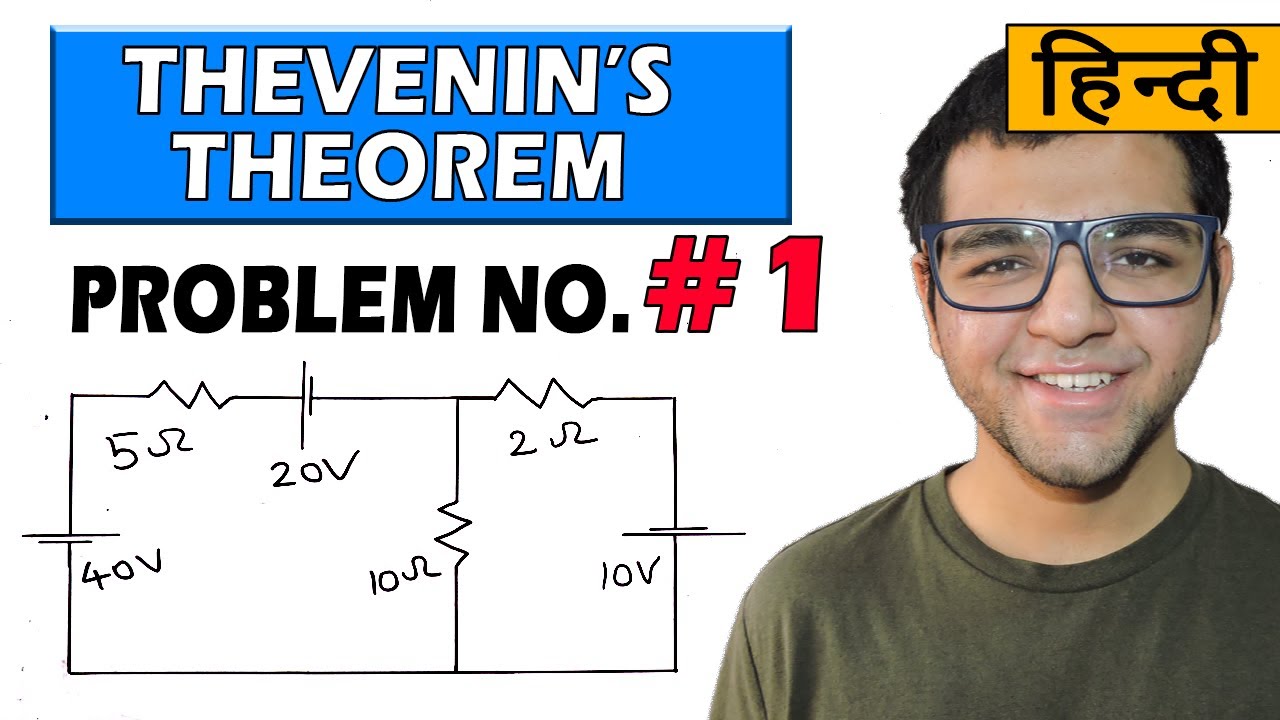
Pembahasan Soal Alat Ukur dan Daya Listrik sederhana
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses various electrical concepts through calculations and diagrams. It explains how to measure current using a scale and calculates resistance using Ohm's law with a voltmeter and ammeter. The script also covers calculating power and energy consumption of a 60W light bulb at different voltages and durations, and determines the required length of a heating wire based on its resistance and voltage. It's a comprehensive tutorial on basic electrical principles and calculations.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The script discusses the calculation of electric current using a scale, where the measured current is 1/3 ampere based on the given scale.
- 🔌 It explains the use of a voltmeter and an ammeter to measure resistance (Rx), with the voltmeter having a resistance of 1 kilo Ohm and the ammeter having a resistance of 1 Ohm.
- ⚡ The calculation of Rx involves using Ohm's law (V = IR), where V is the voltage across the resistor, I is the current through the resistor, and R is the resistance.
- 💡 The script covers the concept of power in electrical circuits, including the calculation of power (P) and energy (E) for a light bulb with a rated power of 60 watts and a voltage of 220 volts.
