Food Webs and Energy Pyramids: Bedrocks of Biodiversity
Summary
TLDRThe video script from the Amoeba Sisters explores the dynamics of food chains and webs, emphasizing the importance of biodiversity in ecosystems. It explains how producers and various levels of consumers interact, with only a fraction of energy transferred between trophic levels. The script highlights the potential consequences of removing species and the resilience provided by a diverse ecosystem. It also introduces the role of decomposers in nutrient recycling, encouraging viewers to stay curious about nature's intricate balance.
Takeaways
- 📺 Nature shows were a fascination for the Amoeba Sisters due to limited TV options and their interest in science.
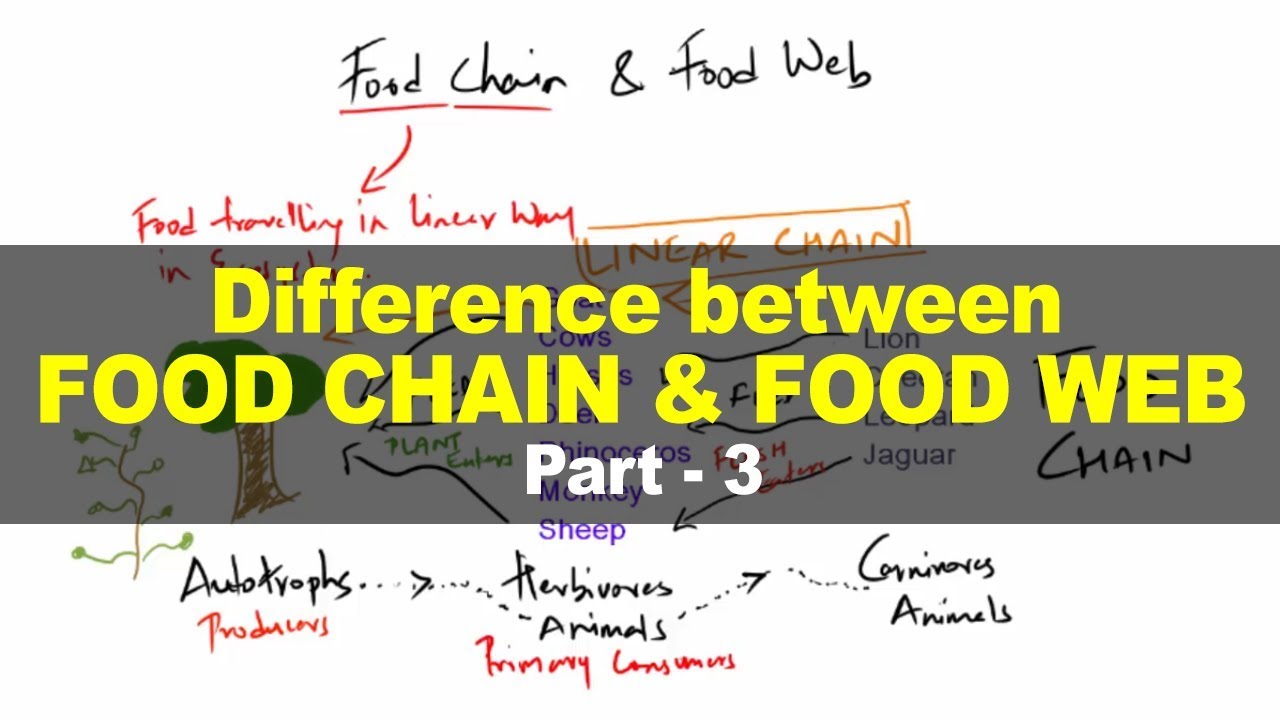
- 🌿 Producers are autotrophic organisms like plants that form the base of a food chain, capable of making their own food.
- 🐦 Consumers are heterotrophic, meaning they must feed on other organisms; they are categorized as primary, secondary, and tertiary based on their position in the food chain.
- 🔄 The direction of arrows in a food chain represents the flow of energy, pointing from the eaten to the eater.
- 🗼 An energy pyramid illustrates the distribution of energy at each trophic level, with producers at the base and energy decreasing as you move up.
- 🔢 Energy transfer between trophic levels is inefficient, with only about 10% of energy being passed on to the next level.
- 💥 Removal of a species from a food chain can disrupt the balance and affect the survival of other species.
- 🐍 Apex predators, like snakes, if removed, can lead to overpopulation of their prey and subsequent scarcity of food for those prey species.
- 🌐 Ecosystems consist of food webs rather than single food chains, showing complex interactions among various species.
- 🌱 Biodiversity contributes to the sustainability and resilience of an ecosystem, allowing it to better adapt to changes.
- 🌳 High biodiversity has economic and ecological benefits, although a full exploration of these benefits is beyond the scope of the script.
- 🕊️ Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in breaking down dead organic matter and are integral to the ecosystem, even though they are not typically represented in food chains or webs.
Q & A
What are the two main reasons the Amoeba Sisters loved nature shows as children?
-The two main reasons were that they didn't have cable, making nature shows one of the few programs they could watch without adjusting the TV antenna for reception, and that they found the science presented in these shows to be cool.
What is the starting point of a food chain?
-A food chain starts with a producer, which is an organism that can make its own food, such as a plant.
What does it mean to be a heterotroph in the context of a food chain?
-Being a heterotroph means that an organism must feed on other organisms because it cannot produce its own food.
How does the energy flow in a food chain?
-The energy flows in the direction of the one doing the eating, as indicated by the arrows pointing towards the consumer.
What is the energy transfer efficiency between trophic levels?
-The energy transfer efficiency is roughly 10%, meaning that each trophic level up only stores about 10% of the energy from the previous level.
What would happen if a primary consumer, like a grasshopper, were removed from a food chain?
-Removing a primary consumer could harm other organisms in the food chain, as they may not have enough to eat, disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
-A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where each is eaten by the next, while a food web is a complex network of multiple interacting food chains.
Why is biodiversity important in an ecosystem?
-Biodiversity is important because it contributes to the sustainability and resilience of an ecosystem, allowing it to better adapt to changes and recover from disturbances.
What role do decomposers play in a food web?
-Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, are heterotrophs that break down dead organisms, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
How does removing an apex predator from a food chain affect the ecosystem?
-Removing an apex predator could lead to an overpopulation of its prey, which may then suffer from a lack of food resources, disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
What does the Amoeba Sisters suggest about the benefits of high biodiversity?
-The Amoeba Sisters suggest that high biodiversity has many benefits, including economic advantages, and that it is critical to protect ecosystem biodiversity.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)