Moral Development by Lawrence Kohlberg Final
Summary
TLDRThis video explores Lawrence Kohlberg's theory of moral development, which outlines three levels and six stages of moral reasoning from infancy to maturity. Kohlberg's stages range from preconventional (obedience and self-interest) to postconventional (universal ethical principles), highlighting the importance of empathy, critical thinking, and moral dialogue. The video also addresses critiques of the theory, including potential biases and the gap between moral reasoning and behavior, emphasizing the theory's enduring influence on moral psychology.
Takeaways
- 📚 Moral development is the process by which individuals distinguish between right and wrong and internalize moral values, influenced by various factors including socialization and cognitive growth.
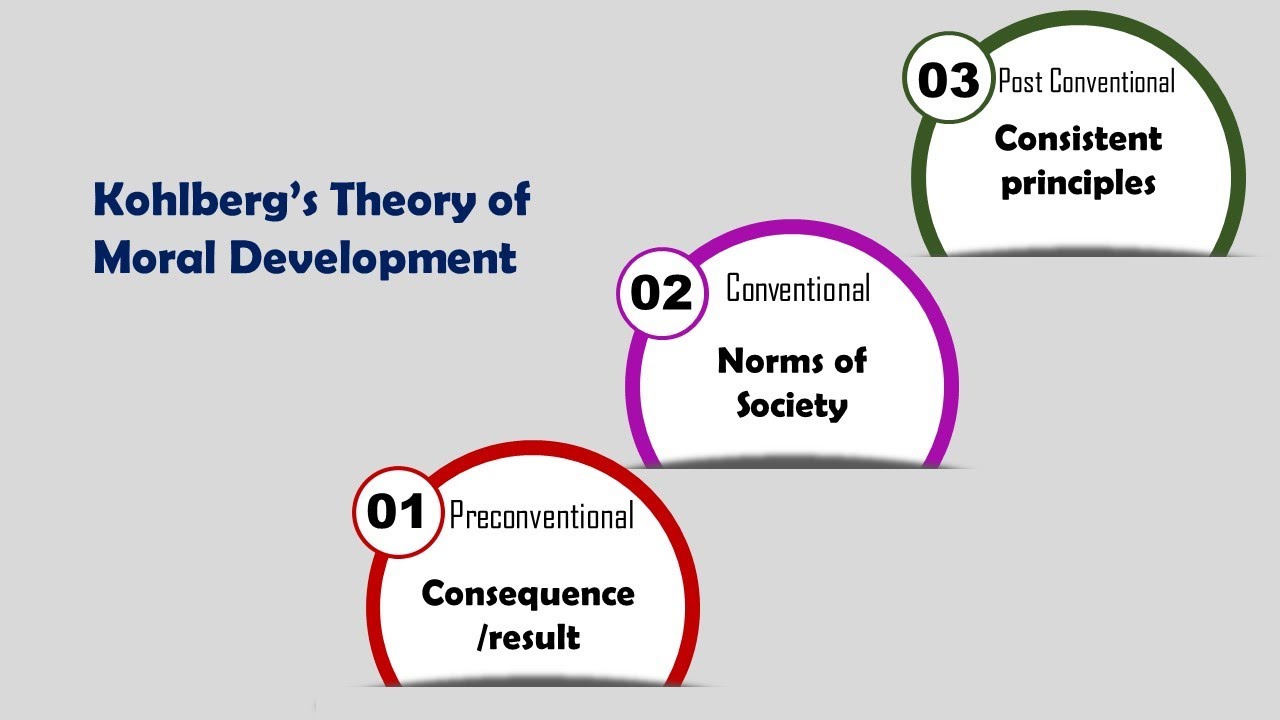
- 🧑🏫 Lawrence Kohlberg's theory of moral development is a fundamental concept in understanding morality, focusing on how people resolve moral dilemmas and change ethically over time.
- 👶 Kohlberg's theory is based on stages of moral reasoning, starting with preconventional morality where children's decisions are influenced by adult expectations and rule consequences.
- 🤝 The conventional level of morality involves acceptance of social rules and norms, emphasizing conformity and maintaining social order through adherence to authority and laws.
- 🌐 Postconventional morality is characterized by understanding abstract principles of morality, where individuals follow internalized principles of justice, even if they conflict with societal rules.
- 🔍 Kohlberg used moral dilemmas and storytelling to gather data on moral reasoning, highlighting the importance of the reasoning process over the actual decision made.
- 🔑 Dissonance and exposure to diverse viewpoints are crucial for moral development, as they prompt individuals to progress through Kohlberg's stages of moral reasoning.
- 🤔 Self-reflection, critical thinking, empathy, and ethical decision-making are key aspects of moral development that Kohlberg's theory encourages for personal growth.
- 👥 The role of mentors and role models is emphasized in moral development, providing guidance and positive examples for individuals to learn from.
- 💬 Engaging in moral dialogue helps in exploring different perspectives and broadening understanding of complex ethical issues, furthering moral development.
- ⚖️ While influential, Kohlberg's theory has been critiqued for not equating moral reasoning with behavior, overemphasizing justice, and potential cultural and gender biases.
Q & A
What is moral development?
-Moral development is the process by which people develop the distinction between right and wrong, known as morality, and engage in justifying between the two. It is a gradual process through which individuals acquire and internalize moral values, beliefs, and behaviors.
Who is Lawrence Kohlberg and what is his contribution to the study of moral development?
-Lawrence Kohlberg was an American psychologist who created one of the most well-known theories on moral development. His theory provides insights into the process by which people resolve moral conundrums and change ethically over time.