- 🕒 The energy consumption of the light bulb is calculated over a period of 30 minutes, taking into account the power rating and the time it is used.
- 🔥 The script also discusses the power rating of a heating device and how it relates to the resistance and voltage of the wire used.
- ⏱ The calculation of the required length of wire for the heating device is based on the resistance per meter of the wire and the desired power output.
- 📏 The resistance of the wire is considered constant, and the voltage used is 125 volts, which is used to determine the necessary wire length.
- 📐 The script provides a step-by-step approach to solving electrical problems, including the use of Ohm's law and Kirchhoff's current law.
- 📋 The final calculations involve simplifying and solving equations to find the unknown variables such as the resistance (Rx) and the length of the wire needed for the heating device.
Q & A
What is the measured current if the scale reads 30 on a maximum scale of 90 with a maximum current of 1 ampere?
-The measured current is 1/3 ampere, calculated by dividing the scale reading (30) by the maximum scale (90) and then multiplying by the maximum current (1 ampere).
What is the resistance (Rx) measured by the voltmeter and ammeter when the voltmeter reads 5 volts and the ammeter reads 25 milliamperes?
-The resistance (Rx) is calculated using Ohm's law, V = I * Rx, where V is 5 volts and I is the total current which is 25 milliamperes (0.025 amperes). The calculated resistance is 5 volts / 0.025 amperes, which equals 200 ohms.
How do you calculate the total current flowing through the circuit when the ammeter reads 25 milliamperes and there's a known current分流 through another path?
-To find the total current, you use Kirchhoff's current law which states that the total current entering a junction is equal to the total current leaving the junction. If the分流 current is known, you add it to the ammeter reading (25 milliamperes) to get the total current.
What is the power consumption of a 60-watt light bulb when connected to a 220-volt supply for 30 minutes?
-The power consumption is calculated by multiplying the power rating of the bulb (60 watts) by the time it is on (30 minutes converted to hours, which is 0.5 hours). So, the energy consumed is 60 watts * 0.5 hours = 30 watt-hours.
How do you determine the resistance of a filament in a light bulb if it's rated for 60 watts at 220 volts?
-Using the formula P = V^2 / R, where P is power, V is voltage, and R is resistance. Rearranging to solve for R gives R = V^2 / P. Substituting the given values (V = 220 volts, P = 60 watts) gives R = 220^2 / 60, which equals approximately 807.67 ohms.
What is the required length of wire for a 200-watt heating element with a resistance of 25 ohms per meter when used at a voltage of 125 volts?
-Using the formula R = (V^2 / P) * L, where R is the resistance per meter, V is the voltage, and P is the power. Rearranging to solve for L gives L = (P / (V^2 / R)). Substituting the given values (P = 200 watts, V = 125 volts, R = 25 ohms) gives L = (200 / (125^2 / 25)), which equals approximately 1.6 meters.
How do you calculate the resistance of a wire if the power rating and voltage are known?
-The resistance can be found using the formula R = V^2 / P, where V is the voltage and P is the power rating. This formula is derived from the power formula P = V * I, where I is the current, and Ohm's law V = I * R.
What is the energy consumption in kilojoules of a 15-watt device running for 30 minutes?
-First, convert the power to watt-minutes (15 watts * 30 minutes = 450 watt-minutes). Then, convert watt-minutes to kilojoules (450 watt-minutes / 60 = 7.5 kilojoules, since 1 watt-minute equals 1/60th of a kilojoule).
How do you find the total resistance in a parallel circuit when the individual resistances and the voltage across the circuit are known?
-In a parallel circuit, the total resistance (Rt) can be found using the formula 1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... + 1/Rn, where R1, R2, ..., Rn are the individual resistances. If the voltage is known, you can also calculate the current through each resistor and then use the above formula.
What is the formula to calculate the power consumption of an electrical device?
-The power consumption (P) of an electrical device is calculated using the formula P = V * I, where V is the voltage and I is the current. Alternatively, if the resistance (R) is known, it can also be calculated using P = V^2 / R or P = I^2 * R.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)