compass and the Earth's magnetic field?
-The north pole of a compass is attracted to the south magnetic pole of the Earth, which is geographically the north pole but magnetically a south pole.
Why is there confusion between the geographic north pole and the magnetic north pole?
-There is confusion because the geographic north pole is determined by the Earth's rotation, while the magnetic north pole is determined by the direction a compass points, which is actually the south magnetic pole of the Earth.
How often do the Earth's magnetic poles switch?
-The Earth's magnetic poles have switched approximately every 200,000 to 300,000 years in the last 20 million years.
What evidence supports the occurrence of magnetic pole reversals?
-Evidence for magnetic pole reversals can be found in the bands of magnetization in the ocean floor, particularly on either side of the mid-Atlantic rift, where solidifying lava records the Earth's magnetic field at the time.
What role does the Earth's magnetic field play in protecting the Earth's atmosphere?
-The Earth's magnetic field protects the Earth's atmosphere from solar wind, which is a flow of charged particles from the sun. Without the magnetic field, the solar wind could strip away the atmosphere.
What phenomenon can be observed if some solar particles manage to bypass the Earth's magnetic field?
-If some solar particles bypass the Earth's magnetic field, they can cause the aurora, also known as the northern lights, which are natural light displays in the sky.
What is one theory about why Mars barely has an atmosphere?
-One theory suggests that if Mars' magnetic field was somehow switched off, its atmosphere would have been broken down by the solar wind.
How does the Earth's magnetic field relate to the concept of pole reversal?
-The Earth's magnetic field is related to pole reversal because the magnetic north and south poles can switch, causing the magnetic north to become the south and vice versa for a period of time.
What is the significance of the Earth being a giant magnet?
-The significance of the Earth being a giant magnet is that it influences the behavior of compasses, contributes to the protection of Earth's atmosphere from solar wind, and is responsible for natural phenomena like the aurora.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

KEMAGNETAN KELAS 9 part 2 - MEDAN MAGNET DAN MAGNET BUMI

Teori Dasar Kemagnetan - IPA Kelas 9 SMP

Earth's Magnetic Field | Earth Itself Is a Huge Magnet | Magnetosphere | Arbor Scientific
INFLUENCIA DEL CAMPO MAGNETICO DE LA TIERRA EN LOS SERES VIVOS

Magnets & Magnetism for kids

Magnets | Magnetism | Physics | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
