Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Net Charge
Summary
TLDRThis educational script introduces the fundamental characteristics of atoms, focusing on atomic number (Z), mass number (A), and net charge. The atomic number, denoted by Z, represents the count of protons in an atom's nucleus, which determines the element type. The mass number, indicated by A, is the sum of protons and neutrons, though the neutron count is not individually named. The net charge, a complex concept, is the balance between protons and electrons, resulting in neutral atoms or ions with positive or negative charges. The script aims to clarify these concepts, using diagrams and examples to illustrate how atoms can be neutral or charged based on the electron-proton balance.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and is crucial for identifying the type of atom.
- 🔡 The atomic number is often abbreviated with a capital 'Z' and is represented by red circles in the provided diagram.
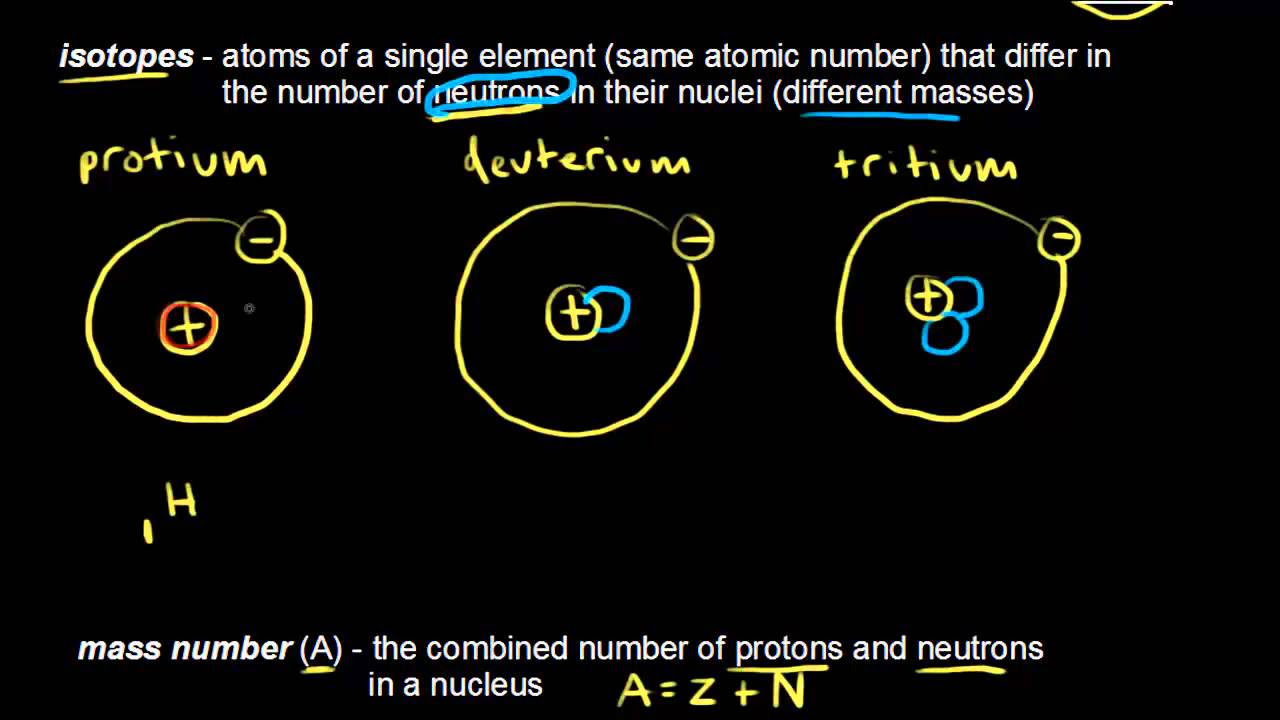
- 🧬 The mass number (A) is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the atom's nucleus, not just the number of neutrons.
- 📊 The mass number is often abbreviated with an uppercase 'A' and helps distinguish between isotopes of the same element.
- ⚖️ Net charge is the balance between the number of protons and electrons in an atom, determining if it's neutral or an ion.
- 🔋 If the number of protons and electrons are equal, the atom is neutral with a net charge of zero.
- ⚡ An atom with more protons than electrons has a positive net charge and is called a cation.
- ⚛ An atom with more electrons than protons has a negative net charge and is called an anion.
- 🌐 The presence of a net charge on an atom classifies it as an ion, regardless of whether the charge is positive or negative.
- 📚 Understanding these characteristics is fundamental to grasping concepts such as isotopes, which will be discussed in a subsequent video.
- 📘 The script uses a simple diagram to illustrate the concepts, making the complex nature of atomic structure more accessible.
Q & A
What is the atomic number and how is it represented?
-The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, and it is often abbreviated by a capital letter Z.
Why is the atomic number important when describing an atom?
-The atomic number is important because it identifies the type of atom, such as carbon, oxygen, or sodium.
What is the mass number and how does it differ from the atomic number?
-The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom, often abbreviated by an uppercase A. It differs from the atomic number, which only counts protons.
How is the number of neutrons in an atom typically referred to?
-There isn't a specific term for the number of neutrons; it is simply referred to as 'the number of neutrons' and is not used as frequently as other atomic properties.
What does the term 'net charge' refer to in the context of atoms?
-Net charge refers to how the number of protons and electrons balance each other out in an atom.
How does the balance of protons and electrons determine the net charge of an atom?
-If the number of protons and electrons is the same, the atom is neutral with a net charge of zero. If there are more protons, the net charge is positive, and if there are more electrons, the net charge is negative.
What is an ion and how does it relate to the net charge of an atom?
-An ion is any atom that has a net charge. It is formed when the number of protons and electrons do not balance each other out, resulting in either a positive or negative net charge.
What happens if an atom has one more proton than electrons?
-If an atom has one more proton than electrons, it will have a net positive charge, making it a positively charged ion.
Can an atom have a net charge of minus 2 as described in the script?
-Yes, if an atom has two more electrons than protons, it will have a net negative charge of minus 2, making it a negatively charged ion.
How many electrons and protons does the example atom in the script have, and what is its net charge?
-The example atom in the script has three protons and four electrons, resulting in a net negative charge of minus 1.
What is the purpose of discussing these atomic characteristics in the script?
-The purpose is to provide a foundation for understanding how to describe atoms and to introduce the concepts that will be further explored in the video on Isotopes.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

3.3 Counting Atoms (2/2)

Nomor Atom dan Nomor Massa // Kimia

Struktur Atom (4) | Apa itu isotop, isoton, dan isobar? | Kimia Kelas 10

Struktur Atom | Elektron Proton Neutron | Notasi Atom | No Massa | Isotop Isobar Isoton Isoelektron
Atomic number, mass number, and isotopes | Chemistry | Khan Academy

مسابقة موهوب - (علوم الكيمياء): البنية الذرية
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
