Evaporator Coil! How it Works- Refrigerant Flow, Phase Change, Saturation Point, Superheat, Tips!
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the presenter from A/C Service Tech explains the function of a vertical evaporator coil in an HVAC system. The script covers the process of air movement, the role of the thermostatic expansion valve in controlling refrigerant flow, and the importance of maintaining superheat to ensure efficient operation. It also discusses potential issues like insufficient airflow and coil freezing, emphasizing the need for proper system maintenance and correct air flow settings.
Takeaways
- 🌀 The evaporator coil is a crucial component of an air conditioning system, functioning to absorb heat and maintain temperature within a building.
- 💧 The coil operates by attracting humidity to its fins, which then drips into a condensate pan and is drained away.
- 📍 The coil can be configured for vertical or downflow operation, depending on how air is directed through it.
- 🔄 High-pressure, high-temperature liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator coil through the liquid line and is regulated by a thermostatic expansion valve (TXV).
- 🌡 The TXV controls the refrigerant flow, ensuring a balance of 20% flash gas and 80% liquid, which is crucial for efficient heat absorption.
- 🔆 As the refrigerant travels through the coil, it absorbs heat, transitioning from a liquid state to a saturated state and eventually to vapor.
- ♨️ The top part of the coil is where the refrigerant turns into complete vapor and begins to superheat, increasing in temperature above the saturation point.
- 🛠 Insufficient airflow across the coil can lead to issues such as freezing, highlighting the importance of proper air circulation for coil performance.
- 🔍 To ensure optimal performance, it's essential to check for adequate air flow, clean filters, and appropriate settings for the blower motor.
- ⚖️ The thermostatic expansion valve plays a key role in maintaining a superheat of 14 degrees, which is vital for the system's efficiency and proper refrigerant charging.
Q & A
What is the primary function of an evaporator coil?
-The primary function of an evaporator coil is to absorb heat from within the building, maintaining the desired temperature by cooling the air that passes over it.
How does the air flow direction vary in a vertical evaporator coil?
-In a vertical evaporator coil, the air can flow in from the bottom and come out through the sides and the top, or it can be used as a downflow where air comes down, passes through the coil, and goes out beneath.
What happens to the humidity when it comes into contact with the evaporator coil?
-The humidity gets attracted to the fins of the evaporator coil and then drips down into the condensate pan.
What are the two main lines that supply the evaporator coil with refrigerant?
-The two main lines that supply the evaporator coil with refrigerant are the suction line and the liquid line.
What is the role of the thermostatic expansion valve in the evaporator coil?
-The thermostatic expansion valve controls the flow of high-pressure, high-temperature liquid refrigerant into the evaporator coil, ensuring it turns into a mixture of 20% flash gas and 80% liquid.
How does the refrigerant change as it moves through the evaporator coil?
-As the refrigerant moves through the evaporator coil, it absorbs heat, transitioning from a liquid state to a saturated state, and finally turning into a complete vapor.
What is superheat and why is it important in the evaporator coil?
-Superheat is the temperature increase above the saturation point after the refrigerant has turned into a vapor. It is important because it indicates the efficiency of the refrigerant's heat absorption and helps maintain the proper functioning of the HVAC system.
How does the thermostatic expansion valve maintain superheat?
-The thermostatic expansion valve maintains superheat by regulating the amount of refrigerant entering the coil, aiming to keep a consistent 14 degrees of superheat.
What should be checked before assessing the refrigerant charge in an evaporator coil?
-Before assessing the refrigerant charge, one should check that the air filter is clean, there is good airflow from the registers, and the blower motor is set to the capacity that matches the TXV and outdoor condensing unit.
What happens if there is not enough airflow across the evaporator coil?
-If there is not enough airflow across the evaporator coil, it can start to freeze as it won't be able to absorb heat effectively, leading to a continuous drop in temperature until it turns into an ice cube.
How does the size of the blower motor affect the airflow across the evaporator coil?
-The size of the blower motor affects the airflow across the evaporator coil by determining the CFM (cubic feet per minute) value. A larger blower motor can provide more airflow, which may require adjusting the airflow to match the capacity of the TXV and outdoor condenser.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Explaining Superheat and Subcooling to Your Apprentice!
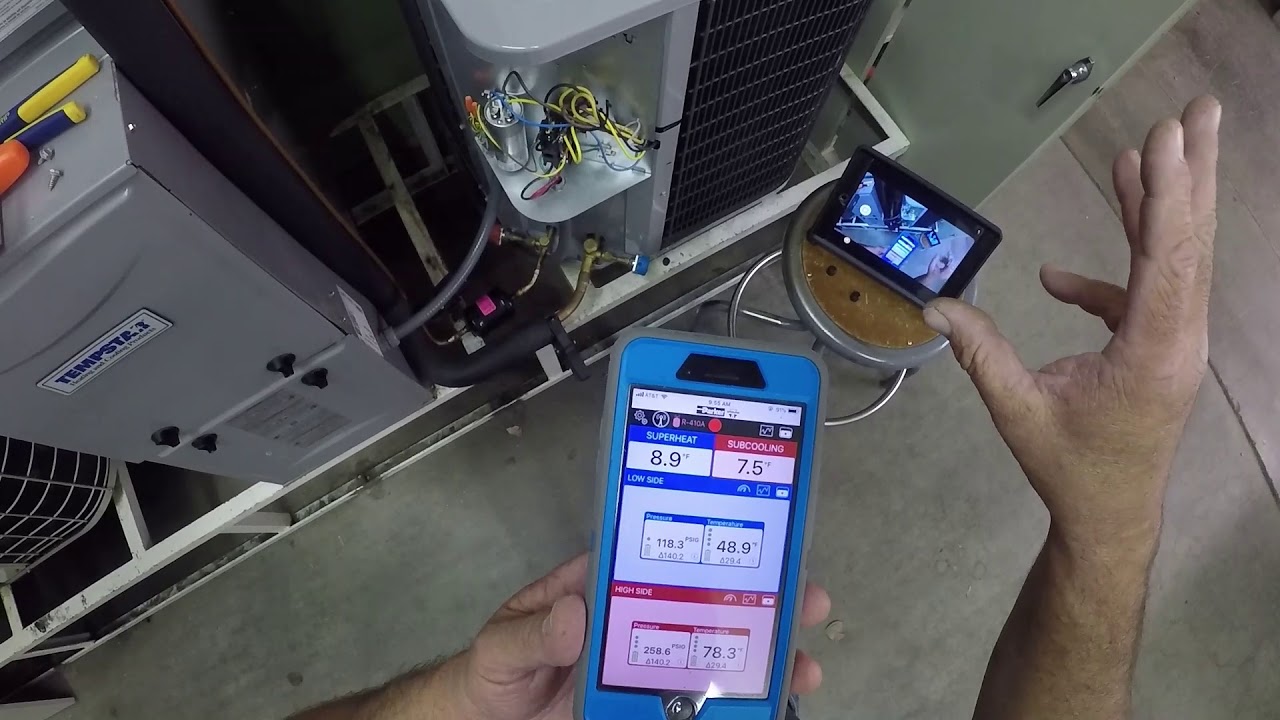

