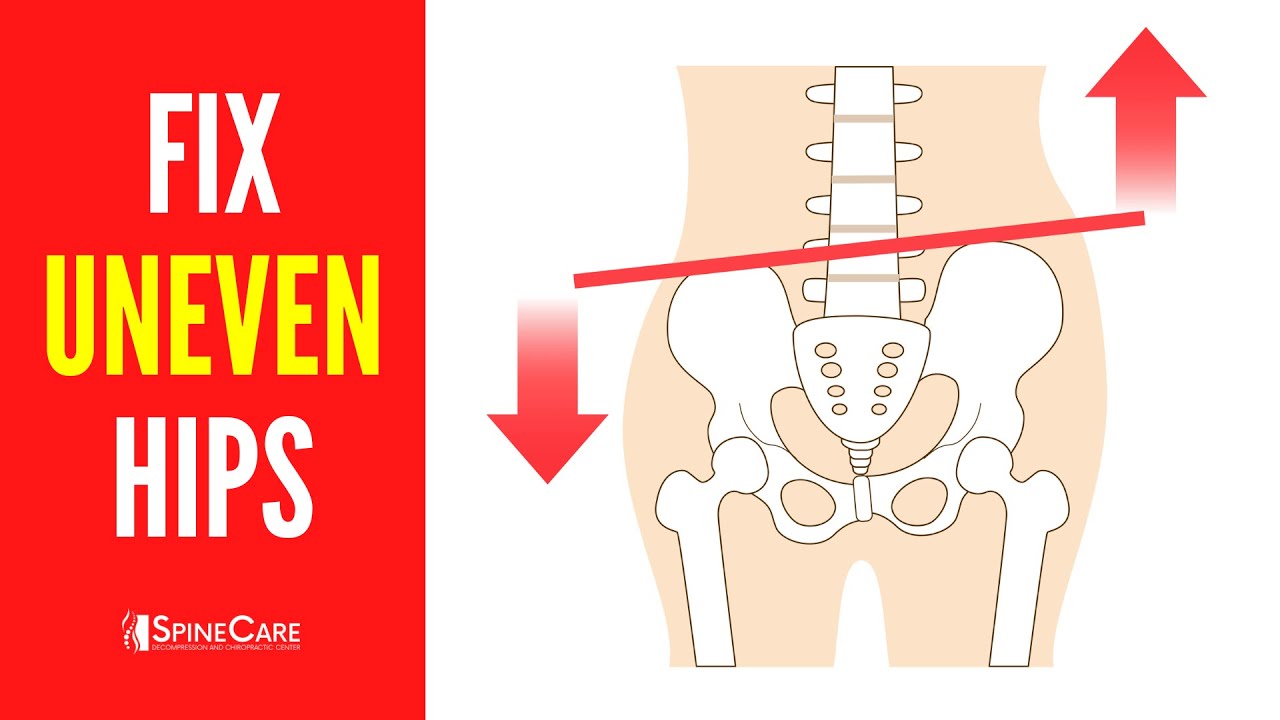
How To Unf*ck Your Hips In 10 Minutes | Corrective Routine
Summary
TLDRThe video explores hip asymmetry, a condition where one hip might be higher than the other due to structural or muscular imbalances. The host explains three tests to identify hip asymmetry and provides a corrective exercise routine focused on mobility and strengthening to restore balance and alleviate discomfort. The video emphasizes the importance of addressing asymmetries to prevent pain and enhance overall movement quality. It concludes with a call to action for viewers to incorporate the exercises into their routine and monitor progress for lasting results.
Takeaways
- 🔄 Hip asymmetry can occur due to muscular imbalances or the way you're built, such as having one leg longer than the other.
- 🤔 Various asymmetries in the body are normal, but they can become problematic if they cause pain or affect movement.
- 🧍♂️ Test 1 involves checking hip height by comparing the level of your hands when placed on your hip bones in front of a mirror.
- 📉 Test 2 is the Trendelenburg test, where a drop in the pelvis while standing on one leg indicates weak hip stabilizers.
- 🦵 Test 3 assesses hip symmetry during squats by checking if your hips rise symmetrically from the bottom of the squat.
- 🧘♂️ Step 1 of the corrective routine focuses on mobility, including exercises like the 90/90 drill to improve hip rotation.
- 💪 Step 2 emphasizes strengthening, starting with exercises like the hip drop and sideline hip abduction to target weak hip muscles.
- 🏋️♂️ Progress to more advanced exercises like hip airplanes and RNT squats to further improve hip stability and symmetry.
- ⏳ Perform the corrective routine two to three times a week, incorporating mobility and strengthening exercises in sequence.
- 🔄 Retest your hip balance periodically to monitor improvement and incorporate these exercises into your weekly routine for long-term results.
Q & A
What is hip asymmetry, and how does it typically occur?
-Hip asymmetry refers to an imbalance in the alignment or function of the hips, which can cause one hip to be higher or function differently than the other. It typically occurs due to muscular imbalances developed from repetitive tasks, lifting, or even sitting in certain ways. In some cases, it may also be due to structural differences, such as one leg being longer than the other.
Is hip asymmetry always problematic?
-No, various asymmetries in the body are expected and perfectly normal. However, hip asymmetry becomes problematic when it causes pain, discomfort, or affects your movement patterns, such as during squats or standing.
What is the first test to check for hip asymmetry, and how is it performed?
-The first test is a static assessment where you stand in front of a mirror and palpate the top of your hip bones. With your hands flat to the floor, compare their level. If one hand sits higher than the other, you may have unevenness in hip height. This test helps identify static asymmetry, but it might not reveal dynamic imbalances.
What does a positive Trendelenburg test indicate?
-A positive Trendelenburg test, where the pelvis of the raised leg drops and the trunk flexes towards the planted leg, indicates weakness in the gluteus medius muscle of the grounded leg. This muscle is responsible for stabilizing the pelvis during single-leg stance.
Why might someone shift to one side when squatting?
-A person might shift to one side when squatting due to strength imbalances, where they favor their stronger hip. It can also be caused by a mobility imbalance, specifically in hip external rotation, leading to a side-to-side shift.
What are the two steps in the corrective program for hip asymmetry?
-The corrective program involves two steps: (1) Mobility exercises, which focus on improving the range of motion in the hips, and (2) Strengthening exercises, which target the weak muscles to restore balance and prevent future imbalances.
How does the 90/90 drill help with hip mobility?
-The 90/90 drill helps with hip mobility by opening up the hips and improving external rotation. It involves sitting with one leg bent in front of you and transitioning from one side to the other while keeping the torso stacked over the hips.
What is the purpose of the 'teapot' exercise?
-The 'teapot' exercise is designed to mobilize the quadratus lumborum (QL) and tensor fasciae latae (TFL) muscles, which can cause the hip to be elevated or depressed if they are tight. It involves bending away from the target side to stretch these muscles.
What are the level 1 strengthening exercises for correcting hip asymmetry?
-The level 1 strengthening exercises include the hip drop, which targets the gluteus medius isometrically, and the sideline hip abduction, which focuses on engaging the gluteus medius by raising the leg slightly backwards while lying on your side.
When and how often should the corrective routine be performed?
-The corrective routine should be performed at least two to three times a week. It can be done at any time of the day or as part of a warm-up routine before a lower body workout. Consistent practice helps improve and maintain hip balance over time.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)