MITOSIS, CYTOKINESIS, AND THE CELL CYCLE
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the cell cycle, detailing the process of cell duplication through division. It explains the phases G1, S, G2, and M, emphasizing the importance of accurate DNA replication and regulatory systems. The script clarifies the distinction between chromosomes and chromatids, highlighting the role of the mitotic spindle and centrosomes in mitosis. It concludes with cytokinesis, the cytoplasmic division, completing the cell cycle.
Takeaways
- 🌱 The cell cycle is the process of duplicating a cell, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells from a parent cell.
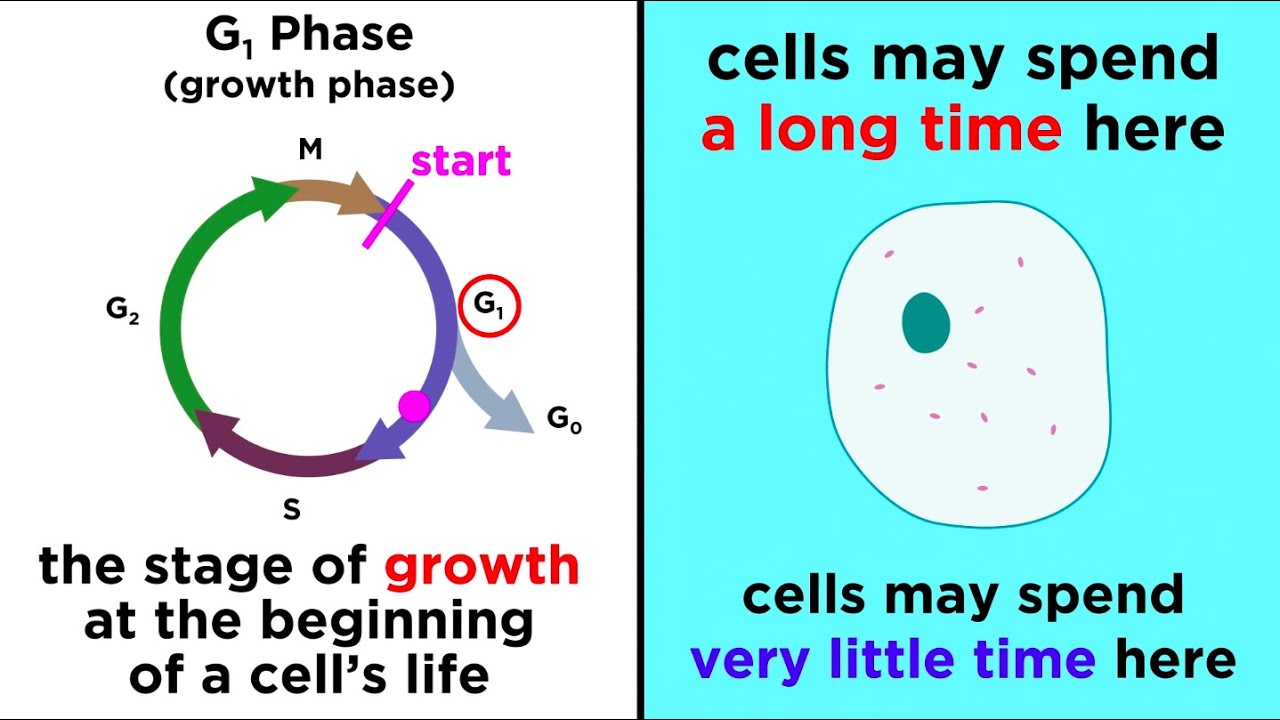
- 🔄 The cell cycle consists of four phases: G1, S, G2, and M, with G1 and G2 being growth phases known as interphase.
- 📈 The purpose of G1 and G2 phases is to allow cell growth, doubling of organelles, and assessment of environmental conditions for division.
- 🛡️ Eukaryotic cells have a cell-cycle control system of regulatory proteins to ensure correct and appropriate cell division.
- 🧬 The S phase is crucial for DNA replication and chromosomal duplication, requiring high fidelity to avoid errors.
- 🔬 Chromosomes can be a single DNA strand or two sister chromatids linked by a centromere, with the latter forming after DNA replication.
- 🤝 Sister chromatids are identical copies of the original chromosome, which separate during cell division to form two daughter chromosomes.
- 🧬 In diploid cells, each chromosome has two copies, one from each parent.
- 🕊️ The M phase includes mitosis and cytokinesis, where mitosis divides the genetic material and cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm.
- 🧭 The mitotic spindle, composed of microtubules, is essential for separating chromosomes and is anchored by centrosomes.
- 🔗 Kinetochores are protein structures that attach to sister chromatids and facilitate their separation by the mitotic spindle.
- 📊 Mitosis has five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, each with specific actions for chromosome separation and nuclear reformation.
- 💧 Cytokinesis involves the formation of a contractile ring that pinches the cell into two, facilitated by actin and myosin filaments.
Q & A
What is the only way to create a new cell?
-The only way to create a new cell is to duplicate a pre-existing one through a process called cell division.
What are the two new cells produced after cell division called?
-The two new cells produced after cell division are called daughter cells, which are genetically identical to the original cell, known as the parent cell.
What is the cell cycle?
-The cell cycle is the series of steps leading to and involving the duplication of a cell, including cell growth, chromosome replication, chromosome segregation, and cell division.
What are the four sequential phases of the cell cycle?
-The four sequential phases of the cell cycle are G1, S, G2, and M, with the first three phases collectively known as interphase.
Why do cells have G1 and G2 phases in the cell cycle?
-G1 and G2 phases, the gap phases, are present in the cell cycle to allow cells more time to grow, double their organelles and biomolecules, and assess whether the environment is favorable for division and if all preparations for cell division have been completed.
What is the role of the cell-cycle control system in eukaryotic cells?
-The cell-cycle control system in eukaryotic cells is a complex system of regulatory proteins that ensures cell division occurs correctly and only when appropriate.
What happens during the S phase of the cell cycle?
-The S phase is when DNA replication and chromosomal duplication take place, which is critical for the accurate copying of every nucleotide.
What is the difference between a chromosome and chromatids?
-A chromosome can be a continuous strand of DNA or, after DNA replication, two sister chromatids linked together by a centromere. Sister chromatids include the original chromosome and its identical replica.
What is the significance of the M phase in the cell cycle?
-The M phase includes mitosis and cytokinesis, which are the processes by which sister chromatids are split up equally between two new daughter nuclei and the cytoplasm is divided, respectively.
What are the functions of the mitotic spindle and centrosomes during cell division?
-The mitotic spindle is a bipolar array of microtubules that separates chromosomes into two new daughter cells, while centrosomes, consisting of centrioles and the pericentriolar matrix, nucleate microtubules and help position the spindle in the cell.
What are the five stages of mitosis?
-The five stages of mitosis are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, each involving specific events in the division of the cell's nucleus.
What is cytokinesis and how does it occur?
-Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm that occurs through the formation of a contractile ring of actin and myosin filaments, which pinch the cell into two new cells.
What is the role of kinetochores in mitosis?
-Kinetochores are large protein structures that allow the plus ends of kinetochore microtubules to attach correctly to sister chromatids, ensuring proper chromosome segregation during mitosis.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)