What are the three levels of moral reasoning identified by Kohlberg?
-The three levels of moral reasoning identified by Kohlberg are preconventional, conventional, and postconventional, each with two substages, reflecting different stages of moral reasoning from infancy to maturity.
What is the significance of the 'Heinz dilemma' in Kohlberg's research?
-The 'Heinz dilemma' is a moral dilemma used by Kohlberg to gather data on moral reasoning. It involves a man who considers stealing a drug to save his wife's life. Kohlberg was interested in the reasons behind the decisions of his subjects rather than the decisions themselves.
What are the two stages of preconventional morality according to Kohlberg?
-The two stages of preconventional morality are obedience and punishment, where individuals view rules as unchangeable to avoid punishment, and individualism and exchange, where actions are judged based on how they serve individual needs.
What does the conventional level of moral development signify?
-The conventional level of moral development signifies the acceptance of social rules regarding what is good and moral. It focuses on living up to social expectations and roles, and maintaining social order by following rules and respecting authority.
What are the two stages of postconventional morality?
-The two stages of postconventional morality are social contract and individual rights, where people begin to account for differing values and beliefs, and universal principles, where individuals follow internalized principles of justice even if they conflict with laws and rules.
How does Kohlberg's theory emphasize the role of empathy and perspective taking in moral development?
-Kohlberg's theory highlights the importance of empathy and perspective taking by suggesting that individuals can deepen their understanding of moral issues and develop a greater sense of compassion by considering the viewpoints and experiences of others.
What are some criticisms of Kohlberg's theory of moral development?
-Criticisms of Kohlberg's theory include the disconnection between moral reasoning and actual behavior, an overemphasis on the concept of justice, potential cultural bias favoring individualist cultures, age bias as most subjects were under 16, and gender bias as all subjects in his sample were male.
How can Kohlberg's theory be applied to personal moral maturation?
-Kohlberg's theory can guide personal moral maturation by encouraging self-reflection on one's moral beliefs and values, practicing critical thinking in moral decision-making, developing empathy and perspective taking, and seeking guidance from mentors and engaging in moral dialogue.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Kohlberg’s Six Stages of Moral Development (Kohlberg’s Theory of Moral Development)

Human Reasoning: Analyzing Piaget's and Kohlberg's Theories via the Heinz Dilemma #3

Kohlberg's Stages of Moral Development

Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development Explained!
Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development (Moral Dilemmas)

Kohlberg moral development | Individuals and Society | MCAT | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
