Wireless Network Technologies - CompTIA A+ 220-1101 - 2.3
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses the technical aspects of 802.11 wireless networks, highlighting the importance of frequency ranges, specifically the crowded 2.4 GHz and the more spacious 5 GHz bands. It explains the concept of channels and their allocation by the IEEE, the role of governmental agencies in regulating wireless spectrum, and the impact of these regulations on network power and interference. The script also contrasts 2.4 GHz with 5 GHz networks, emphasizing the latter's greater number of available channels and bandwidth options, ideal for environments with high access point density. Additionally, it touches on Bluetooth technology, which operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band, and its use in personal area networks with a typical range of about 10 meters.
Takeaways
- 📡 The 802.11 network operates on two main frequency ranges: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, with some standards utilizing both for communication.
- 🌐 Within these frequency ranges, there are specific channels assigned by IEEE for easier reference and management.
- 🔄 To avoid interference, access points in the same area should ideally operate on different wireless channels.
- 🏛 Governmental agencies regulate the use of wireless spectrum, dictating which frequencies can be used and setting power and interference limits.
- 📶 The 2.4 GHz band is commonly used but has limited non-overlapping channels (1, 6, and 11), leading to potential congestion in crowded areas.
- 🚀 The 5 GHz band offers a wider range of non-overlapping channels, providing more options for clear communication paths.
- 🔎 Devices can use bandwidths larger than 20 MHz for better throughput, including 40 MHz, 80 MHz, and up to 160 MHz.
- 📈 At higher bandwidths like 160 MHz, communication may occur in non-contiguous frequency areas.
- 🎧 Bluetooth also operates in the 2.4 GHz unlicensed ISM band, commonly used for short-range personal area networks.
- 🔗 Bluetooth devices typically have a communication range of about 10 meters, suitable for connecting peripherals to mobile devices.
- 🏭 Industrial Bluetooth standards can extend communication distances beyond 100 meters, but this is less common for consumer devices.
Q & A
What are the two primary frequency ranges used by 802.11 networks?
-The two primary frequency ranges used by 802.11 networks are 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
Why is it important to be aware of the frequency and channels used in 802.11 networks?
-It is important to be aware of the frequency and channels to avoid interference and to ensure efficient communication within the network.
How does the IEEE categorize the different frequencies for easier reference?
-The IEEE assigns numbers to these frequencies, allowing for easier reference to specific channels or frequency bands in use.
What is the significance of using different wireless channels for multiple access points in the same area?
-Using different wireless channels for multiple access points helps to reduce interference and improve the overall performance of the network.
Which governmental agencies are typically responsible for managing the wireless spectrum?
-Governmental agencies responsible for managing the wireless spectrum vary by location but are tasked with regulating the use of frequencies for 802.11 networks.
What are the typical regulations set by these governmental agencies for 802.11 networks?
-Regulations often include specifying the allowed frequencies, maximum power usage, and limits on interference caused by 802.11 networks.
Why are 5 GHz networks more popular than 2.4 GHz networks?
-5 GHz networks are more popular due to the availability of more channels and the ability to use larger bandwidths, leading to better throughput and less congestion.
What are the three separate 20 megahertz bandwidths for 2.4 GHz networks as per IEEE channels?
-The three separate 20 megahertz bandwidths for 2.4 GHz networks are IEEE channels 1, 6, and 11, ranging from 2412 MHz to 2482 MHz.
What is the significance of the 5 GHz spectrum in terms of channel availability compared to 2.4 GHz?
-The 5 GHz spectrum offers many more 20 MHz channels than the 2.4 GHz band, providing more options for avoiding interference and improving network performance.
What does ISM stand for and why is it significant for Bluetooth and 802.11 networks?
-ISM stands for Industrial, Scientific, and Medical. It is significant because it refers to the unlicensed part of the 2.4 GHz band that can be used by anyone without special government licensing.
How does the range of Bluetooth devices typically compare to that of industrial Bluetooth?
-Consumer Bluetooth devices typically have a range of about 10 meters, while industrial Bluetooth standards can extend the range to over 100 meters.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
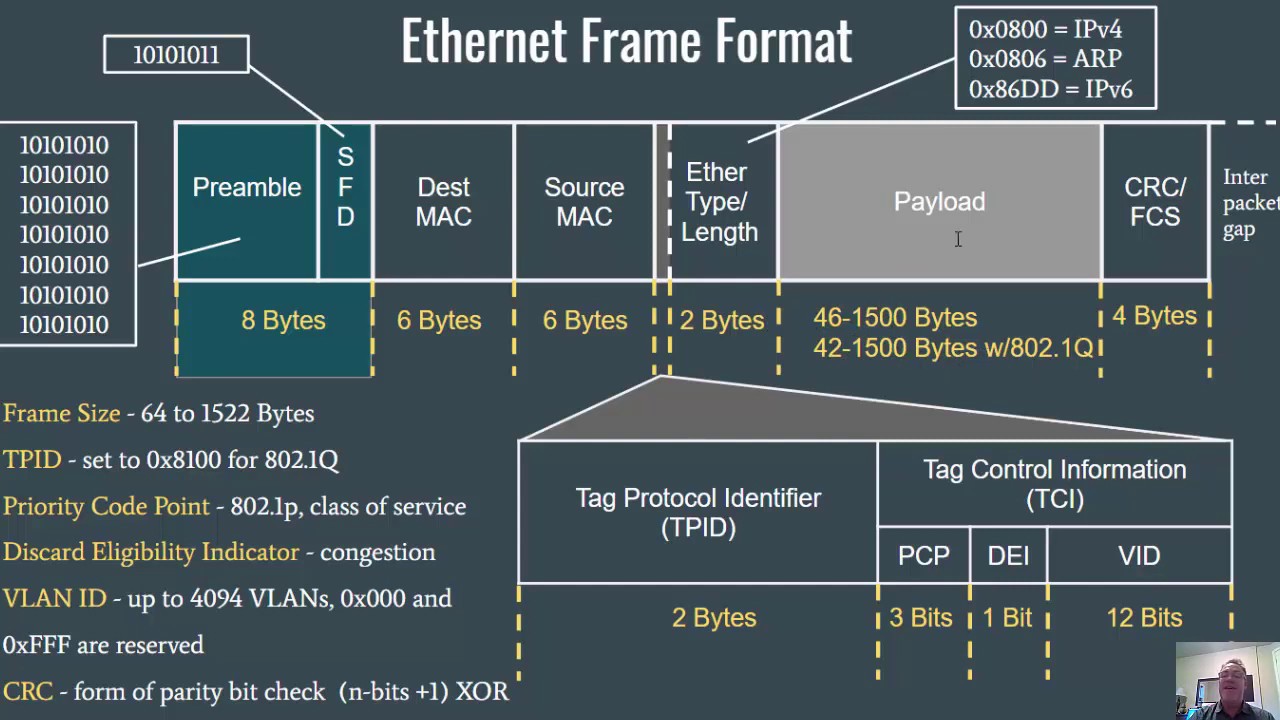
The Data Link Layer, MAC Addressing, and the Ethernet Frame

[Tagalog] Polya's Four-Step Problem-Solving Strategy - Solved Example 1

Full Wave Bridge Rectifier (Basics Electronics) Diode theory & applications Btech 1st year

Cyber Security for beginners || Introduction to Cybersecurity

Power quality monitoring

1. Navigating AutoCAD Software

Semiconductor Company in Defence Sector? | Budget 2024 | CA Rachana Ranade
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
