What do central banks do?
Summary
TLDRCentral banks worldwide manage monetary policy to achieve a balanced economy, controlling inflation and promoting employment. They adjust interest rates and act as lenders of last resort. In scenarios with near-zero interest rates, unconventional measures like quantitative easing are employed to stimulate the economy. Despite their pivotal role, post-2008 financial crisis, some question their efficacy, with experts like Andrew Haldane suggesting a potential paradigm shift in central banking.
Takeaways
- 🏛️ There are over 160 central banks globally, with roles that have evolved over time.
- 📉 Their primary duties include implementing monetary policy to ensure employment, currency stability, and controlled inflation.
- 🌡️ Central banks aim for a 'Goldilocks economy', maintaining a balance between economic growth and inflation.
- 📈 They manage interest rates, reserve requirements, and act as lenders of last resort to the banking sector.
- 💼 They oversee the nation's money supply, foreign exchange, gold reserves, and the government's stock register.
- 📉 In times of high inflation, they raise interest rates to slow growth and lower inflation.
- 📈 Conversely, they lower rates to stimulate growth during economic slowdowns.
- 💸 When traditional interest rate adjustments are ineffective, central banks may resort to quantitative easing (QE).
- 💵 QE involves creating money to buy bonds, increasing financial system liquidity to encourage lending and spending.
- 🌪️ After the 2007-2008 financial crisis, central banks' ability to stimulate economic growth has been questioned.
- 🤔 Some economists argue that central banks' roles in financial stability lack democratic accountability and political legitimacy.
Q & A
What is the primary role of central banks?
-Central banks primarily implement monetary policy to provide employment, currency stability, and controlled inflation.
What is the 'Goldilocks economy' referred to in the script?
-The 'Goldilocks economy' is a term used to describe an economy that is neither too hot (inflationary) nor too cold (deflationary), but just right for sustained growth.
How do central banks manage interest rates to influence the economy?
-Central banks raise interest rates to slow growth and lower inflation, and lower rates to boost growth.
What is quantitative easing (QE), and how does it work?
-Quantitative easing is a process where central banks inject money into the financial system by buying bonds with newly printed money, increasing the money supply and encouraging lending.
What other responsibilities do central banks have besides managing interest rates?
-Central banks are also responsible for controlling the nation's money supply, managing foreign exchange and gold reserves, and overseeing the government's stock register.
How have central banks responded to situations where interest rates are near zero?
-In situations with near-zero interest rates, central banks have adopted tactics like quantitative easing to stimulate the economy.
What challenges have central banks faced since the 2007-2008 financial crisis?
-After the financial crisis, central banks have faced challenges in boosting economic growth, leading to questions about their effectiveness and role.
What does Andrew Haldane suggest about the future of central banking?
-Andrew Haldane suggests that the traditional methods of central banks, such as adjusting interest rates, may no longer be effective.
What concerns does Willem Buiter express about the role of central banks?
-Willem Buiter argues that central banks, as custodians of financial market stability, lack democratic accountability and political legitimacy.
What does Mohamed El-Erian predict about the effectiveness of central bank policies?
-Mohamed El-Erian predicts that central banks are nearing a point where their policy approaches will become increasingly ineffective.
What is the current status of central banks in overseeing the monetary system?
-Despite challenges and questions about their effectiveness, central banks remain responsible for overseeing the monetary system for a nation or a group of nations, like the ECB.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Pengantar Ekonomi Makro - Pengaruh Kebijakan Moneter dan Fiskal terhadap Permintaan Agregat
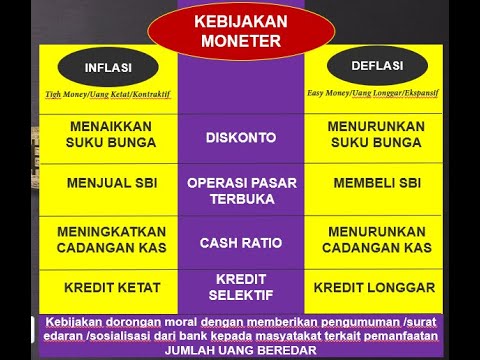
KEBIJAKAN MONETER

What is the purpose of the central banks? (May 2013)

SO SÁNH CHÍNH SÁCH TÀI KHÓA VÀ CHÍNH SÁCH TIỀN TỆ

Monetary and fiscal policy | Aggregate demand and aggregate supply | Macroeconomics | Khan Academy

Monetary Policy explained
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
