The Neuron
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Paul Andersen explains the neuron as the fundamental unit of the nervous system. He details the neuron's anatomy, including the cell body, dendrites, and axon, and how they facilitate the transmission of information via neurotransmitters and action potentials. He also discusses the myelin sheath's role in speeding up signal transmission and the structural and functional classifications of neurons, such as multipolar, bipolar, unipolar, and axonic neurons, as well as sensory, motor, and interneurons. The explanation aims to clarify the neuron's complexity and its crucial role in our body's response to environmental stimuli.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The neuron is the fundamental unit of the nervous system, responsible for receiving and transmitting information.
- 🐛 In simple animals like a nematode worm, the nervous system is composed of only 302 neurons, yet they are intricately connected.
- 🧬 Humans have approximately 100 billion neurons, most of which are located in the brain and spinal cord.
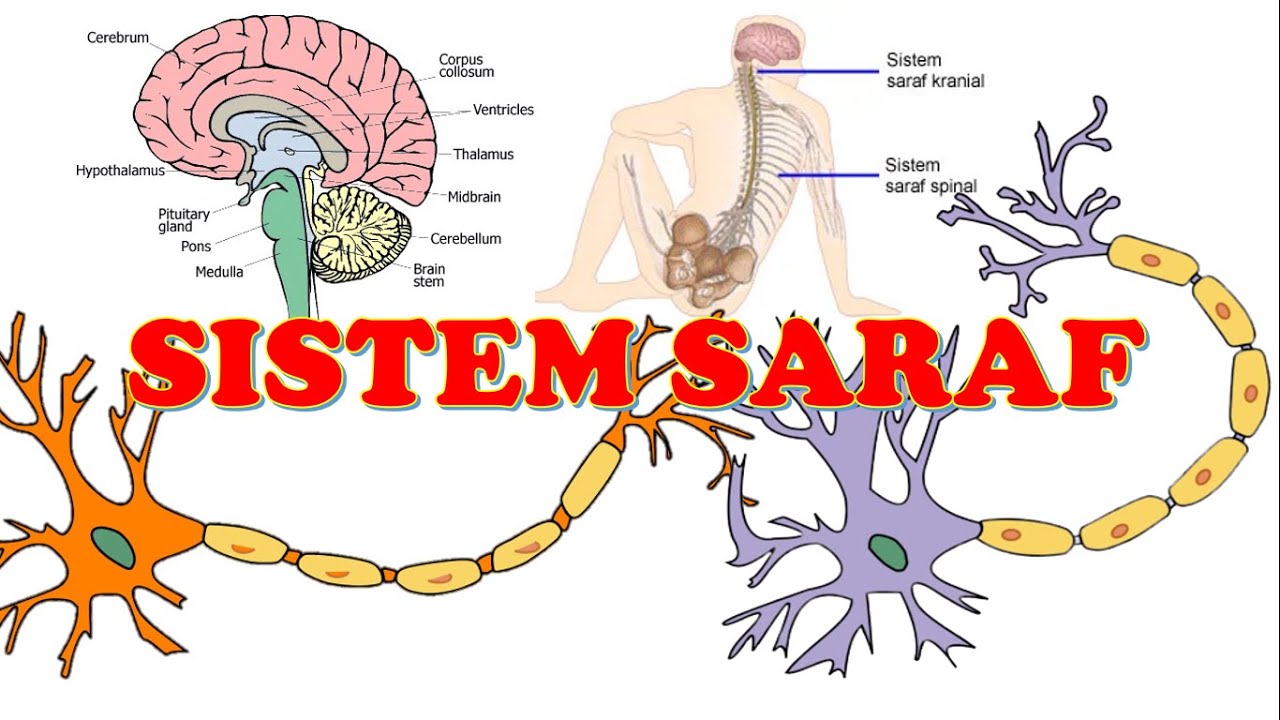
- 🏠 The cell body of a neuron is the central part, containing typical cellular structures like the nucleus and Golgi apparatus.
- 🌐 Dendrites are extensions from the cell body that receive information in the form of neurotransmitters from other neurons.
- 🚀 The axon is the part of the neuron responsible for transmitting information, starting at the axon hillock and extending to the terminals.
- 🔌 Synapses are the gaps between neurons where information is passed from one neuron to another.
- 🛡️ Myelin sheaths are insulating layers that wrap around some axons to facilitate faster transmission of signals.
- 🔍 Neurons can be classified structurally based on the number of poles or extensions coming from the cell body, such as multipolar, bipolar, unipolar, and axonic neurons.
- 🔬 Neurons are also classified functionally into sensory (afferent) neurons that bring information into the central nervous system, and motor (efferent) neurons that send information out to effectors like muscles and glands.
- 🔄 Interneurons are neurons that connect between sensory and motor neurons within the central nervous system, facilitating complex interactions.
Q & A
What is the basic unit of the nervous system?
-The basic unit of the nervous system is the neuron.
How many neurons does a simple animal like a nematode worm have?
-A nematode worm has approximately 302 neurons.
How many neurons are present in the human body?
-The human body contains about a hundred billion neurons.
What is the primary function of the cell body of a neuron?
-The cell body, or soma, is the metabolic center of the neuron, containing the nucleus and organelles like the Golgi apparatus and mitochondria.
What are dendrites and what is their role in a neuron?
-Dendrites are extensions of the neuron cell body that receive information in the form of neurotransmitters from other neurons.
What is the axon and what does it transmit?
-The axon is responsible for transmitting information away from the neuron. It begins at the axon hillock and moves toward the axon terminals.
What is an action potential and how does it relate to the neuron's function?
-An action potential is an electrical signal that travels along the neuron's axon, allowing the neuron to send information to the next neuron.
What is a Myelin sheath and how does it aid in the transmission of information in the axon?
-A Myelin sheath is a protective covering around some axons, made by Schwann cells, that insulates the nerve and allows information to travel more quickly.
What is the structural classification of neurons based on, and what are the common types?
-Neurons are structurally classified based on the number of poles or extensions coming off the cell body. Common types include multipolar, bipolar, unipolar, and axonic neurons.
What is the difference between sensory neurons and motor neurons in terms of their function?
-Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, bring information into the central nervous system from the environment. Motor neurons, on the other hand, send information out to effectors such as muscles and glands.
What are inter neurons and what is their role in the nervous system?
-Inter neurons are neurons that make connections between sensory and motor neurons within the central nervous system, facilitating communication between different parts of the nervous system.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

What is a Neuron? Parts and Function

Motor unit | Organ Systems | MCAT | Khan Academy

Sistem Saraf: Anatomi Neuron | Ilmu Biomedik Dasar | Brainy Panda

How the Body Builds Incredible Strength Without Getting Bigger

central nervous system mcqs with answers | mcq on central nervous system | nervous system mcqs
SISTEM SARAF PADA MANUSIA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
