Il Neurone | NEUROSCIENZE - Lezione 2
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the intricacies of neuron structure and function, highlighting the role of dendrites in receiving signals, the soma (cell body) in processing these signals, and the axon in transmitting them to other cells or organs. It also introduces the concept of the myelin sheath, which insulates the axon, preventing signal loss, and the synaptic terminals that facilitate communication between neurons. The video concludes with a teaser about upcoming content on glial cells, inviting viewers to subscribe for more insights into the nervous system.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The nervous system is composed of two main types of cells: neurons and glial cells.
- 💫 Neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting nerve impulses.
- 🛡️ Glial cells, also known as neuroglia or simply glia, protect and support neurons and constitute a significant part of the brain's mass.
- 🌳 Neurons have unique physiological and chemical properties that allow them to receive, integrate, and transmit nerve impulses.
- 🔌 Neurons produce neurotransmitters, which are substances that facilitate the transmission of signals between neurons or to other types of cells.
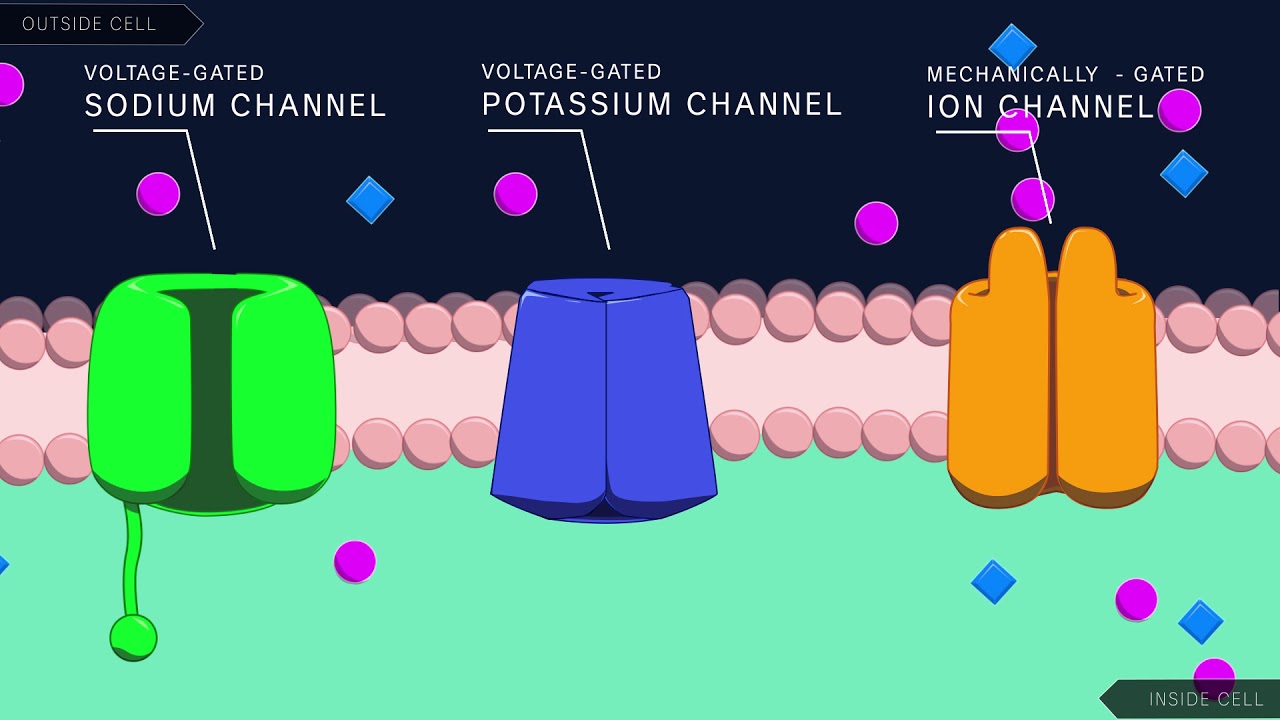
- 🌿 The neuron's structure includes dendrites, which receive signals, and an axon, which transmits the signal to other cells or organs.
- 📦 The cell body (soma) of a neuron contains the nucleus and organelles necessary for basic cellular functions.
- 🧱 The myelin sheath, a fatty insulating layer, wraps around the axon to prevent the dispersion of electrical signals, similar to rubber insulation on electrical wires.
- 🔗 Synaptic terminals are points where neurons interact with other neurons or effector cells, such as muscles or glands.
- 🔎 Neurons can be classified by their morphology into unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar types, each serving different functions in signal transmission.
- 🔄 The signal transmission in neurons involves the reception of stimuli, processing within the cell body, and the relay of the signal via the axon to other cells or organs.
Q & A
What are the two main types of cells that make up the nervous system?
-The two main types of cells that make up the nervous system are neurons and glial cells (also known as neuroglia or simply glia).
What is the primary function of neurons?
-Neurons serve as the structural and functional units of the nervous system, responsible for receiving, integrating, and transmitting nerve impulses.
What is the role of glial cells in the nervous system?
-Glial cells protect and support neurons, provide nutrients, and constitute a significant part of the brain and nervous system's mass.
What is a dendrite and how does it function in a neuron?
-Dendrites are cytoplasmic extensions of a neuron that function to receive signals, allowing the nerve impulse to be transmitted to the neuron.
What is the axon and its significance in the transmission of nerve impulses?
-The axon is a long cellular extension responsible for transmitting the nerve impulse to the next cell or to an effector organ, such as a muscle or gland.
What is the myelin sheath and its role in the nervous system?
-The myelin sheath is a protective covering around the axon, similar to insulation around an electrical cable, that prevents the dispersion of the electrical signal, ensuring efficient transmission of the nerve impulse.
What are synaptic terminals and how do they interact with other neurons?
-Synaptic terminals are specialized points at the end of an axon that allow a neuron to interact with another neuron or an effector organ. They contain neurotransmitters that facilitate signal transmission between neurons.
How can neurons be classified based on their morphology?
-Neurons can be classified based on their morphology into unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar neurons. Unipolar neurons have a single long axon and no dendrites, bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite, and multipolar neurons have multiple dendrites and one axon.
What is a synapse and its importance in the nervous system?
-A synapse is the junction between two neurons (or between a neuron and an effector organ) where the transmission of signals occurs. It is crucial for the communication and integration of information within the nervous system.
How does the neuron's structure facilitate its function in signal transmission?
-The neuron's structure, with its dendrites for receiving signals, a cell body for integrating these signals, and an axon for transmitting the signal, is specifically designed to efficiently receive, process, and relay nerve impulses throughout the nervous system.
What is the significance of the neuron's ability to produce neurotransmitters?
-Neurons' ability to produce neurotransmitters is essential for signal transmission between neurons at the synapse. These chemical messengers cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptors on the next neuron, continuing the signal transmission.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)