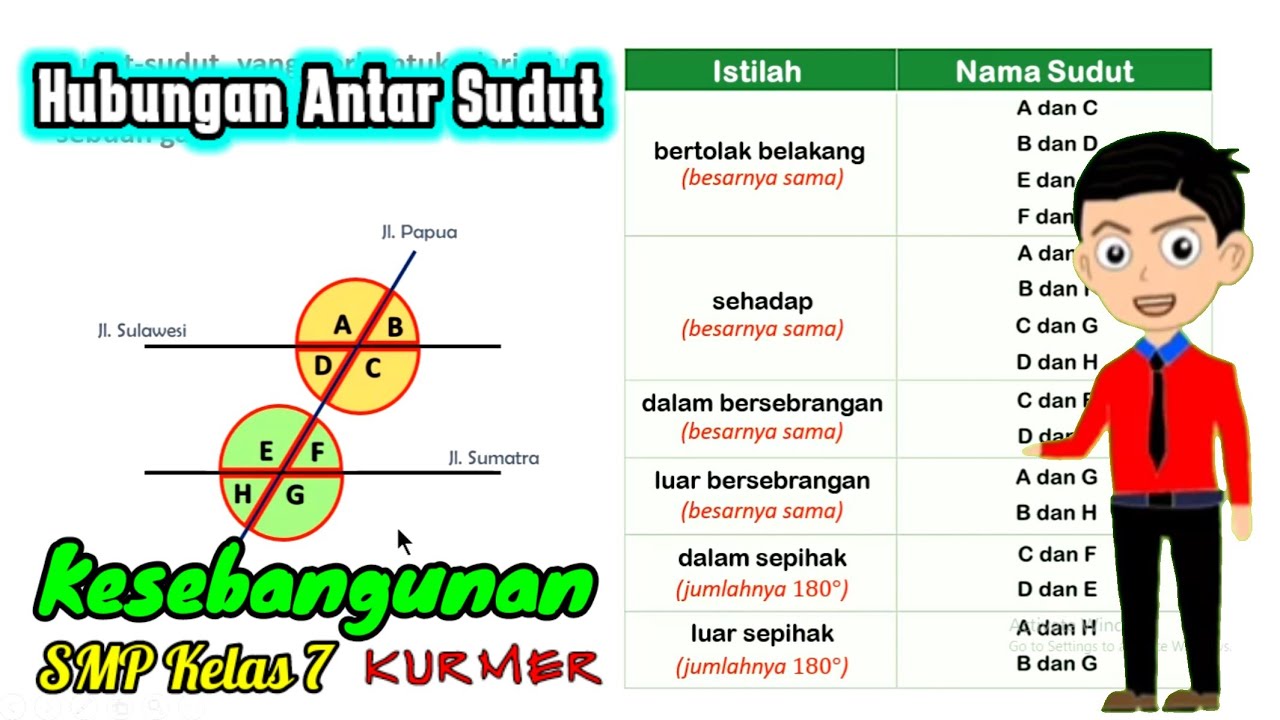
Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the concepts of complementary and supplementary angles, explaining that complementary angles sum to 90 degrees while supplementary angles total 180 degrees. Using a right triangle as an example, the script illustrates these concepts and guides viewers through various practice problems, including finding supplements and complements of given angles, and solving for unknown angles based on their relationships. The script also covers a challenge problem involving the relationship between an angle's supplement and complement, providing a step-by-step solution to engage and educate viewers on these fundamental geometric principles.
Takeaways
- 📐 Complementary angles are two angles that add up to 90 degrees.
- 🔍 In a right triangle, the two non-right angles are always complementary to each other.
- 🌐 Supplementary angles are pairs of angles that add up to 180 degrees.
- 📉 To find the supplement of an angle, subtract the angle from 180 degrees.
- 📈 To find the complement of an angle in degrees, minutes, and seconds (DMS), convert 90 degrees to DMS and subtract the given angle.
- 🤔 If one angle is larger than the other by a certain degree, you can set up an equation to find the measure of both angles.
- 📝 When two angles are in a ratio, you can express each angle in terms of a variable and solve for the ratio to find their measures.
- 🔢 For angles in a ratio, dividing the sum of the angles by the sum of the ratio parts will give you the value of one part.
- 🧩 If one supplementary angle is a certain amount more than a multiple of the other, set up an equation to find the measure of the smaller angle.
- 🔄 The supplement of an angle is four times its complement can be solved by assigning variables and creating equations based on the relationships between the angles.
- 🎯 The video provides a systematic approach to solving geometry problems involving complementary and supplementary angles.
Q & A
What are complementary angles?
-Complementary angles are two angles that add up to 90 degrees. For example, if one angle measures 30 degrees, its complement would measure 60 degrees to make the sum 90 degrees.
Can you explain the concept of supplementary angles with an example?
-Supplementary angles are two angles that add up to 180 degrees. For instance, if one angle measures 120 degrees, its supplement would be 60 degrees because 120 + 60 equals 180.
What is the relationship between supplementary angles and a straight line?
-Supplementary angles form a linear pair when they are positioned along a straight line. The sum of the angles in a linear pair is always 180 degrees, which represents a straight line.
How do you find the supplement of a given angle?
-To find the supplement of an angle, subtract the given angle from 180 degrees. For example, the supplement of a 55-degree angle would be 180 - 55, which equals 125 degrees.
What is the process of finding the complement of an angle given in degrees, minutes, and seconds (DMS)?
-To find the complement of an angle in DMS, subtract the angle from 90 degrees. You may need to convert 90 degrees into DMS and then perform the subtraction, borrowing from minutes and seconds as necessary.
How can you determine the measures of two complementary angles if one is 20 degrees larger than the other?
-Let the smaller angle be 'b' and the larger angle be 'a'. If 'a' is 20 degrees larger than 'b', you can set up the equation a = b + 20. Since they are complementary, a + b = 90. Solving these equations will give you the measures of both angles.
What is the measure of the larger angle if two complementary angles exist in a 2 to 3 ratio?
-If the angles are in a 2 to 3 ratio, let the smaller angle be 2x and the larger angle be 3x. Since they are complementary and add up to 90 degrees, (2x + 3x) = 90. Solving for x gives you the measure of the larger angle as 3x.
How do you calculate the measure of the smaller angle if one of two supplementary angles is 12 more than three times the value of the other?
-Let x be the measure of the smaller angle and y be the measure of the larger angle. If y is 12 more than three times x, you can express y as 3x + 12. Since they are supplementary, x + y = 180. Solving this equation will give you the measure of the smaller angle.
What is the measure of an angle if its supplement is four times the complement of the angle?
-Let a be the measure of the angle, c be the complement, and s be the supplement. If s is four times c, and knowing that a + c = 90 and s + a = 180, you can set up an equation to solve for a, which will be 60 degrees in this case, making the supplement 120 degrees.
How can you verify the solution to the challenge problem where the supplement of an angle is four times the complement?
-After finding the angle to be 60 degrees, the complement would be 30 degrees (90 - 60), and the supplement would be 120 degrees (180 - 60). You can verify the solution by checking if the supplement (120) is indeed four times the complement (30 * 4 = 120).
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)