The Secret to LONG-TERM Relief of a Tight QL: Stop Stretching and Create a "Neurological Event"
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the quadratus lumborum (QL) muscle, often misunderstood and implicated in back pain. It emphasizes the QL's role in a complex muscle system involving the pelvis, abdominals, and diaphragm. The script refutes simple stretching, advocating for neurological inhibition techniques to teach the brain to regulate QL activity, especially in relation to breathing and the asymmetrical forces exerted by the diaphragm. It also discusses the importance of considering the psoas muscle and the individual's unique muscular imbalances, concluding with a detailed explanation of a specific PRI inhibition technique to address these issues.
Takeaways
- 😖 The quadratus lumborum (QL) is often implicated in back pain but is misunderstood as it does not operate in isolation.
- 🔍 Focusing solely on the QL can lead to missing the bigger picture of the muscle complex surrounding the pelvis, abdominals, and diaphragm.
- 🧠 Inhibition techniques are different from stretching; they provide neurological feedback to the brain, teaching it to regulate muscle activity.
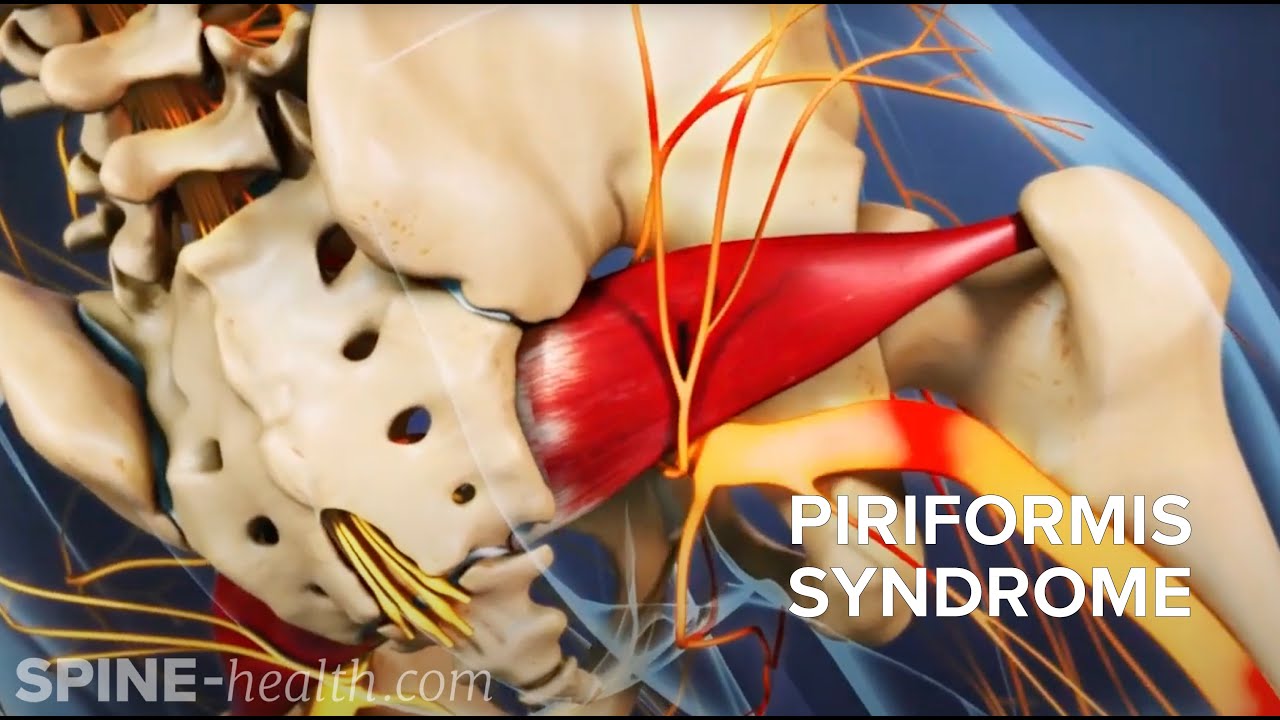
- 💡 The QL and psoas muscles are interconnected due to their shared attachment points on the lumbar vertebrae and ilium.
- 🏗️ The QL also attaches to the 12th rib, highlighting its role in conjunction with the diaphragm and the importance of considering breathing mechanics.
