Zener Diode Construction and Working | Zener Breakdown and Avalanche Breakdown | Electronics Basics
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the working principle of a Zener diode, including its construction, behavior, and applications. It begins by recalling the basics of a regular diode, highlighting the unique reverse-bias behavior of a Zener diode, which allows current to flow beyond a specific voltage, known as the Zener voltage. The script explores two types of breakdowns: Zener and Avalanche, which help regulate voltage. Zener diodes are commonly used for voltage regulation, over-voltage protection, and in switching circuits, making them crucial components in electronic devices.
Takeaways
- 😀 A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only, with an anode and cathode.
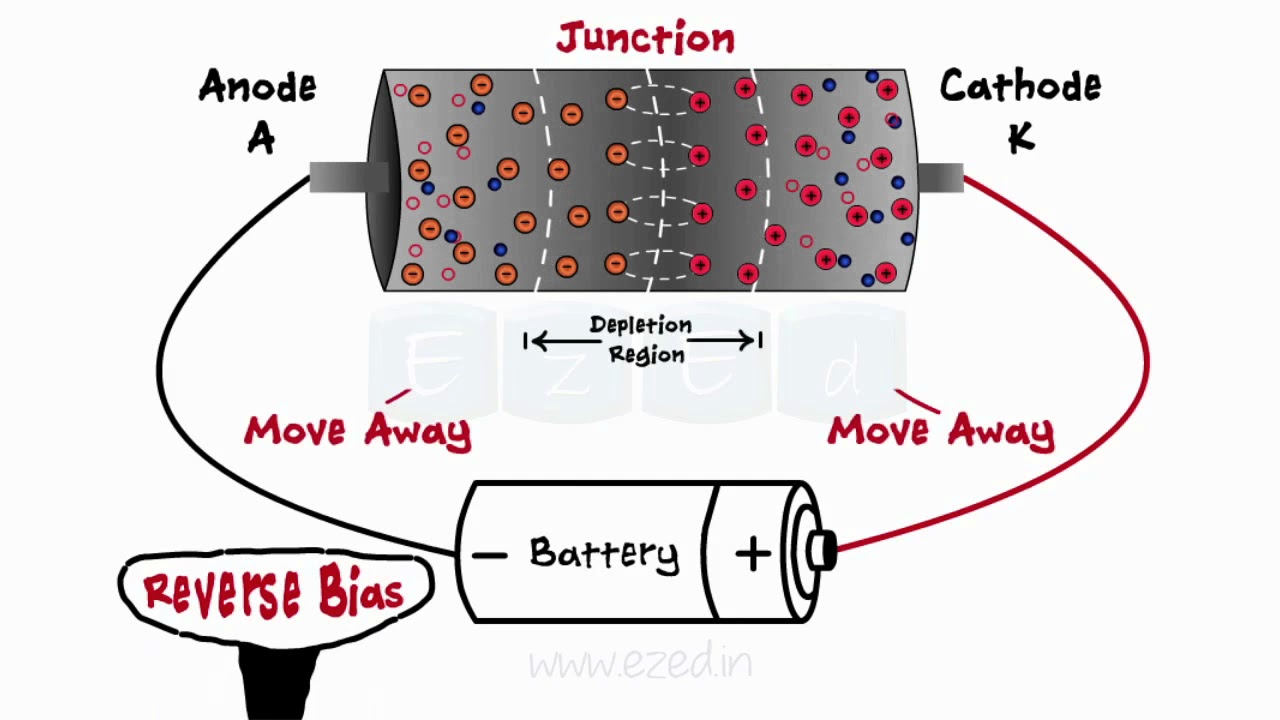
- 😀 In forward bias, a diode allows current to flow from anode to cathode; in reverse bias, ideally no current flows.
- 😀 A Zener diode works both in forward and reverse bias, allowing current to flow in reverse once a certain voltage, called the Zener voltage, is reached.
- 😀 Zener diodes are made of heavily doped semiconductor materials (usually silicon), creating a narrow P-N junction.
- 😀 In forward bias, a Zener diode behaves like a regular diode, allowing current to flow from anode to cathode.
- 😀 The key feature of a Zener diode is its reverse-bias behavior. When the reverse voltage reaches the Zener voltage, it conducts current in reverse.
- 😀 The Zener breakdown occurs at lower reverse voltages (< 5V) through quantum mechanical tunneling, while avalanche breakdown occurs at higher voltages (> 5V) via impact ionization.
- 😀 Zener diodes are used for voltage regulation, where they stabilize the voltage across the load by maintaining a constant Zener voltage.
- 😀 Zener diodes also provide overvoltage protection by conducting when the voltage exceeds the Zener voltage, preventing further voltage rise.
- 😀 Zener diodes are used in switching circuits as voltage-controlled switches, automatically triggering actions based on voltage levels.
Q & A
What is a diode and how does it work?
-A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only. It has two terminals: an anode (positive side) and a cathode (negative side). When forward-biased, current flows from anode to cathode. When reverse-biased, ideally no current flows.
How is a Zener diode different from a regular diode?
-Unlike a regular diode, a Zener diode allows current to flow not only in the forward direction but also in the reverse direction when a specific voltage, called the Zener voltage, is reached.
What materials are used to construct a Zener diode?