TXV HVAC System Refrigerant Charge Check with Sporlan Digital Gage

#Refrigerasi- 001Evaporator

How Air Flows Through the HVAC System of an automobile?

Belajar sirkulasi freon AC untuk pemula agar bisa servis atau perbaiki AC
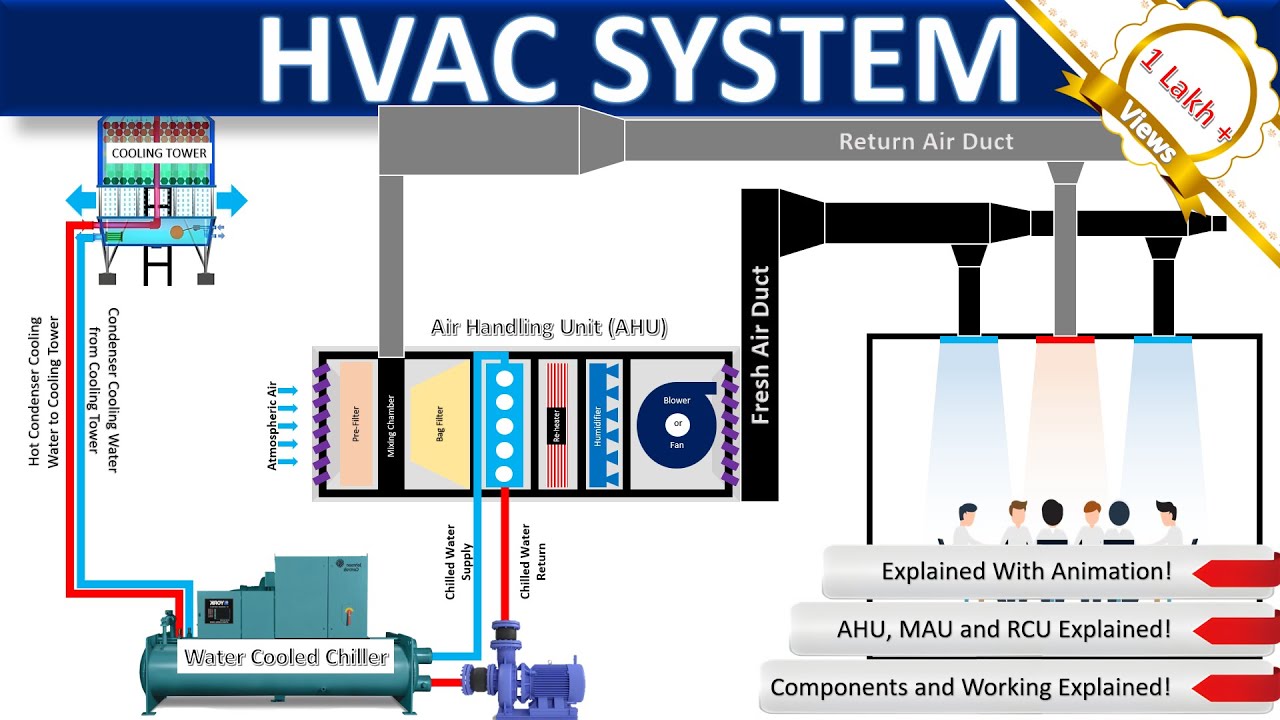
HVAC Systems : Understanding Components and Functionality | Mr. Smart Explains!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