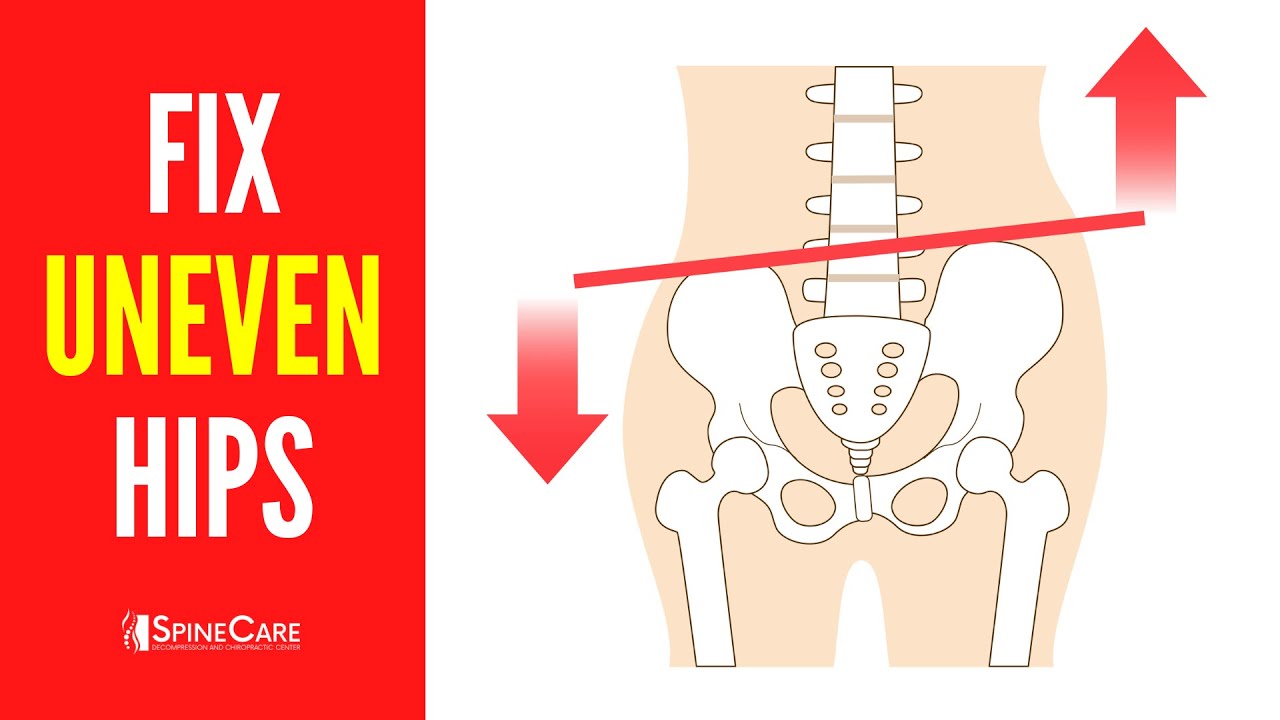
- 🌐 The size difference between the right and left diaphragm affects the muscular forces on the lumbar spine, leading to an imbalance.
- 🤸♂️ The 'left AIC right BC' pattern describes a common postural imbalance where the left pelvis is forward and the right is back, impacting muscle function.
- 💨 In this pattern, the right side of the body is in a state of compression (exhalation), while the left is in extension (inhalation).
- 🤔 Stretching the QL without addressing the underlying postural and breathing issues is ineffective and doesn't provide neurological learning.
- 🛌 A demonstrated technique involves lying on the left side to inhibit the right QL and psoas, emphasizing the importance of proper positioning and breathing.
- 🔄 The process of inhibiting and activating muscles is not one-sided; both the right and left sides of the body need to function optimally to support each other.
Q & A
What is the quadratus lumborum (QL) and why is it often misunderstood?
-The quadratus lumborum (QL) is a muscle in the human body that is frequently implicated in back pain, particularly in the lower back and SI joint pain. It is often misunderstood because people tend to focus on the QL in isolation, missing the bigger picture that it is part of a complex of muscles surrounding the pelvis, abdominals, and importantly, the diaphragm.
What is the difference between a stretch and an inhibition technique?
-A stretch is a physical activity that elongates a muscle, but it doesn't necessarily provide regulatory feedback to the brain. An inhibition technique, on the other hand, is a neurological process where the brain learns something new, such as turning off the inappropriate overactivity of a muscle like the QL.
Why is it important to consider the psoas muscle when dealing with the QL?
-The psoas muscle is of primary importance alongside the QL because they share a common origin point and insertion points on the lumbar vertebrae. They both act on the lower lumbar vertebrae and the QL also attaches to the 12th rib, indicating that they work in conjunction and should not be considered in isolation.
What is the significance of the diaphragm in relation to the QL and psoas muscles?
-The diaphragm is significant because the right and left diaphragms are not the same size, which affects the muscular forces acting upon the lumbar spine where the QL and psoas are attached. This results in unequal forces on both sides, leading to postural and breathing imbalances.
What is the left Anterior-Inferior Complex (AIC) pattern and why does it occur?
-The left AIC pattern is a common postural distortion where the left side of the pelvis is forward, the right side is back, and the entire pelvis and lumbar spine are oriented to the right. This pattern occurs due to the larger right diaphragm exerting greater force on the lumbar spine, creating an imbalance.
How does the left AIC pattern affect the state of the rib cage and breathing?
-In the left AIC pattern, the right side of the rib cage is in a state of compression, akin to exhalation, while the left side is in an extended state, similar to inhalation. This causes an imbalance in breathing, with the right side favoring exhalation and the left side favoring inhalation.
What is the purpose of the QL inhibition technique shown in the script?
-The QL inhibition technique is designed to neurologically teach the brain to use the body differently by inhibiting the overactive QL on one side and promoting appropriate function on the other. It aims to correct postural imbalances and improve breathing coordination.
Why is it not enough to just stretch the QL muscle?
-Simply stretching the QL muscle is not enough because it does not address the underlying postural and breathing imbalances caused by the interaction of various muscles, including the psoas, the diaphragm, and the pelvic floor muscles.
What should be considered when performing the QL inhibition technique?
-When performing the QL inhibition technique, one must consider the position of the pelvis, the state of the rib cage, the activity of the diaphragm, and the need for proper support of the neck. Additionally, it's important to ensure that the technique is not being hindered by overactivity in other muscle groups.
How can the QL inhibition technique be complemented for better results?
-The QL inhibition technique can be complemented by pairing it with activities that strengthen the musculature on the opposite side, such as the left hamstring and adductor muscles, to promote a more balanced and functional body posture.
What are some potential challenges or limitations when attempting the QL inhibition technique?
-Potential challenges include instability or tightness in other areas of the body, such as the left hip or hamstring, which may prevent the technique from working effectively. Additionally, the presence of overactive muscles like the right sternocleidomastoid (SCM) may require additional adjustments or techniques.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)