-A Zener diode is made from semiconductor material, usually silicon. Both the p-type and n-type regions are heavily doped, meaning more impurities are added, which makes the junction narrow and gives the Zener diode its unique properties.
What are the terminals of a Zener diode and how are they identified?
-A Zener diode has two terminals: an anode (positive) and a cathode (negative). The cathode is usually marked with a band to ensure correct connection in a circuit.
How does a Zener diode behave in forward bias?
-In forward bias, a Zener diode behaves like a regular diode, allowing current to flow from the anode to the cathode.
What is the Zener effect and when does it occur?
-The Zener effect occurs when the reverse voltage across a Zener diode reaches the Zener breakdown voltage. The strong electric field at the narrow PN junction allows electrons to tunnel from the valence band to the conduction band, resulting in reverse current flow.
What are the two types of breakdown in a Zener diode?
-The two types of breakdown are Zener Breakdown, which occurs at low reverse voltages (typically below 5V) due to quantum mechanical tunneling, and Avalanche Breakdown, which occurs at higher reverse voltages (above 5V) due to impact ionization.
Why is the voltage across a Zener diode considered constant?
-Once the reverse voltage reaches the Zener voltage, the diode conducts in reverse and maintains a stable voltage across it, even if the input voltage varies. This property makes it ideal for voltage regulation.
How is a Zener diode used in voltage regulation?
-In voltage regulation, a Zener diode is connected in reverse bias across a load with a series resistor to limit current. It maintains a stable voltage across the load, ensuring electronic devices operate correctly.
How does a Zener diode provide over-voltage protection?
-A Zener diode is connected in parallel with a sensitive component. When the voltage exceeds the Zener voltage, the diode conducts and limits the voltage, protecting the component from voltage spikes or surges.
How can a Zener diode be used in switching circuits?
-In switching circuits, the Zener diode acts as a voltage-controlled switch. It is reverse-biased and monitors the voltage level. When the voltage reaches the Zener voltage, the diode conducts and triggers a switch to change the state of another part of the circuit.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Diodes - What Are Diodes - PN Junction - Forward Bias - Reverse Bias - Zener Diodes

Avalanche Breakdown and Zener Breakdown Effect Explained

Prinsip Kerja Rangkaian Charger Baterai – Kalau Sudah Penuh Bisa Mati Sendiri

Dasar Elektronika ; Dioda

Cara Kerja Diode – Lengkap Beserta Contoh Rangkaian Diode

Zener Diode Regulators: Lecture: Part 1 V4VP2 ELE424 DL
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
